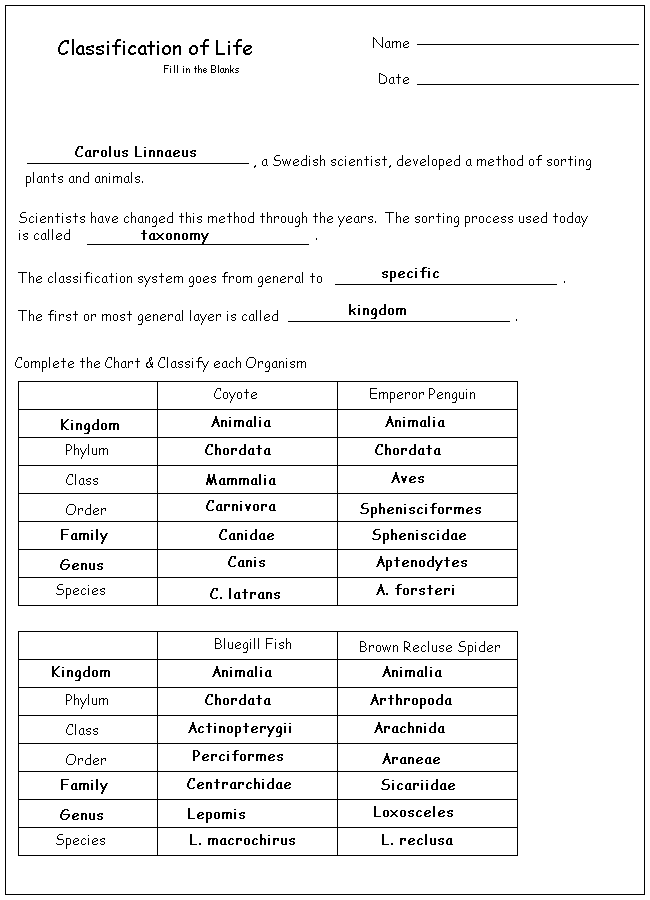
Sea Floor Spreading Worksheet: Answers Included for Easy Learning

In the fascinating world of geology, the concept of sea floor spreading stands as a cornerstone in understanding plate tectonics and the dynamic nature of our Earth. This blog post will guide you through the intricacies of sea floor spreading, providing comprehensive answers to aid in learning this fundamental geological process. We'll explore the phenomenon's theory, mechanism, evidence, and its impact on global tectonics.
What is Sea Floor Spreading?

Sea floor spreading is the geological process by which new oceanic lithosphere is created at mid-ocean ridges, moving away from the ridge due to tectonic forces. This process occurs:
- At mid-ocean ridges where magma rises from the mantle.
- The magma cools and solidifies, forming new oceanic crust.
- This new crust pushes older crust away from the ridge, essentially 'spreading' the sea floor.
Mechanism of Sea Floor Spreading

The mechanism behind sea floor spreading involves several interconnected processes:
- Convection currents in the mantle: These currents generate the forces necessary for the movement of tectonic plates.
- Magma rises to fill the void created by the divergence of plates at mid-ocean ridges.
- Cooling and solidification of magma forms new oceanic crust, which is lighter and buoyant, leading to further divergence.
Evidence Supporting Sea Floor Spreading

Several pieces of evidence have been instrumental in confirming the theory of sea floor spreading:
- Magnetic Stripes: The Earth's magnetic field has reversed periodically, and as new crust forms, it records the prevailing magnetic field's orientation.
- Seafloor Age Gradient: The age of the oceanic crust increases as you move away from mid-ocean ridges, indicating spreading.
- Plate Boundaries: The observed patterns of earthquakes and volcanism align with sea floor spreading zones.
Impact on Plate Tectonics
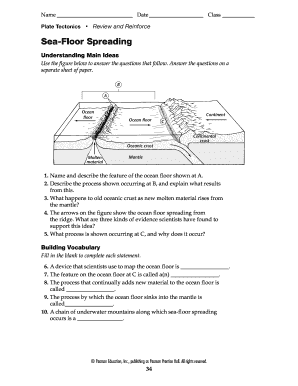
Sea floor spreading has profound implications for plate tectonics:
- It facilitates the movement of continents by pushing older crust towards subduction zones.
- It contributes to the recycling of the Earth's lithosphere, where old crust is recycled into the mantle at subduction zones.
- The process is vital for the Wilson Cycle, where continents break apart and eventually come back together.
The Process in Detail

Here's a detailed look at how sea floor spreading happens:
- Mid-Ocean Ridges: These are the divergent boundaries where tectonic plates move apart, allowing magma to rise from the mantle.
- Magma Upwelling: The magma is less dense, so it rises, filling the gap created by the moving plates.
- Cooling and Solidification: Once the magma reaches the ocean floor, it cools and solidifies, forming new crust. This new crust is then pushed outward, causing the sea floor to spread.
- Seafloor Morphology: The result is a central rift valley at the ridge axis and parallel ridge segments.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Mid-Ocean Ridge | Site of divergence and magma upwelling |
| Central Rift Valley | Narrow trough where initial crustal separation occurs |
| Magnetic Stripes | Record Earth's magnetic field changes over time |

Effects on the Environment

Sea floor spreading influences the Earth's environment in several ways:
- Climate: It can alter ocean currents and thus the global climate. For example, the opening of the Drake Passage contributed to the cooling of the planet.
- Biodiversity: It creates unique habitats like hydrothermal vents, promoting the evolution of extremophile organisms.
- Geothermal Energy: Ridges are rich in geothermal activity, potentially useful for energy exploration.
🌊 Note: Sea floor spreading is a key factor in the continuous process of plate tectonics, influencing not just geological but also environmental processes on Earth.
🔎 Note: The evidence supporting sea floor spreading has helped scientists understand the past and predict future tectonic movements.
To wrap up, sea floor spreading provides critical insights into Earth's geological activities. It explains the continuous renewal of oceanic crust, the movement of continents, and the dynamic interaction of plate tectonics. By understanding this process, we gain knowledge about the Earth's past, present, and potential future movements.
What is the primary evidence for sea floor spreading?

+
The primary evidence includes magnetic stripes on the ocean floor, the age progression of oceanic crust, and the distribution of earthquake and volcanic activity along mid-ocean ridges.
How does sea floor spreading affect the continents?

+
Sea floor spreading moves continents apart as new oceanic crust is created, pushing older crust toward subduction zones where it eventually sinks back into the mantle.
Can sea floor spreading occur in continental rifts?

+
Yes, similar processes occur in continental rift zones, like the East African Rift, which might eventually lead to the formation of new oceans.