Mastering Slope and Rate of Change: Interactive Worksheet
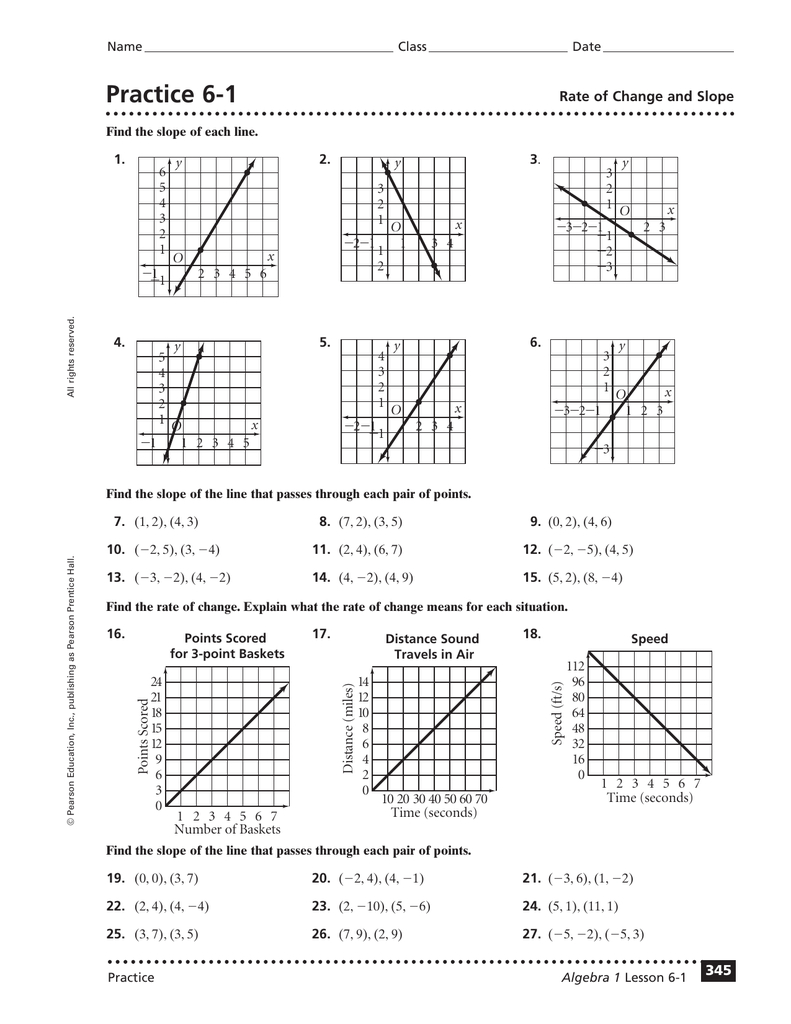
Slope is a fundamental concept in algebra that measures the steepness or incline of a line. Whether you're studying for an exam or working on a project, understanding slope and the rate of change can unlock a deeper understanding of how different variables relate to each other. This blog post will guide you through what slope and rate of change are, how they are calculated, and why they are important. We'll also provide you with interactive resources to help you master these concepts.
What is Slope?

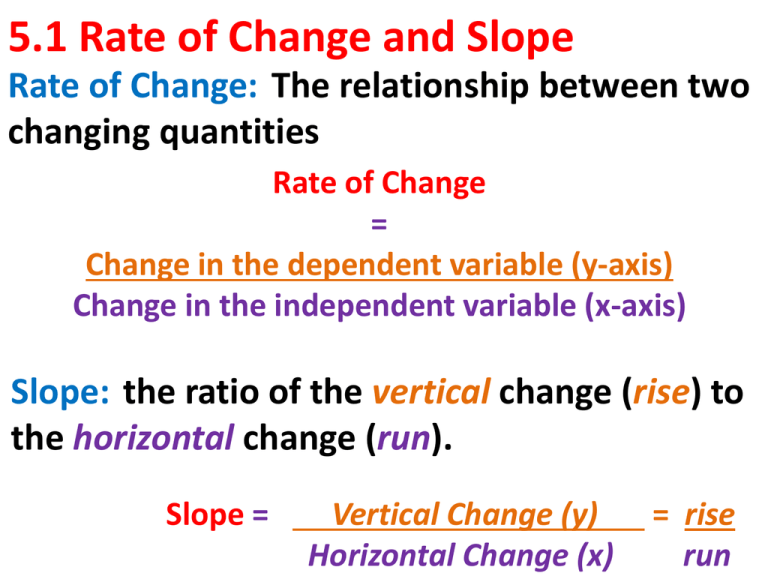
In algebra, the slope of a line represents the ratio of the vertical change to the horizontal change between any two points on the line. This is commonly expressed as:
Slope (m) = (change in y) / (change in x) = Δy / Δx
This simple yet powerful equation can tell you how steep a line is, whether it's rising or falling, and how fast it changes. Here are some key aspects of slope:
- Positive slope: The line ascends from left to right (graph increases as x increases).
