Exploring Shapes of Molecules Worksheet for Chemistry Students

Understanding Molecular Geometry
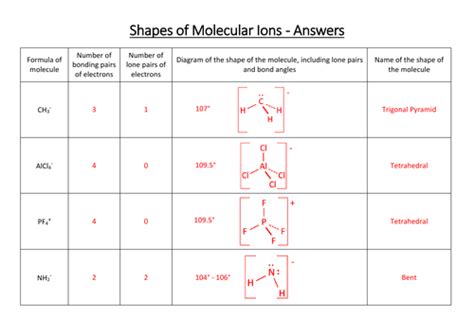
Molecular geometry is a crucial concept in chemistry that helps us understand the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms within a molecule. It is essential to comprehend the shapes of molecules to predict their physical and chemical properties, such as polarity, reactivity, and biological activity. In this article, we will delve into the world of molecular geometry and provide a comprehensive guide to help chemistry students master the concept.
Theories Behind Molecular Geometry

Two primary theories explain the shapes of molecules: the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory and the Molecular Orbital (MO) theory. VSEPR theory states that electron pairs in the valence shell of an atom repel each other, resulting in a specific arrangement of atoms. MO theory, on the other hand, describes the distribution of electrons within a molecule using molecular orbitals.
VSEPR Theory and Electron Geometry

VSEPR theory is a straightforward approach to predicting molecular geometry. It involves the following steps:
- Determine the central atom: Identify the atom in the molecule that is bonded to the most other atoms.
- Count the number of electron groups: Count the number of electron groups (bonding and non-bonding pairs) around the central atom.
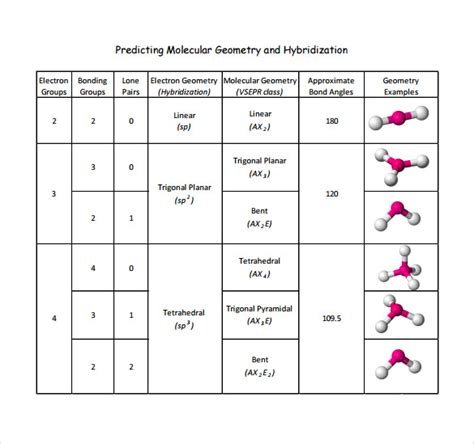
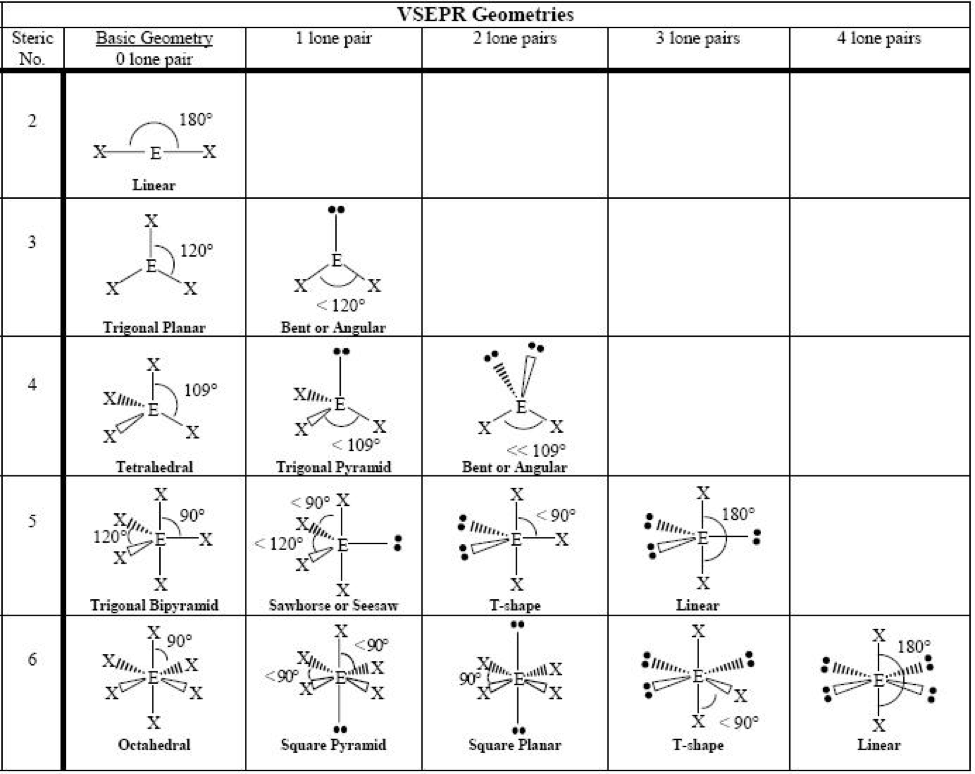
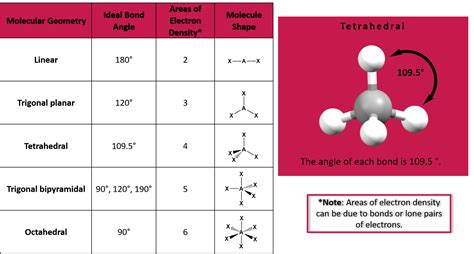
- Determine the electron geometry: Use the number of electron groups to determine the electron geometry (e.g., linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral).
- Determine the molecular geometry: Use the electron geometry to predict the molecular geometry (e.g., bent, trigonal pyramidal).
| Number of Electron Groups | Electron Geometry | Molecular Geometry |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | Linear | Linear |
| 3 | Trigonal planar | Trigonal planar or bent |
| 4 | Tetrahedral | Tetrahedral or trigonal pyramidal |
Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory
MO theory is a more advanced approach to understanding molecular geometry. It involves the combination of atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals. The number of molecular orbitals is equal to the number of atomic orbitals combined. MO theory can be used to predict molecular geometry, bond order, and magnetic properties.
Shapes of Common Molecules

Here are some common molecules and their corresponding shapes:
- Water (H2O): Bent or V-shape
- Carbon dioxide (CO2): Linear
- Methane (CH4): Tetrahedral
- Ammonia (NH3): Trigonal pyramidal
📝 Note: Molecular geometry can be affected by the presence of lone pairs, which can occupy more space than bonding pairs.
Practice Problems

To reinforce your understanding of molecular geometry, try solving the following practice problems:
- What is the molecular geometry of a molecule with the formula XeF4?
- Predict the shape of the molecule CIF3.
- Determine the electron geometry and molecular geometry of the molecule SF4.
Conclusion

Understanding molecular geometry is crucial for chemistry students to grasp the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms within a molecule. By applying VSEPR theory and MO theory, students can predict the shapes of molecules and understand their physical and chemical properties. With practice and patience, students can master the concept of molecular geometry and become proficient in predicting the shapes of molecules.
What is the difference between electron geometry and molecular geometry?

+
Electron geometry refers to the arrangement of electron groups around the central atom, while molecular geometry refers to the arrangement of atoms in space.
How does VSEPR theory predict molecular geometry?

+
VSEPR theory predicts molecular geometry by counting the number of electron groups around the central atom and using this information to determine the electron geometry and molecular geometry.
What is the molecular geometry of a molecule with the formula CO2?
+
The molecular geometry of CO2 is linear.
Related Terms:
- Shapes of molecules worksheet pdf
- Shapes of molecules pdf
- Molecular Polarity Worksheet PDF
- Shapes of molecules in chemistry
- Molecular Geometry Worksheet with Answers
- Molecular Polarity Worksheet answer key