Sheep Brain Dissection Guide with Worksheet Answers

In the realm of biological studies, particularly within anatomy and physiology, dissecting a sheep brain offers an invaluable opportunity to explore the complexities of the mammalian brain. This guide is designed to assist students, educators, and curious individuals through the process of sheep brain dissection, providing not only procedural instructions but also educational insights and answers to common questions found in dissection worksheets. Here, you will gain a deep understanding of brain structures, their functions, and their interconnections.
Preparation for Dissection

Before embarking on the dissection journey:
- Obtain a preserved sheep brain. You can usually source these from educational supply stores or institutions that supply biological materials.
- Gather tools: dissecting tray, scalpel, blunt probe, forceps, and dissecting scissors.
- Don protective gear: gloves, lab coat or old shirt, eye protection, and ensure you’re working in a well-ventilated area or under a fume hood if possible.
Dissection Procedure

External Examination

Begin by placing the sheep brain in the dissecting tray, noting the following:
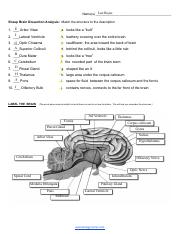
- Cerebrum: The largest part of the brain, characterized by its folded outer layer (cerebral cortex).
- Cerebellum: Posterior to the cerebrum, identifiable by its tightly packed folds.
- Brainstem: Including the pons and medulla oblongata, connecting the brain to the spinal cord.
Observe the size, shape, color, and any protective layers (meninges).

Internal Examination

- Coronal Section: Make a cut along the coronal plane (front to back) to expose internal structures:
- Identify the corpus callosum connecting the two hemispheres.
- Locate the lateral ventricles, and trace the flow of cerebrospinal fluid.
- Sagittal Section: Slice the brain in half along the midline:
- Observe the internal structure of the cerebral hemispheres.
- Locate the thalamus, hypothalamus, and pituitary gland.
- Transverse Cuts: Make horizontal slices to view brain structures from different angles:
- This helps to see structures like the brainstem, basal ganglia, and internal capsule.

Worksheet Answers

Below are some typical questions found in sheep brain dissection worksheets along with their answers:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the function of the cerebral cortex? | The cerebral cortex is responsible for higher brain functions including sensory perception, generation of motor commands, spatial reasoning, conscious thought, and language. |
| Identify the main parts of the brainstem. | The brainstem comprises the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata. These structures control functions like respiration, heart rate, and reflexes. |
| What does the cerebellum regulate? | The cerebellum coordinates voluntary movements, balance, posture, and complex motor skills like those needed for playing music or sports. |

📌 Note: Ensure you're disposing of biological waste according to your institution's guidelines to maintain safety and compliance with environmental regulations.
In the concluding segment of our sheep brain dissection guide, we've uncovered not only how to perform this fascinating process but also the significance of each brain region. Understanding the structure and function of the brain through hands-on experience is crucial for grasping the complexity of neurological operations. Each cut and observation serves to deepen your appreciation for the biological intricacies that allow us to think, move, and survive. Engaging in such activities not only bolsters your knowledge but also fosters a profound respect for neuroscience and the journey of learning about the brain.
How does a sheep brain differ from a human brain?

+
The main differences include the size, with the human brain being larger and more complex due to higher cognitive functions. Sheep brains lack the extensive frontal lobe development seen in humans, which correlates with problem-solving abilities and personality traits. Also, the sheep brain’s meninges are thicker for protection against falls and injuries common in livestock.
Why use sheep brains for dissection instead of other animals?
+
Sheep brains are widely used in educational settings due to their availability from the meat industry, making them both economical and ethical for dissection. They are also sufficiently similar to human brains in structure for educational purposes but different enough to highlight unique biological traits.
What are the ethical considerations when dissecting animals?

+
Key ethical concerns include using animals that have already been sacrificed for the food industry, ensuring that the dissections serve an educational purpose, and using the specimens respectfully. It’s also important to explore alternatives like virtual dissections or models when possible to minimize animal use.