5 Essential Tips for Sea Star Dissection Worksheet
Exploring the intricate world of marine biology can be a fascinating adventure, especially when it involves dissecting a sea star, scientifically known as an echinoderm. The dissection of a sea star is not only an excellent learning opportunity for students and marine enthusiasts alike, but it also opens up a window into the fascinating biological mechanisms that govern these creatures' lives. Here, we provide you with 5 essential tips for creating or using a Sea Star Dissection Worksheet that can enrich your educational experience.
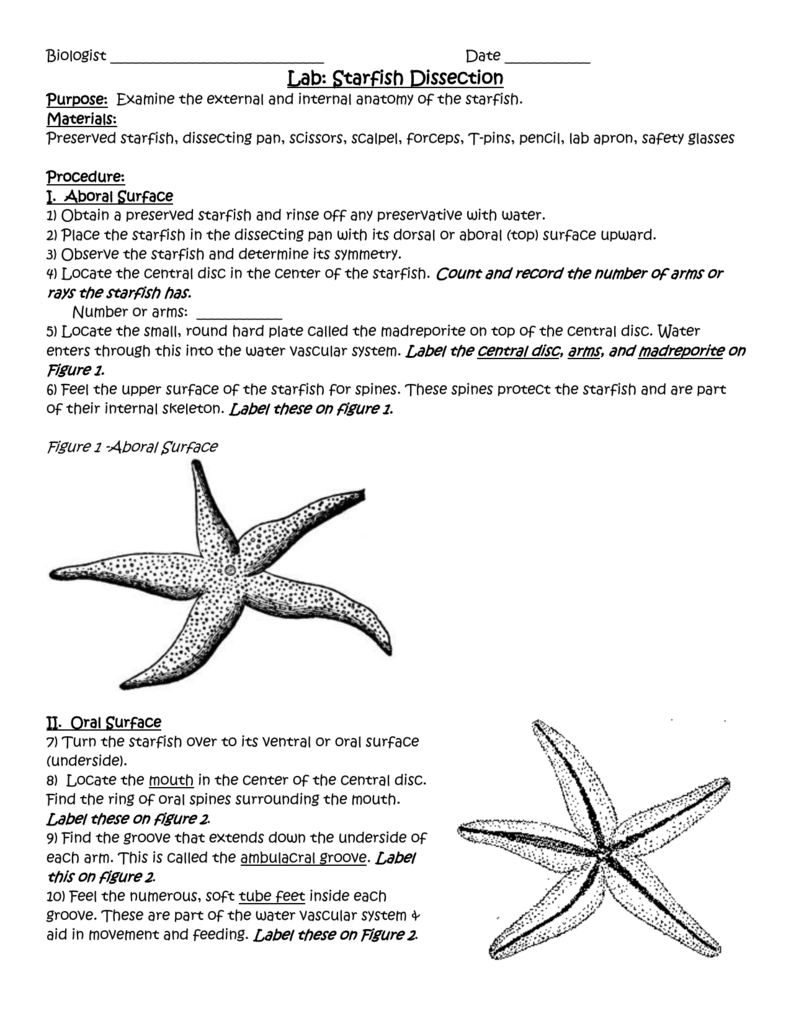
Understanding Sea Star Anatomy

