Sea Floor Spreading Worksheet: A Comprehensive Guide

Understanding sea floor spreading is fundamental for anyone interested in marine geology and the processes that shape our planet. This guide provides an in-depth look at how continents move, the formation of new oceanic crust, and the overall dynamics of plate tectonics. Here, we delve into the concepts, evidence, and methods to study sea floor spreading, which is crucial for educational, research, and practical applications in geoscience.
What is Sea Floor Spreading?
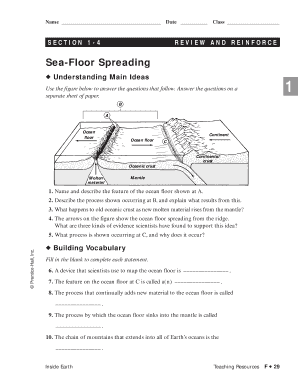
Sea floor spreading is a geological process where new oceanic crust is formed by volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the mid-ocean ridge. This process is integral to the theory of plate tectonics:
- New crust forms at mid-ocean ridges from upwelling magma.
- The crust is pushed away from the ridge, leading to the widening of the ocean basin.
- This movement contributes to the drift of continents known as continental drift.

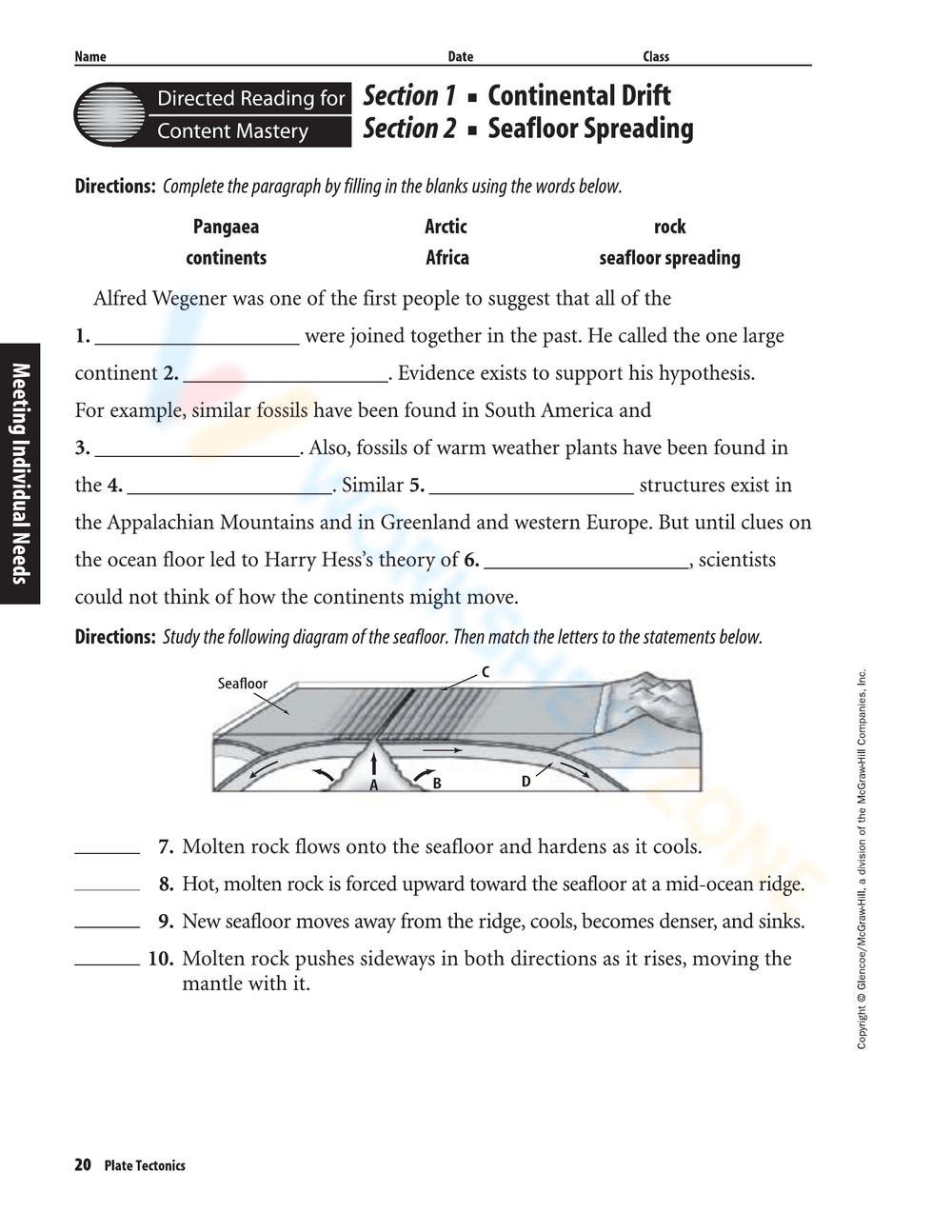
Evidence of Sea Floor Spreading

Here are some compelling pieces of evidence supporting sea floor spreading:
- Magnetic Striping: The ocean floor displays alternating stripes of magnetic anomalies parallel to mid-ocean ridges, which correspond to Earth's magnetic reversals over time.
- Age of Oceanic Crust: The age of oceanic crust increases as one moves away from mid-ocean ridges, with the oldest crust being farthest.
- Heat Flow: Heat flow from the Earth's interior is highest at mid-ocean ridges and decreases as you move away, indicating recent volcanic activity.
- Ocean Floor Topography: The rugged terrain and the presence of rift valleys near spreading centers also provide physical evidence.
How to Study Sea Floor Spreading

Studying sea floor spreading involves a combination of:
- Geophysical Surveys: Techniques like sonar mapping, magnetic surveys, and gravimetry to understand the ocean floor's features.
- Seismology: Using seismic waves to map the interior structure of the earth and detect plate movements.
- Direct Sampling: Collecting rock samples through drilling or submersible operations to study the composition and age of the crust.
🔍 Note: Advances in technology like Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs) have significantly enhanced our ability to gather precise data from the ocean floor, contributing to a better understanding of sea floor spreading.
Teaching Sea Floor Spreading
If you're an educator or a student looking to grasp or explain sea floor spreading, here's how you can approach it:
