5 Tips for Mastering Set and Interval Notation Worksheet

"Set and interval notation are fundamental concepts in mathematics, especially in fields like calculus, algebra, and analysis." This opening statement captures the essence of why mastering set and interval notation is essential for students and professionals alike. Whether you're graphing functions, solving inequalities, or analyzing data sets, being adept in these notations simplifies problem-solving and enhances communication. Let's delve into five comprehensive tips that will not only help you master set and interval notation but also enhance your overall mathematical proficiency.
Tip 1: Understand the Basics
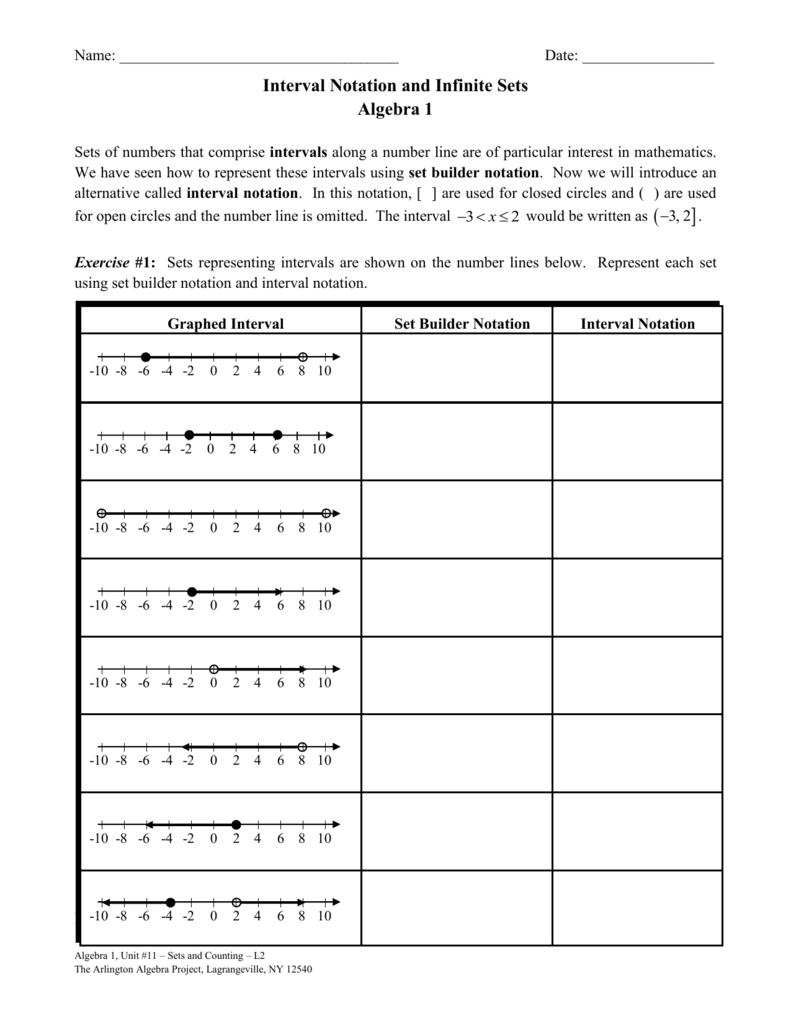
To excel in set and interval notation, you must start with a solid foundation. Here’s what you need to know:
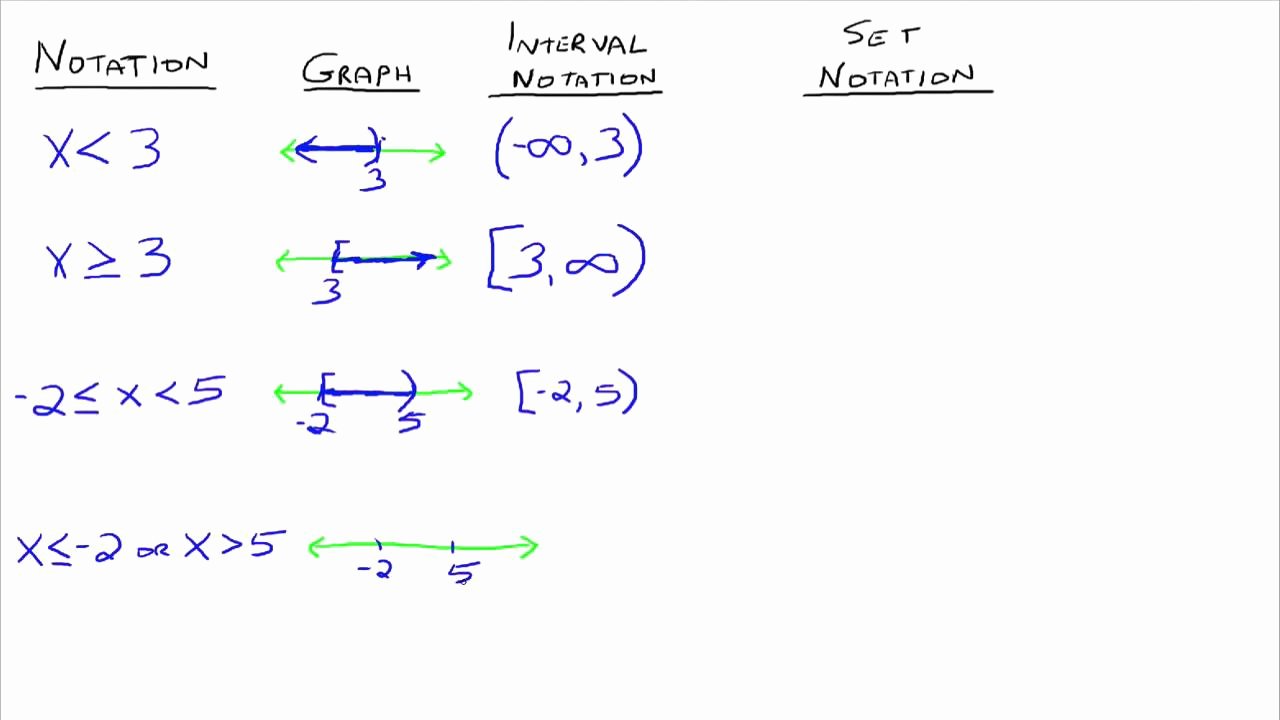
- Set Notation: A set is a collection of objects, typically numbers, where each element is unique. You denote sets using curly braces { }, and if the set contains an infinite number of elements, you use ellipses ( … ).
- Interval Notation: Intervals are subsets of the real numbers, typically represented on the number line. There are different types of intervals:
- Closed intervals [a, b]: Includes both endpoints.
- Open intervals (a, b): Excludes both endpoints.
- Half-open intervals [a, b) or (a, b]: Includes one endpoint but not the other.
- Union and Intersection: Understand how to combine or find common elements between sets or intervals.
🔍 Note: The union (U) of sets/ intervals is everything that belongs to at least one set or interval. The intersection (ꓵ) is what belongs to both.
Tip 2: Visualize Intervals
