Separation of Mixtures Worksheet: Quick Answers Guide

Educators and parents looking to impart the fundamentals of mixture separation techniques to students or children can benefit greatly from engaging activities that make learning both interactive and fun. A worksheet focused on the separation of mixtures can serve as an invaluable tool, providing quick answers and practical examples to reinforce key concepts. Here's a comprehensive guide to help you navigate through the core methods of separating mixtures.
Understanding Mixtures

A mixture is a physical combination of two or more substances that are not chemically bonded. Before delving into separation techniques, it's crucial to understand what mixtures are:
- Homogeneous mixtures: Uniform composition (e.g., salt water).
- Heterogeneous mixtures: Non-uniform composition (e.g., sand and gravel).
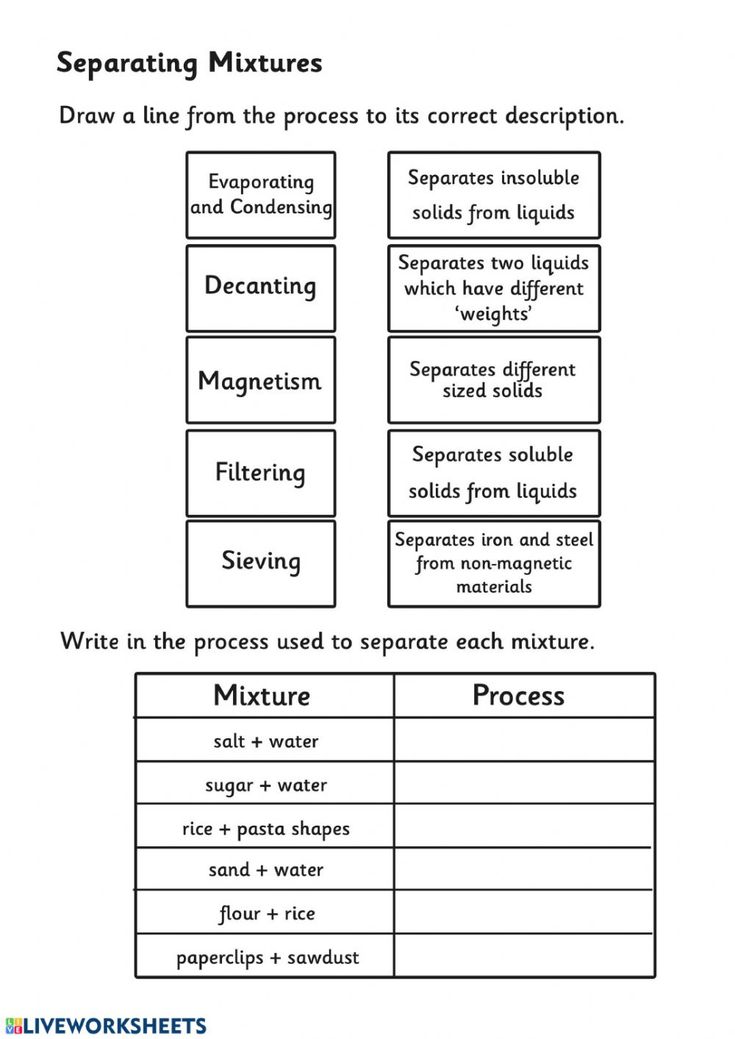
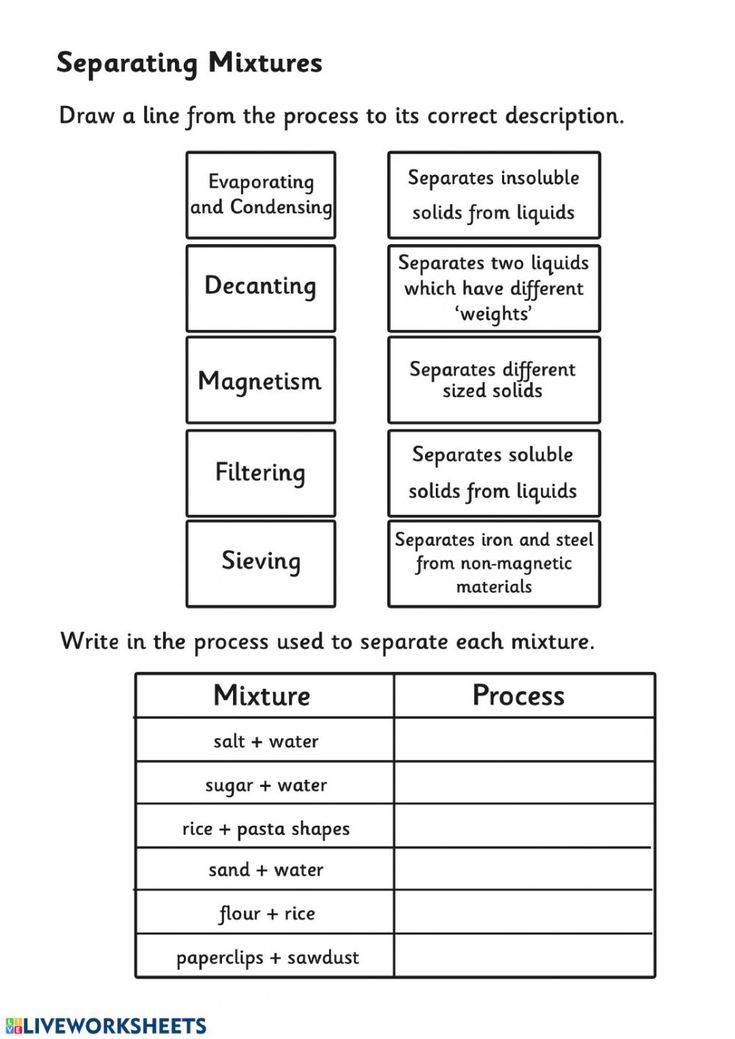
Separation Techniques