- Negative slope: The line descends from left to right (graph decreases as x increases).
- Zero slope: The line is horizontal, indicating no change in y.
- Undefined slope: The line is vertical, indicating no change in x.
Calculating Slope

Let's delve into how you calculate the slope with an example:
Consider two points on a line: (x1, y1) and (x2, y2). The formula for calculating slope between these two points is:
m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)
Example:
- Points: (2,3) and (5,7)
- Slope calculation:
- m = (7 - 3) / (5 - 2) = 4 / 3
- Thus, the slope of the line passing through these points is 4/3.
Here's a table showing different slopes and their corresponding graphical behavior:
| Slope Type | Steepness | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Positive | Line rises from left to right | 3/2, 1, 7 |
| Negative | Line falls from left to right | -2, -5/3, -1 |
| Zero | Flat horizontal line | 0 |
| Undefined | Vertical line | Not defined numerically |
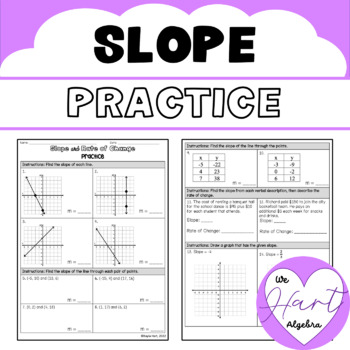
🌟 Note: The slope between two points gives you the average rate of change of the function between those points.
What is the Rate of Change?
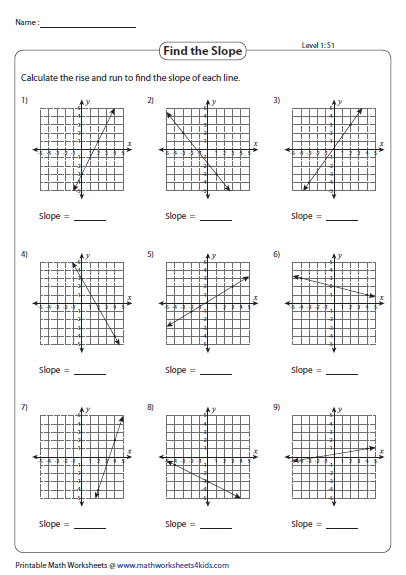
The rate of change is essentially the slope interpreted over time or another continuous variable. It describes how one variable changes relative to another:
- In finance, it might be the rate of return.
- In physics, it could be velocity (rate of change of displacement with respect to time).
- In economics, it can represent growth rate of an economy or company.