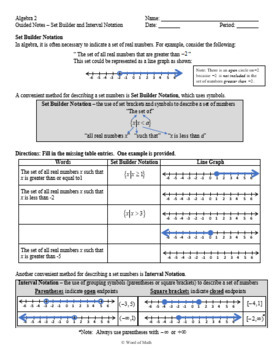
Visualization is a powerful tool in understanding interval notation:
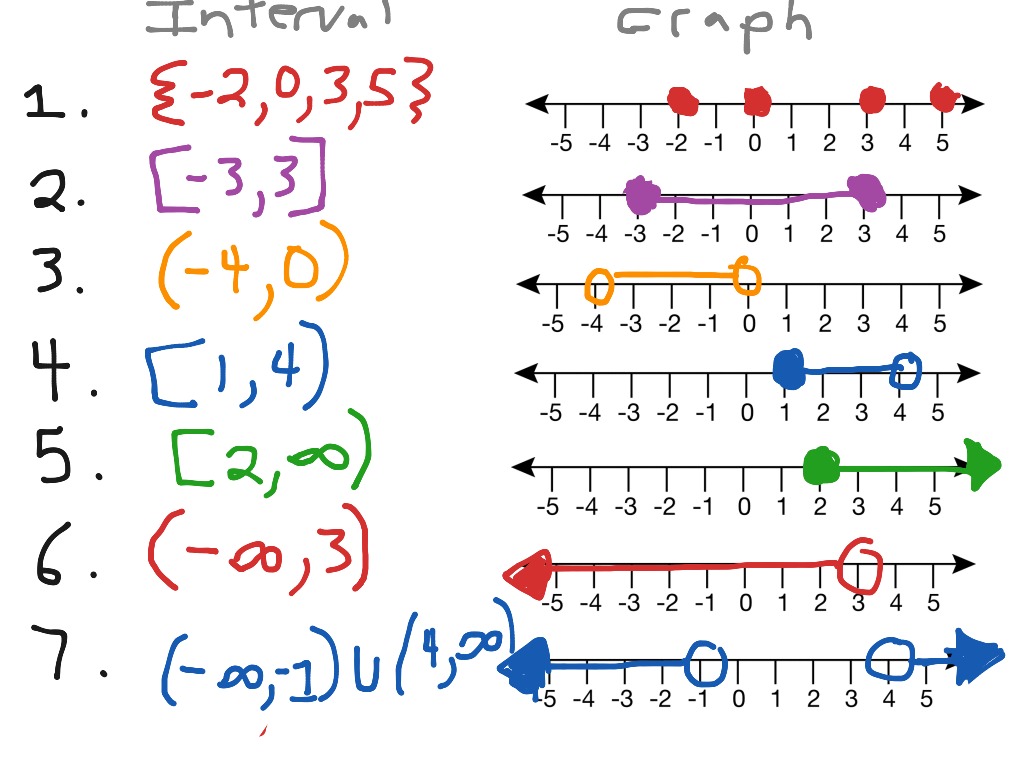
- Number Line: Plotting intervals on a number line can help you understand which points are included or excluded:
- Use solid dots for included endpoints (closed intervals).
- Use hollow circles for excluded endpoints (open intervals).
- Color Coding: Assign different colors for different intervals or sets to see their overlap visually.
- Software Tools: Utilize graphing software like Desmos, GeoGebra, or even Excel to visualize complex sets or intervals.
Tip 3: Practice with Real-Life Examples
Mathematics becomes relevant when you apply it to real-world scenarios:
- Health and Fitness: Using interval notation to describe heart rate zones during exercise.
- Finance: Representing investment thresholds or stock price ranges.
- Statistics: Handling data sets within specific intervals or sets.
By solving problems from these fields, you’ll develop a practical understanding of set and interval notation.
Tip 4: Master the Art of Converting

Converting between different notations is crucial for a comprehensive understanding:
- Set to Interval: Converting a set {1, 2, 3, …, 10} to interval notation would be [1, 10].
- Interval to Set: The interval (1, 5) could be described as {x | 1 < x < 5}, which is set-builder notation.
- Practice: Regularly convert between these notations, especially when solving inequalities or working with functions.
Tip 5: Utilize Technology

Leverage technology to enhance your learning:
- Online Practice Platforms: Websites like Khan Academy, Mathway, and MyMathLab offer interactive exercises on interval and set notation.
