Unlock Solubility Secrets: Easy Worksheet Answers

Unlocking the solubility of various compounds is not just an academic exercise; it's pivotal for both chemistry enthusiasts and professionals in industries such as pharmaceuticals, materials science, and environmental chemistry. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the essentials of solubility, guiding you through easy worksheet answers to demystify these solubility secrets.
Understanding Solubility

Solubility is the maximum amount of solute that can dissolve in a given solvent at a specific temperature and pressure. Here are the key points to understand:
- Definition: The capability of a substance (solute) to dissolve in a solvent to form a solution.
- Influential Factors: Temperature, pressure, nature of solute and solvent, and their chemical interactions.
Solubility Rules for Common Ions
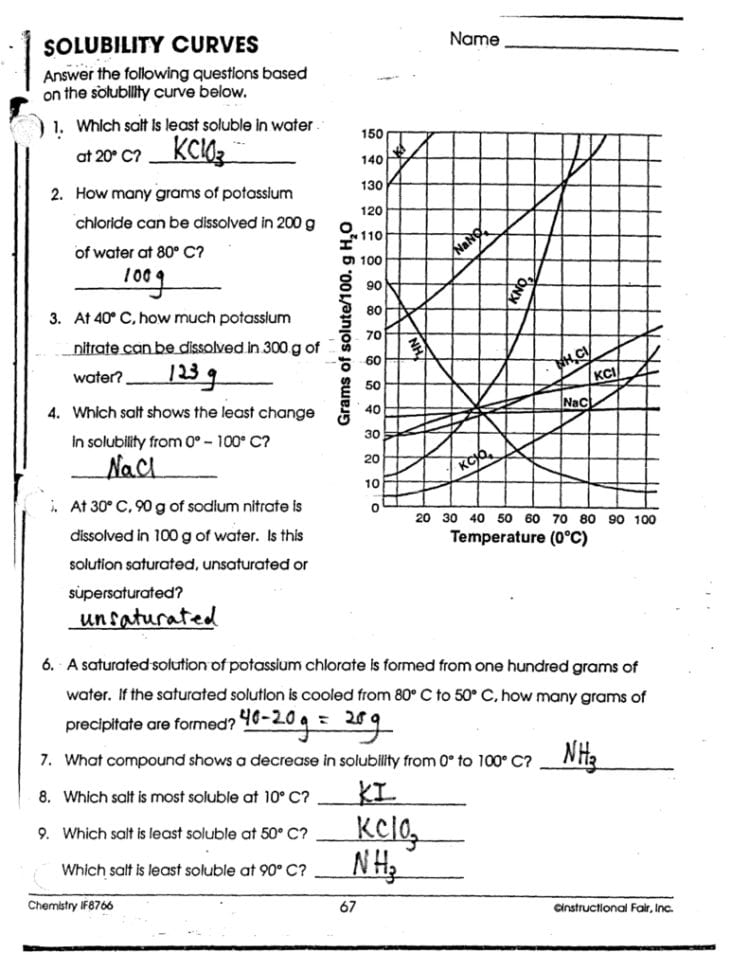
When it comes to solving solubility worksheets, knowing the solubility rules for common ions is crucial. Here are some guidelines:
| Ion | Solubility Rule |
|---|---|
| Group 1 elements (Li+, Na+, K+, Rb+, Cs+) | Most salts are soluble. |
| Ammonium (NH4+) | All salts are soluble. |
| Nitrates (NO3-) | All nitrates are soluble. |
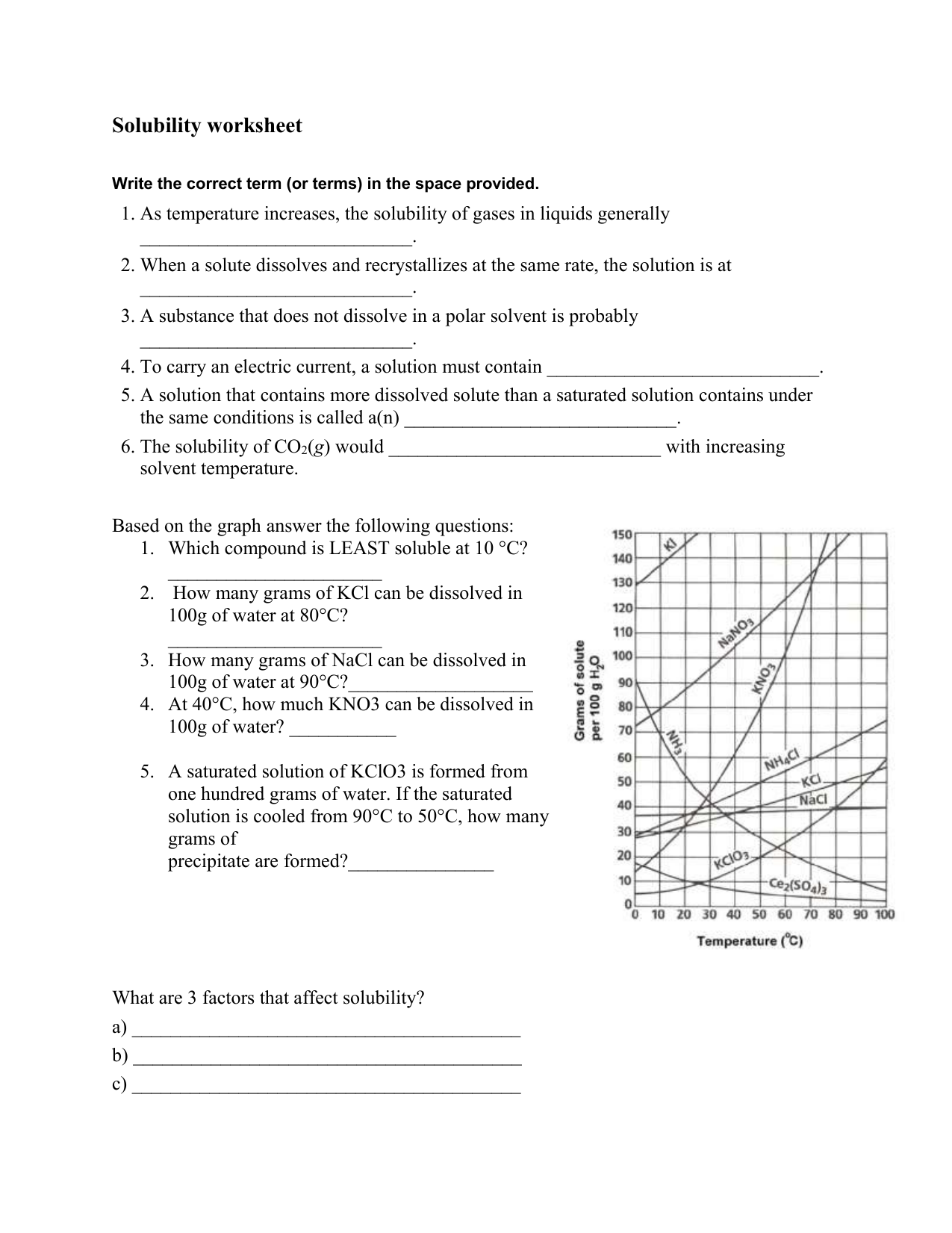
Steps to Solve Solubility Problems

