5 Essential Sea Floor Spreading Worksheet Answers
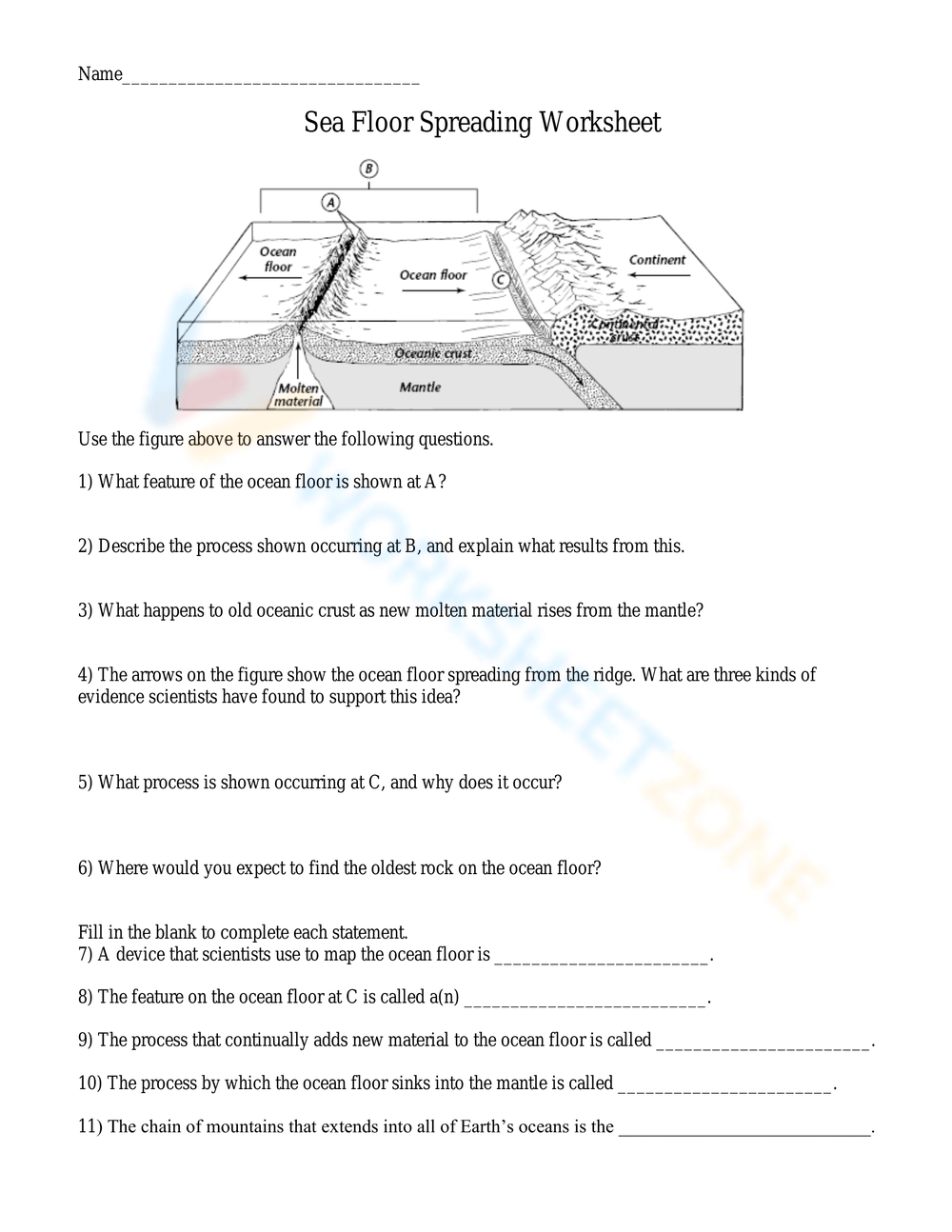
The dynamic process of sea floor spreading is a pivotal concept in understanding the movements of Earth's tectonic plates. This phenomenon, described by the Theory of Plate Tectonics, sheds light on the creation of new oceanic crust and helps explain various geological features on Earth's surface. This article delves into five key aspects of sea floor spreading, offering comprehensive answers often sought in worksheet assignments and classroom discussions.
What is Sea Floor Spreading?
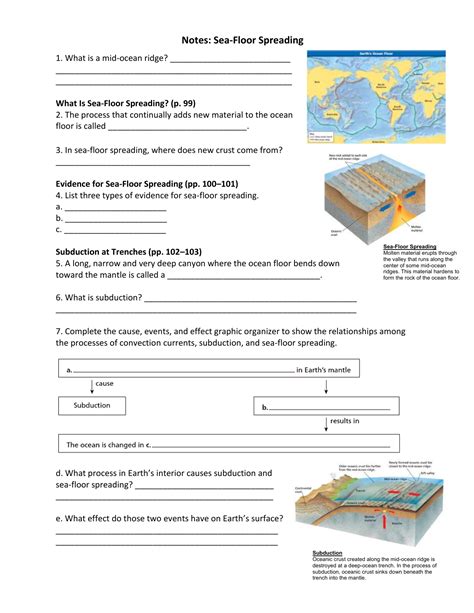
Sea floor spreading occurs at mid-ocean ridges, where molten material rises from the mantle, cools, and solidifies, forming new ocean crust. Here’s how it unfolds:
- Rise of Magma: Magma, driven by the heat from the mantle, rises due to convection currents, reaching the ocean floor.
- Cooling and Solidification: As this magma reaches the cold sea water, it cools, solidifies, and creates new basaltic rock, pushing apart the existing sea floor.
- Magnetic Striping: The newly formed crust captures Earth’s magnetic polarity at the time, creating alternating stripes of magnetic reversals.