- Apps: Apps like Photomath can help you check your work by providing step-by-step solutions to interval notation problems.
- Spreadsheets: Excel or Google Sheets can be used to simulate interval and set operations visually and compute results.
🔗 Note: These tools don’t replace understanding but augment your ability to apply concepts swiftly.
In closing, mastering set and interval notation isn't just about memorizing definitions but about understanding, visualizing, and applying these concepts in various contexts. By employing these five tips, you'll not only become adept at solving problems involving these notations but also enhance your mathematical thinking. From visualizing intervals on a number line to applying these concepts to real-life scenarios, the journey to mastery is one of both practical application and theoretical insight.
What is the difference between open and closed intervals?
+
An open interval does not include its endpoints (e.g., (2, 6)), while a closed interval includes both endpoints (e.g., [2, 6]).
How do I convert a set into interval notation?

+
If your set contains all real numbers between two points, you write it in interval notation by determining if the endpoints are included or not. For example, the set {x | 2 < x < 6} can be converted to (2, 6).
Can you have an interval where only one endpoint is included?
+
Yes, intervals can have one included and one excluded endpoint. These are called half-open or half-closed intervals, like [2, 6) or (2, 6].
What’s the best way to practice interval notation?
+
Practicing with visual aids like number lines, solving inequalities, and using online resources for interactive exercises are effective ways to practice.