Skills Worksheet Graphing Skills Answer Key Revealed

If you're an educator or a student interested in biology or any related field, you understand the importance of mastering graphing skills. Graphs are not merely tools for displaying data but also essential instruments for data analysis, interpretation, and scientific communication. This article dives deep into the world of graphing skills, particularly focusing on the "Graphing Skills Answer Key" for Skills Worksheet, a document designed to help students better understand how to interpret and create graphs. Whether you're preparing for an exam, teaching a class, or just wanting to enhance your scientific literacy, this guide will provide you with the key insights you need.
Understanding the Graphing Skills Worksheet
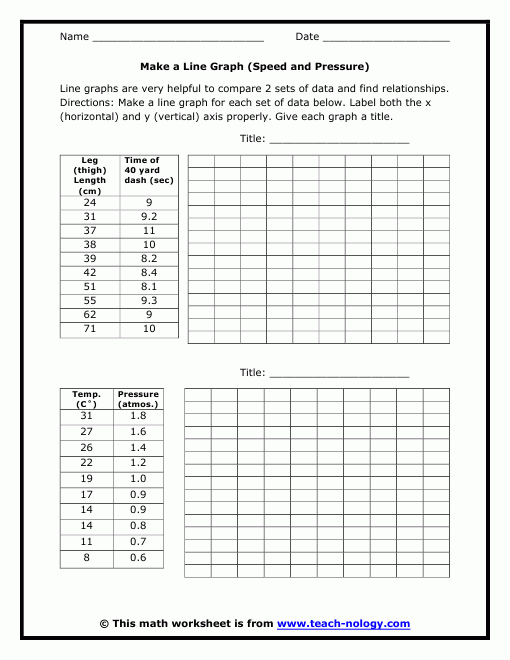
The Graphing Skills Worksheet is typically used to teach students how to present, interpret, and analyze data through graphs. Here are the core components:
- Types of Graphs: Understanding when to use pie charts, bar graphs, line graphs, histograms, and scatter plots.
- Graph Components: Identifying and labeling axes, choosing appropriate scales, and creating a legend or key if necessary.
- Data Interpretation: Making inferences from the data, understanding trends, and making predictions.
How to Use the Answer Key

The answer key for graphing skills worksheets is not just about verifying the correctness of answers but also about learning from the methodology:
- Reviewing Graph Construction: The key explains how graphs should be constructed correctly, highlighting common mistakes and how to avoid them.
- Data Analysis: It guides students through analyzing the data presented, ensuring they understand what the graphs are conveying.
- Feedback and Learning: Through comparison with the answer key, students can see where they went wrong and learn from their mistakes, promoting self-improvement.
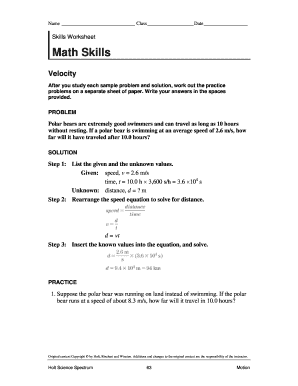
Step-by-Step Guide to Graphing