Let's explore the various separation of mixtures methods:
Filtration

Filtration involves using a filter medium (like paper or a sieve) to separate solids from liquids or gases:
- Used for: Heterogeneous mixtures where the solid particles are much larger than the filter pores.
- Examples: Coffee filtration, separating sand from water.
Decantation

Decantation is a process of separating an immiscible liquid from a solid or another liquid by slowly pouring off the top layer:
- Used for: When liquids have different densities, like oil and water.
- Examples: Pouring off the liquid layer after allowing sediments to settle.
Evaporation

This technique involves heating a solution to convert the solvent into vapor, leaving behind the solute:
- Used for: Separating soluble solids from liquids.
- Examples: Obtaining salt from seawater.
Distillation

Distillation separates mixtures based on differences in boiling points:
- Used for: Liquid mixtures where one component has a lower boiling point.
- Examples: Purifying alcohol or separating ethanol from water.
Chromatography
Chromatography involves the separation of mixtures based on the differential movement of their components through a stationary phase:
- Used for: Identifying and separating pigments or amino acids.
- Examples: Paper chromatography for ink separation.
Magnetic Separation

This method uses magnets to attract and separate magnetic materials from non-magnetic ones:
- Used for: Mixtures containing magnetic materials like iron.
- Examples: Separating iron fillings from a mixture with sulfur.
Each technique has its application, and understanding when to use which method can simplify the process significantly.
Common Separations in Daily Life
| Mixture | Separation Technique |
|---|---|
| Tea leaves and water | Filtration |
| Water and alcohol | Distillation |
| Iron filings and sawdust | Magnetic Separation |

📝 Note: Ensure to guide students to conduct these experiments in a controlled environment to avoid any hazards related to chemicals or heat sources.
To conclude, teaching the separation of mixtures can be an enjoyable and educational journey. Through understanding the basic principles, exploring various techniques, and seeing real-world applications, students can grasp the essence of this vital scientific concept. This knowledge not only enriches their academic understanding but also prepares them for practical applications in daily life or advanced science studies.
What makes a mixture homogeneous or heterogeneous?

+
The uniformity or non-uniformity of a mixture’s composition determines its classification. If the mixture has the same properties throughout, it’s homogeneous. If the properties vary from one part to another, it’s heterogeneous.
Can we always use evaporation to separate mixtures?

+
No, evaporation is not suitable for all mixtures. It works best for solutions where the solvent can be easily vaporized, leaving behind the solute. For immiscible liquids or mixtures with heat-sensitive components, alternative methods are preferable.
Why is distillation more complex than evaporation?

+
Distillation requires the careful control of temperature to separate substances based on their boiling points, making it more complex. Evaporation simply involves heating a mixture until one component evaporates, usually the solvent.
How does chromatography help in separating mixtures?

+
Chromatography allows for the separation of mixtures by exploiting differences in how their components interact with a stationary phase. As the mobile phase moves through the stationary phase, components travel at different rates, causing separation.