5 Key Answers for Solubility Curve Worksheet 1

In chemistry, understanding how different substances dissolve in various solvents is crucial for both theoretical knowledge and practical applications. Solubility curves provide a visual representation of how solubility changes with temperature for different substances. Here, we delve into some of the critical insights you can derive from analyzing a solubility curve worksheet, with a focus on Worksheet 1.
What Information Can You Gather From a Solubility Curve?

A solubility curve, when plotted on a graph with temperature on the x-axis and solubility in grams per 100 grams of solvent on the y-axis, gives us:
- Temperature-Solubility Relationship: How solubility changes with temperature.
- Solubility at Different Temperatures: Exact solubility at any given temperature.
- Curve Comparison: Comparing solubility curves of different substances.
- Relative Solubility: Identifying which substances are more or less soluble.
How Does Temperature Affect Solubility?
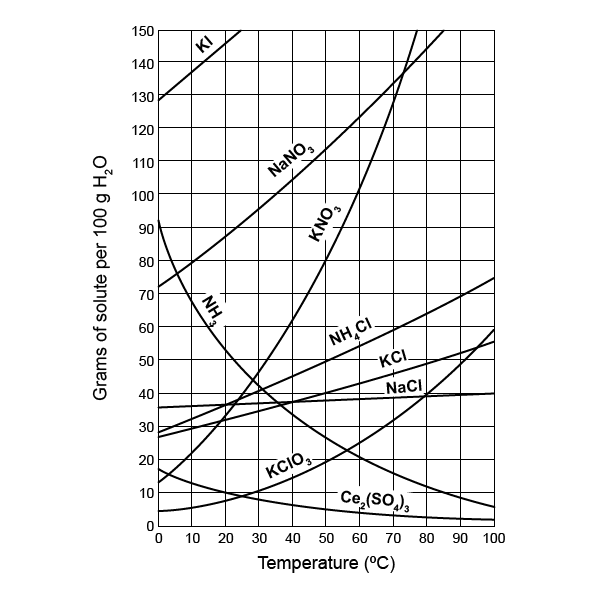
Temperature typically increases the solubility of solid solutes in liquid solvents. Here's why:
- Increased Molecular Motion: With rising temperature, solvent particles move more vigorously, increasing the likelihood of solute particles being surrounded and dissolved.
- Energy for Dissociation: Solute particles require less energy to dissociate into the solvent because the solvent molecules are moving faster, offering more opportunities for interaction.
- Exceptions: Gases in liquids usually see solubility decrease with temperature due to the kinetic theory. Higher temperatures allow gas molecules to escape from the liquid more readily.
What Are Unsaturated, Saturated, and Supersaturated Solutions?
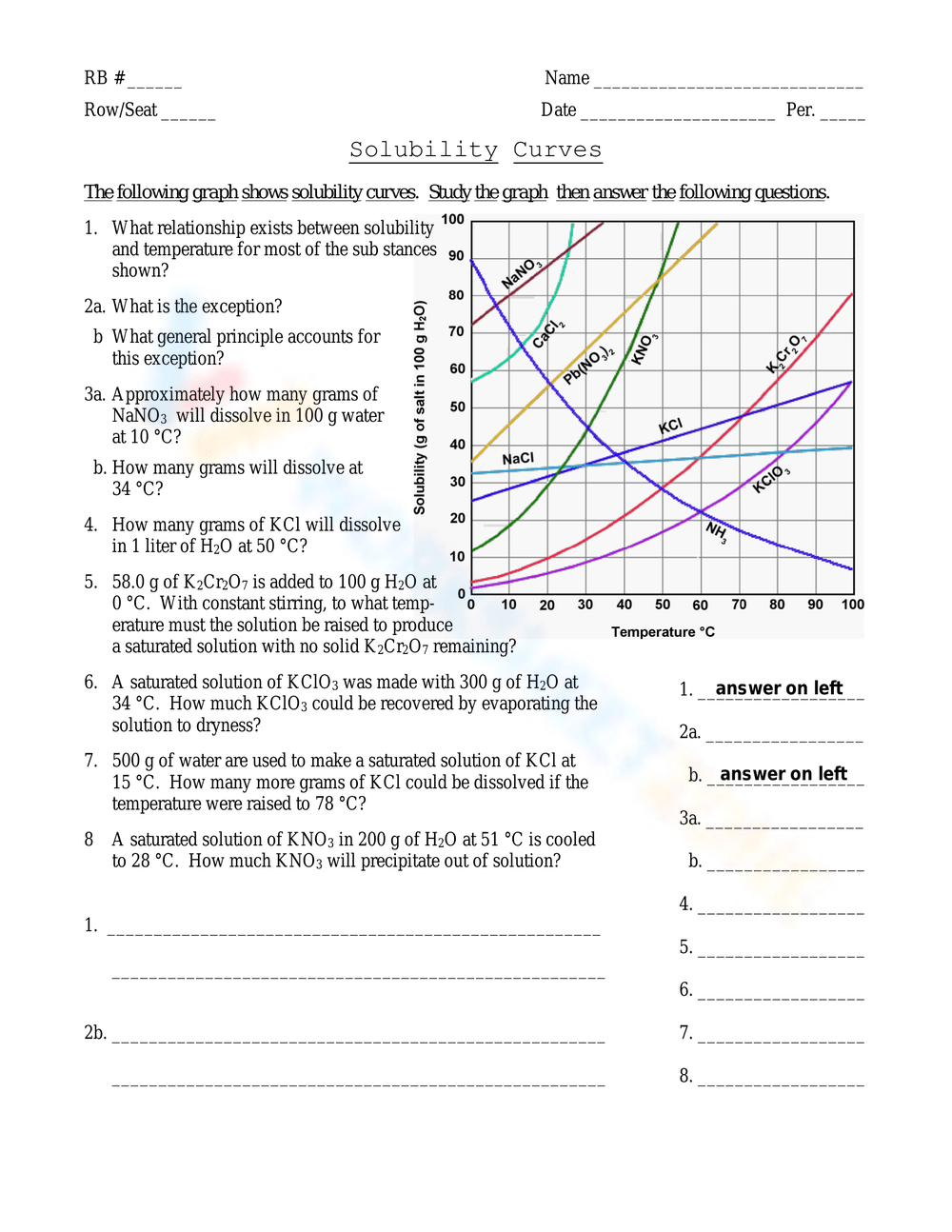
Understanding these terms is key when working with solubility curves:
| Type of Solution | Description |
|---|---|
| Unsaturated | A solution that can still dissolve more solute at a given temperature. The concentration is below the saturation point. |
| Saturated | The solution is in equilibrium with undissolved solute; it contains the maximum amount of solute at that temperature. More solute can be dissolved only with an increase in temperature. |
| Supersaturated | A solution that contains more dissolved solute than is normally possible at a given temperature. It's an unstable state, and adding a seed crystal can cause excess solute to precipitate out. |