To further aid your understanding, here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Identify Data Type: Determine if the data is categorical or numerical, continuous or discrete.
- Choose the Right Graph: Based on the data type, decide whether to use a line graph, bar graph, pie chart, etc.
- Set Up Axes: Label the axes with variables, include units of measurement, and ensure the scale is appropriate.
- Plot Points or Bars: Plot the data points or create bars accurately.
- Draw Lines or Connect Points: If using a line graph, decide if you will connect the points directly or use a line of best fit.
- Add Titles and Labels: Title the graph, label each axis, and add a legend if needed.
- Analyze: Look for patterns, trends, or outliers in your graph.
- Summarize Findings: Draw conclusions based on the graph.
📘 Note: Always ensure that your graph title is descriptive, giving viewers immediate context.
Tips for Effective Graphing
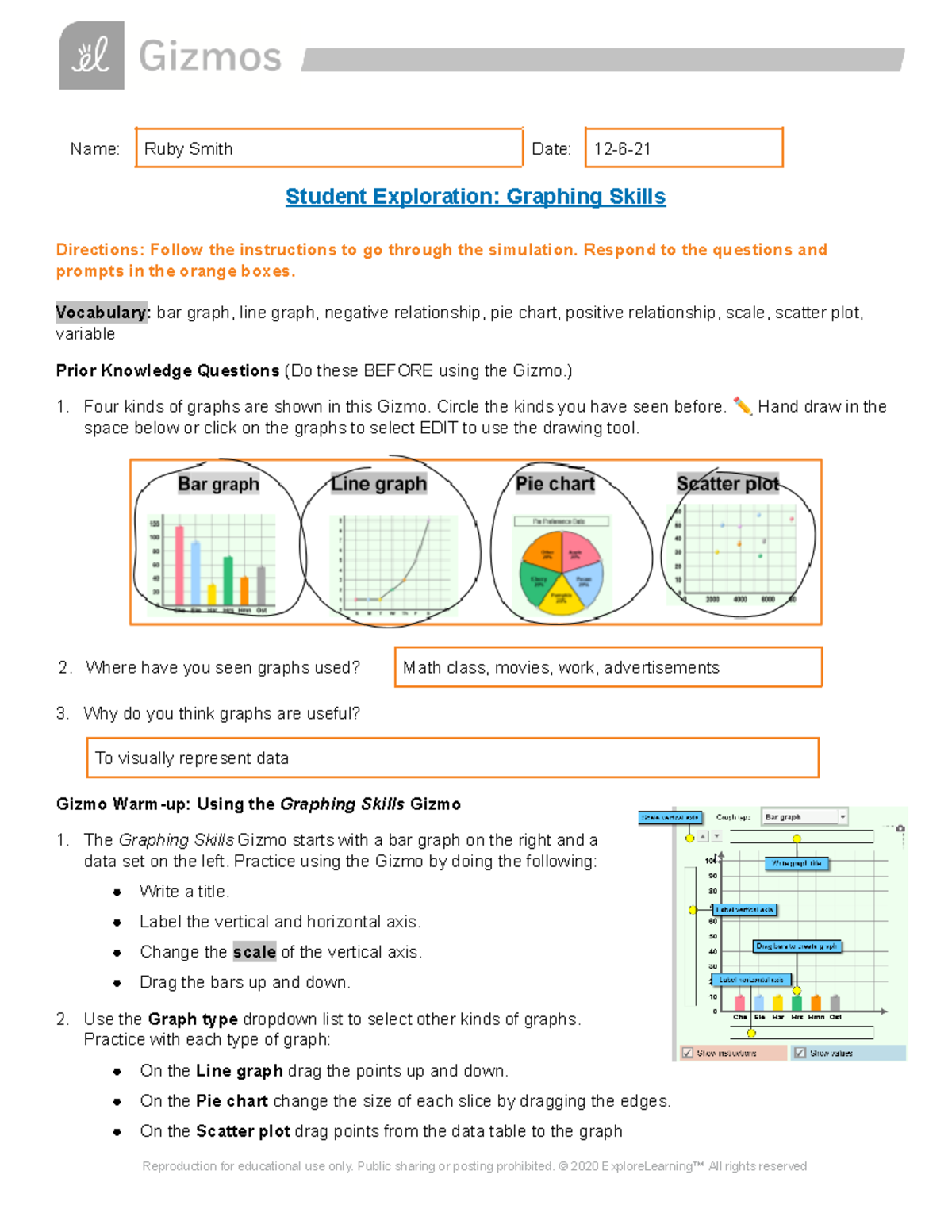
- Start with a Plan: Sketch a rough draft or outline before creating your final graph.
- Use Proper Scale: Incorrect scaling can lead to misinterpretation of data.
- Be Consistent: Use similar color schemes or styles if you’re creating multiple graphs for a single presentation.
- Check for Accuracy: Double-check your data points and calculations to avoid inaccuracies.
Integrating Technology in Graphing
Today’s digital age offers numerous tools to enhance graphing:
- Excel, Google Sheets: For basic to moderate graph creation.
- R: A powerful tool for statistical computing and graphics.
- Matlab: Used in engineering and scientific graphing.
- Python with Libraries like Matplotlib, Seaborn: Provides extensive graph customization for data scientists.
💡 Note: While technology can help create graphs quickly, understanding the manual process fosters a deeper comprehension of data representation.
Final Thoughts