The formula for the average rate of change is the same as that for slope, but it's often used in a more applied context where x might represent time, distance, or another measure:
Average rate of change = (change in y) / (change in x) = Δy / Δx
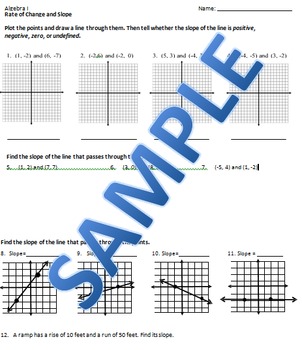
Interactive Worksheet for Slope and Rate of Change
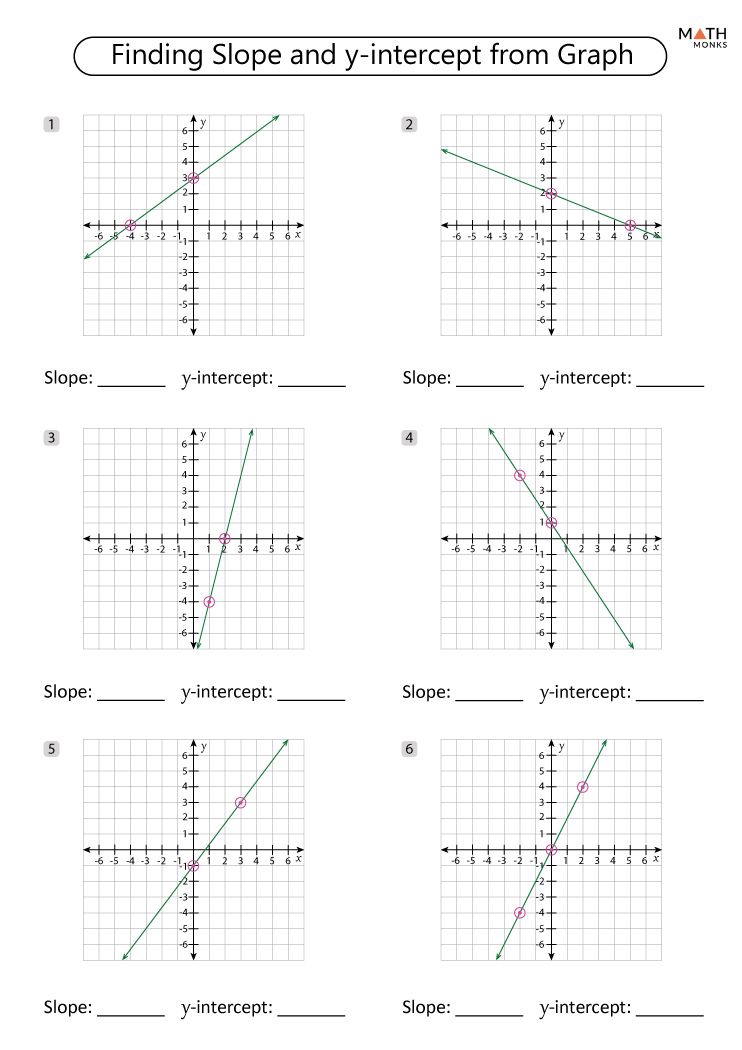
To help you understand these concepts better, here's an interactive worksheet where you can practice:
- Identify the slope: Given two points, calculate the slope.
- Graph the line: Draw a line with a given slope through a point.
- Rate of change in real-life scenarios: Interpret the slope in contexts like finance or physics.
This interactive approach allows you to:
- See immediate feedback on your calculations.
- Visualize how changes in slope affect the line's direction.
- Apply concepts to real-world situations, making the learning process more dynamic and engaging.
In mastering slope and the rate of change, this worksheet provides an indispensable tool to practice, learn, and apply these concepts:
📌 Note: Use this worksheet consistently to reinforce your understanding through repetition and application.
Summing Up
Understanding slope and the rate of change isn't just about solving algebraic problems; it's about interpreting how things change in the world around us. These concepts allow us to analyze trends, make predictions, and understand relationships in a multitude of fields. Through our exploration of slope calculation and its real-world applications, we've seen how essential these skills are for anyone dealing with data or trying to understand the natural and economic systems.
What if the slope is zero?

+
A zero slope means the line is horizontal, indicating that there is no change in the y-variable as x changes.
How can slope help in understanding velocity?

+
Slope can be interpreted as velocity when x represents time. For instance, in a position-time graph, the slope at any point gives you the object’s speed or direction (positive or negative) of motion at that time.
Can the rate of change be negative?
+
Yes, a negative rate of change indicates that as one variable increases, the other decreases, showing an inverse relationship.
Related Terms:
- Average rate of change Worksheet
- Rate of change Worksheet Kuta
- Slope Worksheet