To tackle solubility problems effectively, follow these steps:
- Identify the ions: Break down the compound into its constituent ions.
- Apply solubility rules: Use the rules to determine solubility. If you’re unsure, consider:
- Is the compound formed by Group 1 elements?
- Does the anion have specific solubility exceptions?
- Consider temperature effects: At higher temperatures, solubility generally increases.
📌 Note: Always check the solubility tables for precise data as exceptions exist.
Worksheet Example
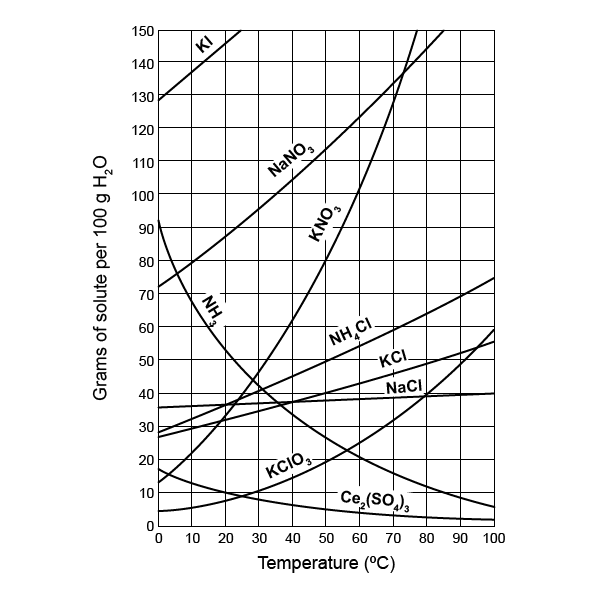
Let’s examine a worksheet example to clarify how these rules work in practice:
Problem:

