Similar Triangles Word Problems Worksheet With Answers
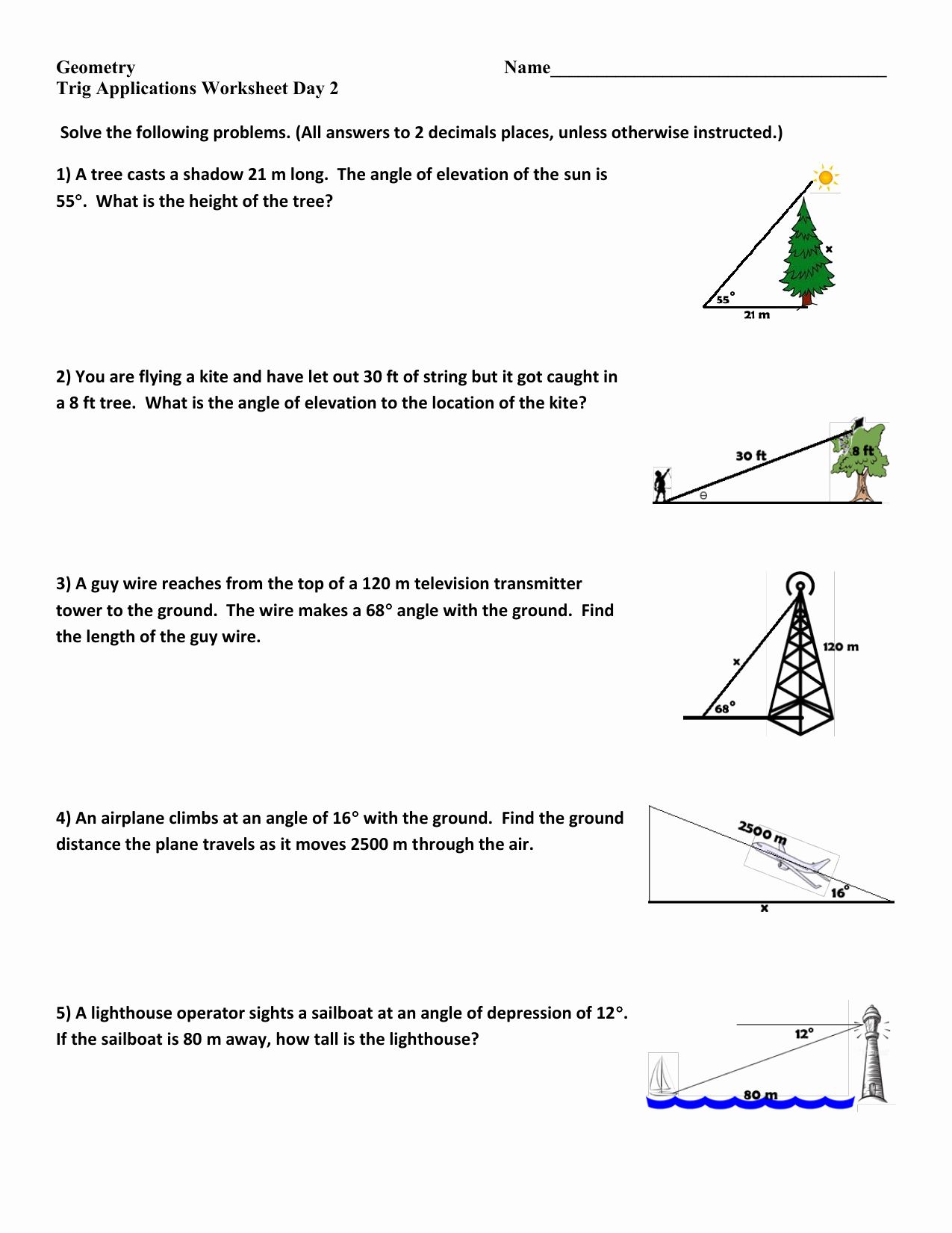
Learning about similar triangles can be quite intriguing, especially when you dive into practical applications through word problems. This worksheet is designed to help you not only understand the concept of similar triangles but also to apply this understanding in solving real-world scenarios. Here, we'll explore various problems, dissecting them step-by-step to find solutions.
Understanding Similar Triangles
Similar triangles are triangles with corresponding sides in proportion and corresponding angles equal. When two triangles are similar:
- The ratios of the corresponding sides are equal
- The corresponding angles are congruent
Let's delve into some word problems to see how these properties can be applied.
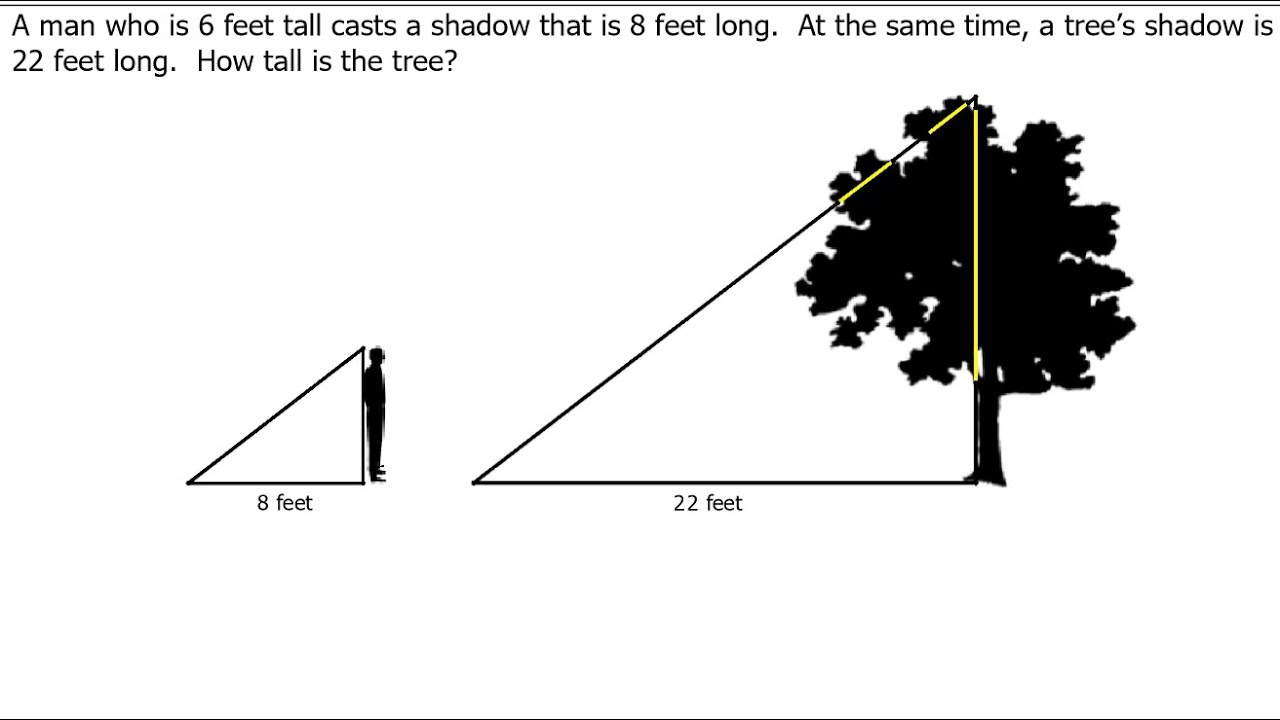
Problem 1: Height of a Tree