⚗️ Note: Supersaturation can be achieved by carefully heating a saturated solution above the saturation point and then slowly cooling it back down.
How Can Solubility Curves Help in Predicting Crystal Formation?

Solubility curves allow chemists to predict:
- When Crystals Form: By identifying the temperature at which a solution becomes saturated, we can predict crystal formation.
- Quantity of Crystals: The difference between the solubility at one temperature and another can indicate how much solute will precipitate out as the solution cools.
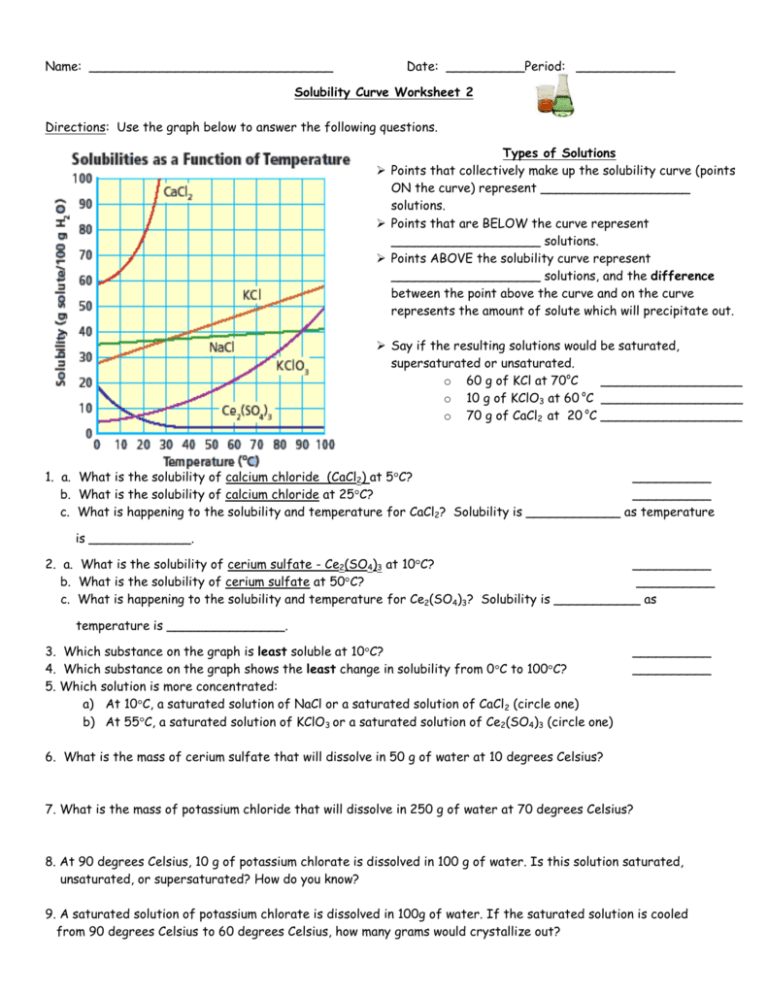
What Are the Practical Applications of Solubility Curves?
Solubility curves are not just theoretical tools but have real-world applications:
- Industrial Crystallization: Used to control crystal size and number in manufacturing processes like pharmaceuticals.
- Water Treatment: Helps in removing impurities from water by understanding solubility changes with temperature.
- Environmental Impact: Predicting how pollutants dissolve in water bodies at different temperatures.
- Food Science: Optimizing solubility for ingredient interactions and food preservation.
In summary, solubility curves are indispensable in chemistry. They provide a clear understanding of how different substances behave under various temperature conditions, allowing for accurate prediction and control in chemical processes, ensuring quality in industrial production, and advancing our knowledge of the natural world.
Why does solubility increase with temperature for most solids?

+
The increased kinetic energy at higher temperatures makes it easier for solvent molecules to disrupt the intermolecular forces holding the solute together, allowing the solute to dissolve more readily.
Can you create a supersaturated solution from an unsaturated one?

+
Yes, you can by carefully heating the unsaturated solution above the saturation point and then cooling it slowly to avoid crystallization. However, this process is delicate and requires precise control.
How do solubility curves help in the pharmaceutical industry?
+
They are used to control the crystallization process, ensuring that drugs are produced in a consistent crystalline form, which affects solubility, dissolution rate, and bioavailability.