Determine if the following salts are soluble or insoluble:
- NaCl
- CaCO3
- AgBr
Answer:
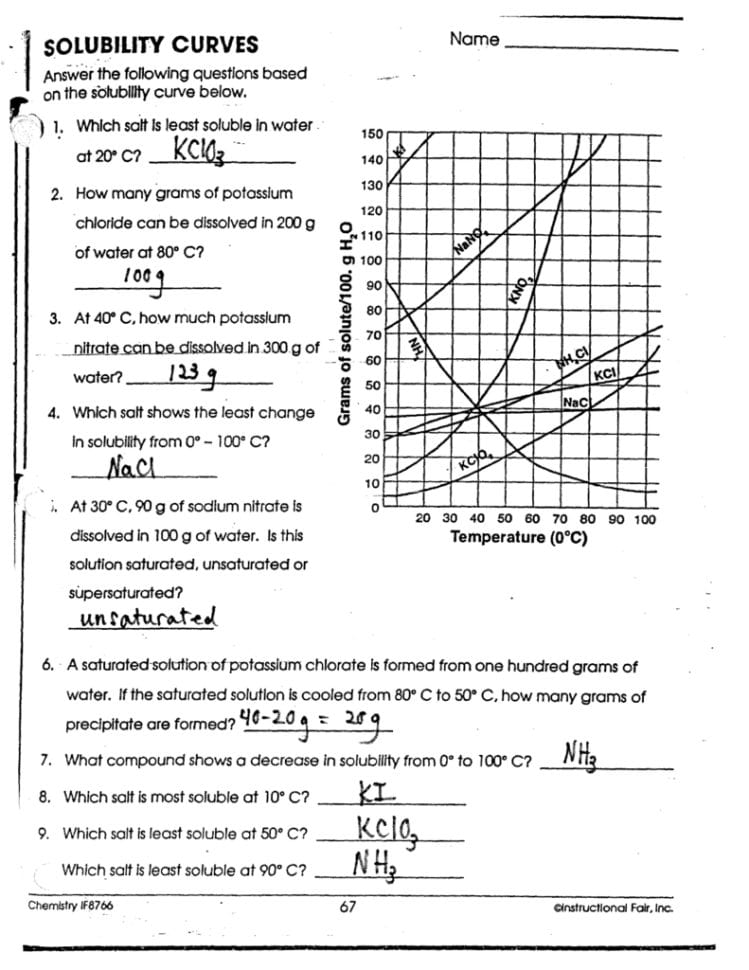
Using the solubility rules:
- NaCl (Sodium Chloride): Group 1 elements are soluble. Therefore, NaCl is soluble.
- CaCO3 (Calcium Carbonate): Carbonates are generally insoluble except when paired with Group 1 elements or ammonium. CaCO3 is insoluble.
- AgBr (Silver Bromide): Bromides are soluble, but Ag+ is an exception. Thus, AgBr is insoluble.
Wrapping Up the Solubility Adventure

Through this guide, we’ve ventured into the world of solubility, arming you with the tools to confidently navigate solubility worksheets. Remember, understanding solubility is not just about memorizing rules; it’s about recognizing patterns, exceptions, and the underlying principles of chemical interactions. By mastering these, you’ll not only excel in your academic tasks but also find real-world applications in industries that rely heavily on solubility for product formulation, waste management, and environmental assessments.
Why is solubility important in chemistry?

+
Solubility determines how substances interact in solutions, influencing reactions, material science, drug formulation, and environmental processes. Understanding solubility helps predict how substances will behave in different conditions, crucial for both theoretical and practical chemistry.
Can solubility be increased or decreased?

+
Solubility can be manipulated through changes in temperature, pressure (especially for gases), and by altering the solvent. For example, heating a solution can increase solubility, while cooling it can decrease solubility or cause precipitation.
How do I remember solubility rules?

+
Here are some tips:
- Use mnemonic devices or songs to remember common ions and their solubility behaviors.
- Create a cheat sheet or flashcards with the rules and exceptions.
- Practice, practice, practice. The more you work with solubility problems, the more these rules will stick.
What are some practical applications of solubility?
+
Solubility plays a role in:
- Pharmaceuticals: Drug solubility affects absorption in the body.
- Environmental science: Solubility determines how pollutants spread in water.
- Materials engineering: Solubility impacts the formation of alloys and the efficacy of coatings.