Mastering Slope Graphs: Free Worksheet and Tips

In the realm of data visualization, slope graphs serve as an exceptional tool for depicting changes or comparisons over time or between different categories. This technique not only provides clarity in understanding data trends but also simplifies the complex information into an easily digestible format. In this blog post, we delve into the intricacies of creating and mastering slope graphs, offering insights into its construction, best practices, and the tools you can use to create your own. Additionally, we have curated a free worksheet that you can download to practice making your slope graphs. Let's embark on this journey to enhance your data visualization skills.
Understanding Slope Graphs

A slope graph is a type of line chart that is particularly useful for visualizing how the values of two variables have changed from one point in time to another. Unlike traditional line graphs that might show trends over multiple points, slope graphs focus on the comparison between only two points:
- Initial Value - This is where your data starts.
- End Value - This is where your data ends up.
📝 Note: Slope graphs are not suited for datasets with more than two time points or categories. If your data involves more, consider using other types of charts like area charts or bar charts.
Why Use Slope Graphs?

Slope graphs are particularly valuable because:
- They clearly show the magnitude of change.
- They enable quick comparisons between different categories.
- They simplify complex data sets into a more understandable format.
- They are visually less cluttered than other chart types when showing changes over two time points.
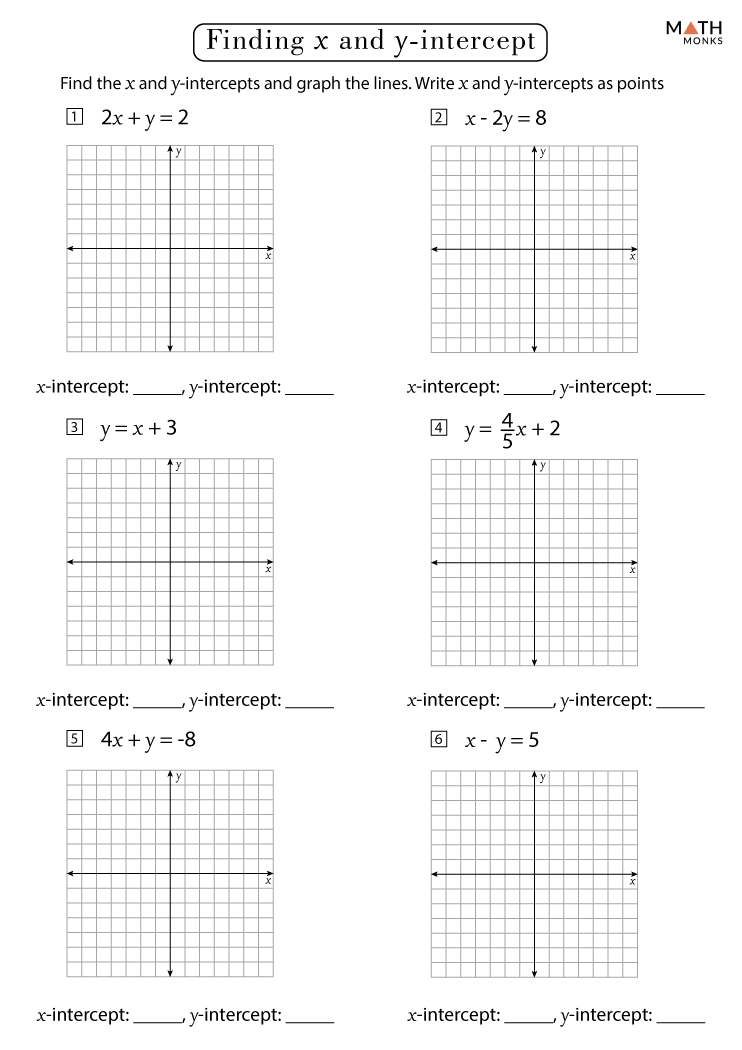
Steps to Create a Slope Graph

To create a slope graph, follow these detailed steps:
1. Gather Your Data

Collect the data points you wish to compare:
- The initial value for each category
- The end value for each category
2. Choose Your Tools

Select software or tools for chart creation:
- Microsoft Excel offers good basic features for creating slope graphs.
- Google Sheets is accessible and free for everyone.
- Data visualization tools like Tableau or Python with libraries such as Matplotlib or Seaborn provide more advanced options.
3. Prepare Your Data

Organize your data into a spreadsheet or table:
| Category | Initial Value | End Value |
|---|---|---|
| Category 1 | 100 | 120 |
| Category 2 | 200 | 180 |

4. Create the Graph

Here’s how to set up your graph:
- Plot your initial values on the left side of the graph.
- Plot your end values on the right side.
- Draw lines connecting these points to visualize the change.
📘 Note: Ensure your graph's axes are properly labeled, with time periods or categories clearly indicated on the horizontal axis.
5. Design and Formatting

Consider these aspects for better readability:
- Choose colors that are visually appealing yet accessible (avoid color blindness issues).
- Label lines or use legends to indicate which line represents which category.
- Format your axes so that they’re easy to read, and avoid cluttering with unnecessary tick marks or gridlines.
6. Review and Adjust
Look over your graph for:
- Accuracy in data representation.
- Visual appeal and readability.
- Clarity in conveying the intended message.
Tips for Better Slope Graphs
To make your slope graphs more effective:
- Focus on Clarity: Avoid overcrowding the graph. If too many lines intersect, it might confuse the reader.
- Use Consistent Scale: Make sure the vertical scale is consistent across both axes for accurate comparison.
- Label Appropriately: Ensure that all points and lines are clearly labeled, especially when dealing with multiple categories.
- Emphasize Trends: Highlight significant trends or anomalies with color or line thickness to draw attention.
- Annotations: Add annotations to clarify points of interest or significant changes.
🖌️ Note: If using digital tools, explore features like annotations, legends, or even a brief text overlay to provide context for the viewer.
In summary, mastering slope graphs offers a clear, concise method for displaying how values change over time or between different categories. They are particularly effective for showcasing trends, anomalies, or shifts in data. With the provided steps and tips, you can craft slope graphs that are both informative and visually appealing. The journey to create an effective visualization starts with understanding your data, choosing the right tools, and applying design principles that enhance comprehension. Utilize the free worksheet provided to practice these skills, and you’ll find that slope graphs can become a powerful addition to your data visualization toolkit.
What are the main uses of slope graphs?

+
Slope graphs are mainly used to compare changes over time between two points or to show relative change between different categories. They are excellent for highlighting trends, differences, or shifts in data.
How do you choose colors for a slope graph?

+
Choose colors that are distinct yet accessible to all viewers, including those with color vision deficiencies. Tools like Color Oracle or Contrast Checker can help ensure your graphs are readable by everyone.
Can I use slope graphs for more than two time points?

+
Technically, you can, but it’s not advisable. Slope graphs work best for visualizing changes between two time points or categories. For more points, consider other visualizations like area charts or time series plots.