🌍 Note: Sea floor spreading is a part of the broader phenomenon of plate tectonics, which also includes subduction zones, where old crust is recycled back into the mantle.
How does Sea Floor Spreading Affect Global Geography?

Sea floor spreading has profound impacts on Earth’s geography:
- Continental Drift: The spreading of the ocean floor contributes to the separation of continents, like how Africa and South America are drifting apart.
- Creation of Ocean Basins: Continuous spreading results in the expansion of ocean basins over geological time.
- Mountain Formation: Over time, as plates move, they can collide, causing the uplift of mountain ranges like the Himalayas through the process of orogenesis.
This phenomenon demonstrates how the Earth’s crust is constantly being created and destroyed, shaping the planet’s surface features.
Evidence Supporting Sea Floor Spreading

Scientists have gathered compelling evidence supporting sea floor spreading:
- Magnetic Anomalies: Maps showing symmetrical magnetic stripes on either side of mid-ocean ridges indicate the reversal of Earth’s magnetic field over time.
- Age Distribution: Radiometric dating of ocean crust reveals it gets progressively older away from the ridge.
- Seismic Data: Seismic surveys provide insight into the structure of the ocean floor, showing its relatively young age compared to the continents.
| Evidence | Description |
|---|---|
| Magnetic Anomalies | Symmetrical stripes parallel to mid-ocean ridges |
| Age Distribution | Age gradient away from the ridge |
| Seismic Data | Indicates structure and age of the ocean floor |
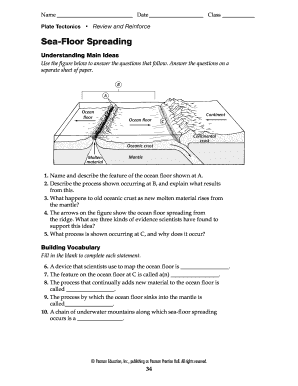
Is Sea Floor Spreading Happening Today?

Yes, sea floor spreading is an ongoing process. Here’s how:
- Geological Observations: Earthquake epicenters and volcanic activity align along mid-ocean ridges, indicating active crustal movement.
- Satellite Data: Satellite altimetry and GPS measurements track the widening of the ocean basins.
- Mid-Ocean Ridge Activity: Continuous eruptions of lava at mid-ocean ridges form new crust, which is then spread outward by the forces of spreading.
The Atlantic Ocean is a prime example where sea floor spreading is actively shaping the Earth today.
Why is Understanding Sea Floor Spreading Important?

Understanding sea floor spreading offers several benefits:
- Geological Insights: It helps explain the age distribution of the ocean floor, the formation of continents, and the mechanisms behind earthquakes and volcanic activity.
- Environmental Impact: It aids in understanding oceanic circulation patterns and the global climate system, which are influenced by the formation of ocean basins.
- Economic Benefits: Knowledge about sea floor spreading is crucial for locating mineral resources like cobalt, gold, and manganese from ocean floor deposits.
Through studying sea floor spreading, we gain a deeper comprehension of Earth’s complex geological systems and our planet’s dynamic nature.
By exploring the fundamentals of sea floor spreading, we not only learn about the geological processes shaping our world but also gain insights into how our planet has evolved over time. This understanding enriches our knowledge of Earth's past, present, and the potential future of its dynamic geography. With this in mind, we can better appreciate the marvels of our planet and perhaps predict or mitigate geological hazards.
What causes sea floor spreading?
+
Sea floor spreading is caused by the upwelling of molten material from the mantle due to convection currents, which then cools and solidifies to form new oceanic crust.
How does sea floor spreading contribute to continental drift?

+
As new crust is formed at mid-ocean ridges, it pushes the older crust apart, causing the continents to move away from each other, contributing to the phenomenon of continental drift.
Can we observe sea floor spreading in real-time?

+
Yes, through technologies like satellite altimetry and GPS, we can measure the rate of spreading and track changes over time.