Before diving into the dissection, it’s crucial to understand the basic anatomy of a sea star. Here are the key components:
- Water Vascular System: This system, unique to echinoderms, includes tube feet used for locomotion and feeding.
- Madreporite: A sieve-like structure that serves as an entrance point for water into the sea star’s water vascular system.
- Digestive System: Sea stars have a simple digestive tract but can perform a form of external digestion through their stomach.
- Nervous System: They lack a centralized brain but possess a primitive nervous system with nerve rings and radial nerves.
- Reproductive System: Sea stars reproduce sexually, with distinct male and female individuals.
Prepare the Work Environment
A well-prepared dissection environment ensures safety, accuracy, and an optimal learning experience. Here’s how to set it up:
- Clean Surface: Use a disposable pad or a clean, easily sterilizable surface.
- Tools: Ensure you have a dissecting kit with fine scissors, a scalpel, tweezers, and pins.
- Preservative Solutions: If using preserved specimens, keep formaldehyde or ethanol on hand for cleaning tools.
- Personal Protective Equipment: Gloves, lab coats, and eye protection are essential for safety.
- Disposal Containers: Have bins for biological waste and sharps.
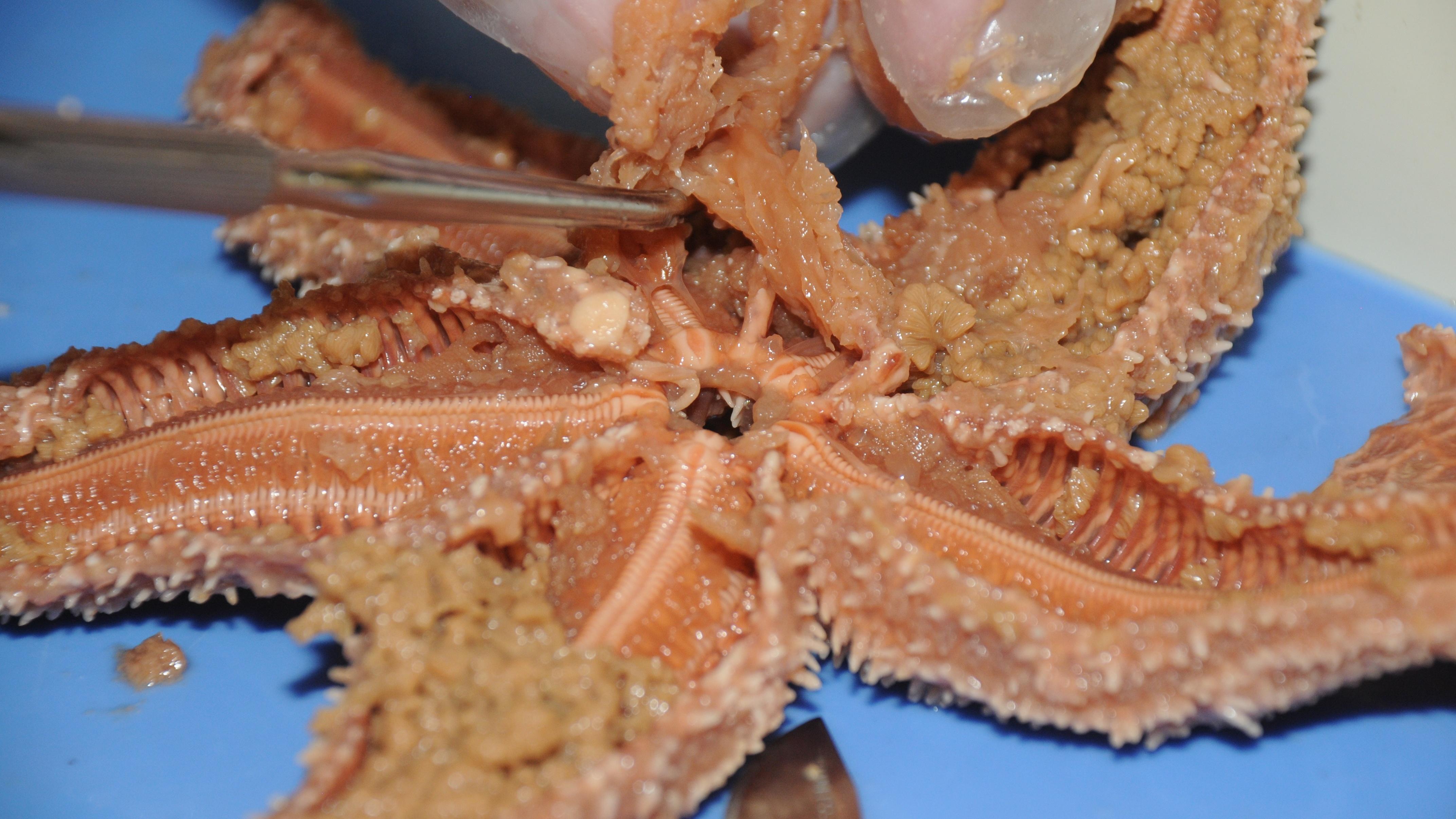
Structured Approach to Dissection

Dissecting a sea star involves more than just cutting open; it requires a methodical process:
- External Observation: Before making any cuts, observe and note the color, texture, and number of arms.
- Initial Cuts: Use a scalpel to make a careful incision along the dorsal side.
- Internal Examination: Look for the organs listed above, gently dissecting to avoid damage.
- Documentation: Take notes, drawings, or photos as you proceed through each step.
🔍 Note: Ensure you maintain the correct orientation of the specimen during dissection to avoid confusion.
Educational Reinforcement

Maximize the learning potential from the dissection:
- Worksheet Integration: Use the worksheet to guide the dissection steps, ask questions, and prompt observations.
- Discussion Points: Discuss sea star biology, their ecological role, and adaptation mechanisms.
- Comparative Analysis: Compare sea star anatomy with other organisms, emphasizing their unique features.
Proper Cleanup and Disposal

Post-dissection hygiene and environmental care are paramount:
- Clean Tools: Disinfect all tools and surfaces used.
- Specimen Disposal: Follow local guidelines for the disposal of biological specimens.
- Safety Disposal: Properly dispose of sharps and gloves.
♻️ Note: Always consider the environmental impact of your dissection materials and dispose of them responsibly.
Engaging in a sea star dissection worksheet can offer a profound insight into marine biology. This hands-on approach allows individuals to explore the complexity of life forms in the ocean, understand evolutionary mechanisms, and appreciate the biodiversity of our marine ecosystems. With the right preparation, a structured approach, and attention to detail, your dissection experience can be both educational and inspiring, connecting you to the wonders beneath the sea.
What are the main differences between sea stars and starfish?

+
Sea stars (Asteroidea) and starfish are essentially the same; ‘starfish’ is a common name for sea stars. There is no biological difference; the terms are interchangeable. However, “sea star” is preferred to avoid confusion since starfish aren’t fish.
How do I ensure safety during sea star dissection?

+
Ensure you wear gloves, lab coats, and eye protection. Handle tools with care to avoid injuries, and use preservatives and cleaning agents as directed to maintain a clean and safe environment.
What ecological role do sea stars play in their environment?

+
Sea stars act as keystone predators in many marine ecosystems. They control the population of their prey, often leading to a more diverse and balanced environment by preventing one species from dominating.