Snell's Law Worksheet: Master Light Refraction Now

Light refraction, the bending of light as it moves from one medium into another, is a fundamental concept in physics that impacts everything from how we see objects to the design of optical devices. Snell's Law provides a mathematical model for understanding this phenomenon. If you're ready to delve into the mechanics of light and improve your understanding, this Snell's Law worksheet will guide you through the necessary calculations and exercises to master light refraction.
Understanding Snell’s Law

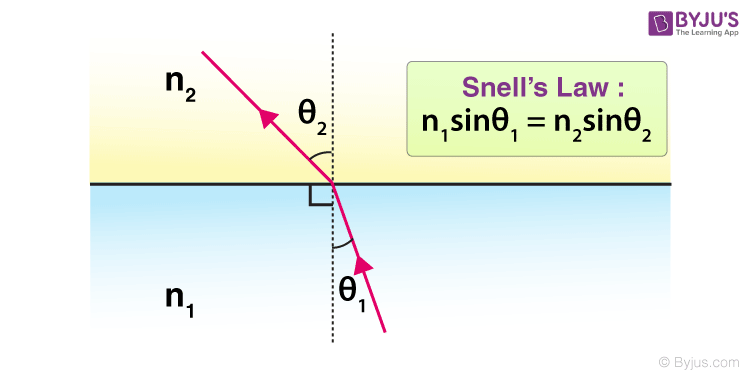
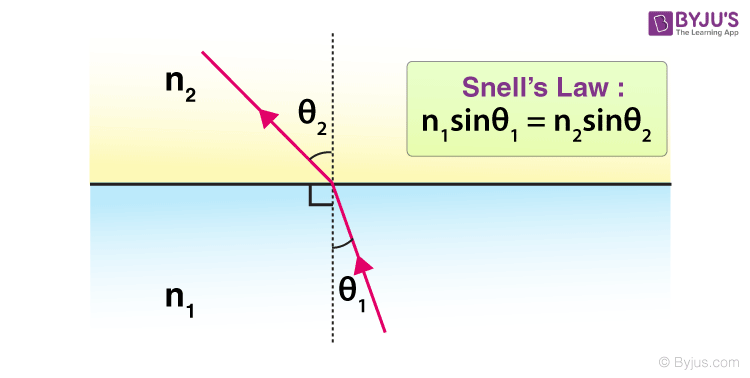
Before diving into the exercises, let’s revisit Snell’s Law:
- Snell’s Law: (n_1 \sin \theta_1 = n_2 \sin \theta_2)
Where:
- (n_1) and (n_2) are the refractive indices of the first and second medium, respectively.
- (\theta_1) is the angle of incidence.
- (\theta_2) is the angle of refraction.
This equation describes how light bends when passing from one medium to another with different refractive indices.
Worksheet Exercises
Let’s apply Snell’s Law to practical problems:
Problem 1: Finding the Angle of Refraction

Given:
- Refractive index of air ((n_1)) = 1.00
- Refractive index of glass ((n_2)) = 1.52
- Angle of incidence ((\theta_1)) = 30°
Find:
- The angle of refraction ((\theta_2))
Solution:
- Using Snell’s Law: (1.00 \sin 30° = 1.52 \sin \theta_2)
- (\sin \theta_2 = \frac{\sin 30°}{1.52})
- (\sin \theta_2 = 0.3289)
- (\theta_2 = \sin^{-1}(0.3289) \approx 19.4°)
🔍 Note: Remember to verify your answer using a calculator for precise calculations, as approximations can lead to small deviations.
Problem 2: Refractive Index Calculation

Given:
- Angle of incidence ((\theta_1)) = 45°
- Angle of refraction ((\theta_2)) = 30°
Find:
- The refractive index of the second medium ((n_2))
Solution:
- Using Snell’s Law: (1.00 \sin 45° = n_2 \sin 30°)
- (n_2 = \frac{\sin 45°}{0.5})
- (n_2 = \frac{0.7071}{0.5} = 1.4142)
🧐 Note: Remember that the refractive index is unitless and is a measure of how much light slows down in the medium compared to a vacuum.
Problem 3: Total Internal Reflection
Given:
- Refractive index of glass ((n_1)) = 1.52
- Refractive index of air ((n_2)) = 1.00
Find:
- The critical angle ((c)) for total internal reflection
Solution:
- Using Snell’s Law for critical angle: (\sin c = \frac{n_2}{n_1})
- (\sin c = \frac{1.00}{1.52})
- (\sin c = 0.6579)
- (c = \sin^{-1}(0.6579) \approx 41.3°)
💡 Note: Total internal reflection occurs only when light travels from a medium with a higher refractive index to one with a lower refractive index, and the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle.
Understanding Refractive Index

The refractive index is crucial in understanding how light behaves in different materials. Here’s a table of common refractive indices:
| Medium | Refractive Index |
|---|---|
| Vacuum | 1.000 |
| Air (STP) | 1.000293 |
| Water (20°C) | 1.333 |
| Glass (Typical) | 1.52 |
| Diamond | 2.417 |

📚 Note: The refractive index can vary slightly depending on the wavelength of light, a phenomenon known as dispersion.
Applications of Refraction

Refraction is not just an academic exercise; it’s used in numerous applications:
- Lenses: Used in eyeglasses, microscopes, and telescopes.
- Optical Fibers: Crucial for telecommunications to guide light through fiber optic cables.
- Photography: Manipulating light to create sharp or blurred images.
- Atmospheric Phenomena: Rainbows, mirages, and the twinkling of stars.
Understanding Snell's Law and its implications allows for precise manipulation of light, crucial in fields like optics, engineering, and atmospheric science. The practice problems and theory provided here are a stepping stone towards mastering the principles of light refraction. Whether it's for academic purposes, professional development, or simple curiosity about the world of physics, this worksheet should have given you a practical insight into the behavior of light at interfaces.
Why does light bend when it passes through different media?
+
Light bends, or refracts, due to a change in its speed when it moves from one medium into another. This change in speed causes the light to alter its direction in accordance with Snell’s Law.
Can light refract more than once?

+
Yes, light can refract multiple times as it passes through different layers or materials with varying refractive indices. Each interface presents an opportunity for refraction.
What is the significance of the critical angle in refraction?

+
The critical angle is the angle of incidence beyond which light will not refract into another medium but will instead undergo total internal reflection. This is significant in designing optical instruments and understanding light behavior at boundaries.