| Concept | Teaching Method |
|---|---|
| Magnetic Striping | Use magnetometers in class or simulations to demonstrate magnetic field changes over time. |
| Age of Oceanic Crust | Create a timeline with colored markers to show the progressive aging of the sea floor. |
| Heat Flow | Conduct heat flow experiments using geothermal models or thermal imaging technology. |

🧑🏫 Note: Interactive models and virtual reality can provide an immersive learning experience for complex geological concepts like sea floor spreading.
Sea Floor Spreading and Global Implications

Sea floor spreading has significant implications:
- Earthquakes and Volcanoes: Movement at plate boundaries often leads to seismic and volcanic activity.
- Ocean Currents: The shape of ocean basins influences global circulation patterns, which affect climate.
- Mineral Resources: The discovery of hydrothermal vents associated with spreading centers has opened up new fields for mineral exploration.
This process of continuous crust formation and movement shapes our planet in numerous ways, underscoring the dynamic nature of Earth's geology.
⚠️ Note: Ocean exploration is crucial for understanding sea floor spreading, but it comes with environmental considerations like preserving deep-sea ecosystems.
Sea floor spreading remains one of the cornerstone theories in geology, explaining not just the movement of continents but also the very creation of new ocean floors. By understanding this process, we gain insights into the past, present, and future of our planet's geological evolution. Its study continues to enlighten us on how Earth functions as a system, how continents have drifted over time, and how these dynamics might influence future geological phenomena. The evidence and methods we've discussed are key to demystifying these processes, offering both educational value and practical insights for geology students and professionals alike.
What causes sea floor spreading?

+
Sea floor spreading is primarily caused by mantle convection, where hotter, less dense material rises at mid-ocean ridges, pushing the tectonic plates apart.
How does sea floor spreading contribute to plate tectonics?

+
Sea floor spreading is the mechanism through which new oceanic crust is formed and plates move, driving the dynamics of plate tectonics, including continental drift.
What are the environmental impacts of sea floor spreading?

+
It influences ocean currents, global climate patterns, and can lead to the creation of new habitats like hydrothermal vents, while also potentially causing volcanic eruptions and earthquakes.