Mastering graphing skills transcends mere academic exercises; it’s about fostering critical thinking, analytical skills, and effective communication in science. By reviewing the Graphing Skills Answer Key, practicing graph creation, and using technology wisely, students and educators can unlock the full potential of graphical data representation. Remember, graphs are not just a means of presenting information but a powerful tool for understanding and exploring the intricate patterns of our world.
Why are graphing skills important in science?
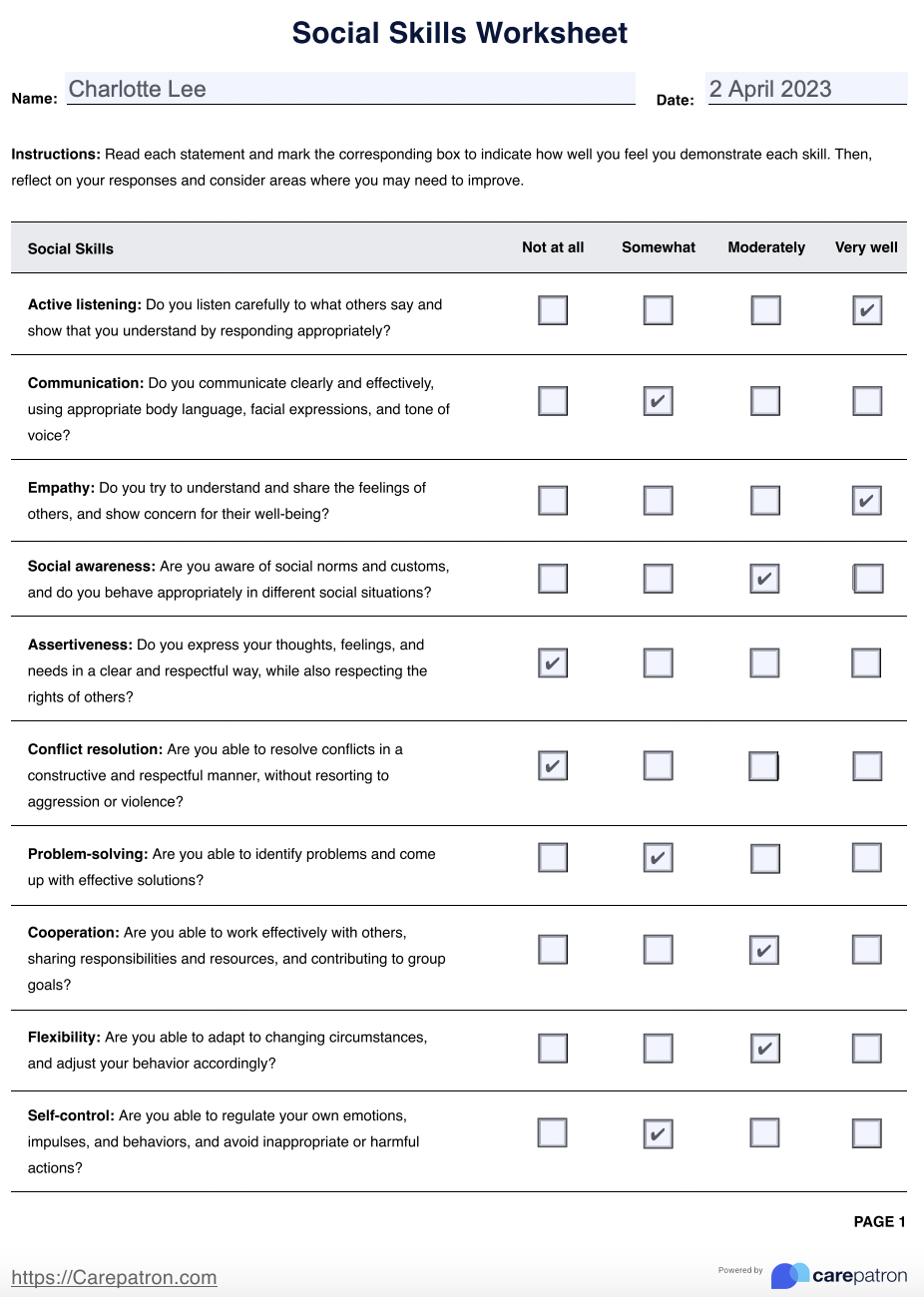
+
Graphing skills are crucial in science because they help visualize data, making complex information more digestible, facilitating the identification of trends, and aiding in data analysis and communication of scientific findings.
Can I use any type of graph for any data?

+
No, different graphs are suited for different types of data. Line graphs are best for showing changes over time, bar graphs for comparing quantities, pie charts for showing parts of a whole, and scatter plots for indicating relationships between two variables.
What are common mistakes when creating graphs?

+
Common mistakes include improper scaling, unclear titles or labels, not using the appropriate type of graph, and misrepresenting data through selective or misleading presentation.
How can I improve my graphing skills?

+
Practice is key. Start with manual graphing, then move to software tools. Understand data types, graph rules, and common errors. Analyze examples from textbooks or scientific journals, and always review the Graphing Skills Answer Key for guidance.