Eclipse Education: Solar and Lunar Eclipse Worksheet

Understanding celestial events like solar and lunar eclipses not only broadens our astronomical knowledge but also our appreciation of the natural world. These events, although sporadic, carry both cultural significance and scientific intrigue. Whether you're an educator looking to inspire, a student eager to learn, or a curious enthusiast, this comprehensive guide aims to illuminate the captivating phenomena of solar and lunar eclipses. Let's embark on a journey through the stars, exploring these natural spectacles through engaging educational worksheets.
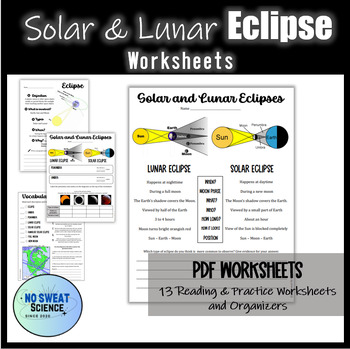
What is an Eclipse?

An eclipse happens when one astronomical object is temporarily obscured by another. In our case, we’re talking about:
- Solar Eclipses: When the Moon moves between the Earth and the Sun, casting a shadow on Earth.
- Lunar Eclipses: When the Earth moves between the Sun and the Moon, blocking the Sun’s light and casting a shadow on the Moon.
The Solar Eclipse

Here’s what happens during a solar eclipse:
- New Moon Phase: It only happens when the Moon is in its New Moon phase.
- Alignment: The Moon aligns directly between Earth and the Sun.
- Shadow Projection: The Moon’s shadow casts on Earth, causing darkness in some parts of the world.
Types of Solar Eclipses include:
- Total Solar Eclipse: The Moon completely covers the Sun.
- Partial Solar Eclipse: Only a part of the Sun is obscured by the Moon.
- Annular Solar Eclipse: When the Moon is too far from Earth to cover the Sun entirely, creating a ring of sunlight around the Moon.

Worksheet Activities:

Let’s delve into interactive ways to learn about solar eclipses:
- Diagram Drawing: Ask students to draw and label the phases of a total solar eclipse.
- Shadow Play: Use light sources and small spheres to simulate and observe the phenomenon.
- Data Analysis: Provide real eclipse data for students to analyze the frequency and path of eclipses.
The Lunar Eclipse

Lunar eclipses occur when:
- Full Moon Phase: The Earth is positioned directly between the Sun and the Moon, with the Moon being in its Full Moon phase.
- Earth’s Shadow: The Earth’s shadow falls on the Moon, making it appear darker or even reddish due to the Earth’s atmosphere refracting sunlight.
Types of Lunar Eclipses:
- Total Lunar Eclipse: The entire Moon moves into the Earth’s umbral shadow.
- Partial Lunar Eclipse: Only part of the Moon moves into the Earth’s umbral shadow.
- Penumbral Lunar Eclipse: The Moon travels through the Earth’s penumbra, causing a subtle darkening.

Worksheet Activities:

- Timeline Creation: Students can create a timeline of a lunar eclipse, showing how long each phase lasts.
- Color Observation: Discuss why the Moon might turn red during a lunar eclipse (Rayleigh scattering).
- Space Modeling: Using small balls and lights, simulate and observe a lunar eclipse.
Eclipse Safety and Viewing Tips
Observing these natural phenomena comes with responsibilities:
- Never look directly at the Sun during a solar eclipse: Use specialized eclipse glasses or indirect viewing methods.
- Lunar eclipses are safe to watch with the naked eye; however, using binoculars or a telescope can enhance the experience.
Engaging Classroom Activities

Here are some dynamic activities to engage students:
- Paper Moon: Create cutouts of the Moon’s phases to visualize lunar and solar eclipses.
- Video Analysis: Watch footage or live streams of past eclipses, followed by discussions.
🌍 Note: For teachers, ensure to incorporate educational standards and align activities with curriculum requirements.
In this journey through solar and lunar eclipses, we’ve explored not just the phenomena themselves, but also how we can effectively teach and learn about them. From understanding the phases to hands-on activities that bring these events to life, we’ve covered a wide spectrum of educational techniques. As we continue to look up at the night sky or observe a rare solar event, let’s remember that the beauty of eclipses lies in their rarity and the profound connection they foster with the universe. They remind us that our place in the cosmos is both significant and minuscule, inspiring a lifelong curiosity and respect for the celestial bodies that dance above us.
What safety measures should I take to observe a solar eclipse?

+
Always use certified eclipse glasses or employ indirect viewing methods like pinhole projectors. Never use regular sunglasses, binoculars, or telescopes without proper solar filters as they can cause permanent eye damage.
How often do solar and lunar eclipses occur?

+
Solar eclipses happen about 2-4 times per year, but any specific location on Earth might see a total solar eclipse only once every 375 years on average. Lunar eclipses are slightly more frequent, with at least two and up to three per year.
Why does the Moon sometimes appear red during a lunar eclipse?

+
This phenomenon, known as a ‘Blood Moon,’ occurs when Earth’s atmosphere scatters the shorter blue wavelengths of sunlight, while the longer, red wavelengths bend around the Earth and continue towards the Moon.