A tree casts a shadow that is 12 meters long. At the same time, a 6-meter-tall person standing beside the tree casts a shadow that is 4 meters long. Determine the height of the tree using similar triangles.
| Trees/Trees | Shadows |
|---|---|
| Height of Tree | 12 meters |
| Height of Person | 4 meters |

To solve:
- Set up the proportion based on the similarity of triangles:
- Substitute known values:
- Solve for the height of the tree:
Height of Tree / Length of Tree's Shadow = Height of Person / Length of Person's Shadow
Height of Tree / 12 = 6 / 4
Height of Tree = (6 * 12) / 4 = 18 meters
Problem 2: Scale of a Map

On a map, a road measures 3 inches, while its actual length is 15 miles. A trail next to the road measures 1.5 inches on the map. How long is the trail in reality?
| Map Measurement | Real Length |
|---|---|
| Road | 3 inches - 15 miles |
| Trail | 1.5 inches - ? |
To solve:
- Set up the proportion:
- Substitute known values:
- Solve for the length of the trail:
Length of Trail / Map Length of Trail = Actual Road Length / Map Road Length
Length of Trail / 1.5 = 15 / 3
Length of Trail = (1.5 * 15) / 3 = 7.5 miles
Problem 3: Elevation of a Building

A person standing 50 feet from the base of a building looks up at an angle of 45 degrees to see the top. If the person is 6 feet tall, how tall is the building?
🌟 Note: Remember that in a right triangle with a 45-degree angle, the other two angles are also 45 degrees, making the triangle isosceles with the two legs equal.
To solve:
- Recognize that the triangle formed by the person, the building, and the sight line is an isosceles right triangle:
- The height of the building plus the height of the person forms the hypotenuse:
- Let
hbe the height of the building. Thus,sqrt(2)(h + 6) = 50 - Solve for
h:
h + 6 = 50/sqrt(2)
h + 6 ≈ 35.36
h ≈ 29.36 feet
Summarizing Our Findings

We've explored the concept of similar triangles through various word problems, demonstrating how similarity can help solve real-life issues involving distances, heights, and measurements. From understanding how to determine the height of objects like trees and buildings to calculating real distances from scaled maps, similar triangles provide a foundation for logical problem-solving in geometry.
Why are similar triangles important in problem-solving?

+
Similar triangles help in establishing relationships between distances, lengths, and angles which are essential for solving various real-world problems in areas like architecture, engineering, and even daily life.
Can you find similarity between triangles without knowing the angle measurements?
+
Yes, if the ratios of corresponding sides are equal, the triangles are similar, even if angles aren’t directly known.
What are some common errors when solving similar triangle problems?
+
Confusing corresponding sides, not setting up proportions correctly, or misunderstanding the rules of similarity can lead to incorrect answers. Also, over-relying on visual estimation without calculation can be misleading.
To sum up, by mastering similar triangles, you gain a powerful tool for problem-solving that opens up numerous applications in various fields, making it an invaluable part of your mathematical toolkit.