5 Creative Worksheets: Same Area, Different Perimeters
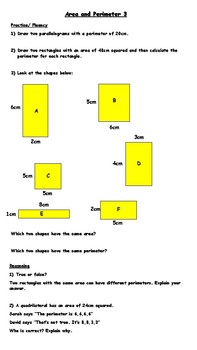
The concept of having different shapes with the same area but different perimeters is fascinating and a great way to explore both mathematics and creativity. Here, we dive into five creative worksheet ideas that can be used to engage students in learning about this concept in an interactive and enjoyable manner.
Worksheet 1: Shape Shifters
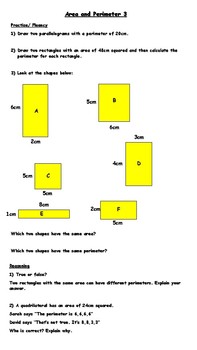
In this worksheet, students start with a fixed area, let's say 20 square units:
- Activity: Students are given the task to create at least three different shapes (e.g., rectangle, square, L-shape, etc.) each with the same area of 20 square units.
- Challenge: They are then asked to calculate the perimeter of each shape and discuss why the perimeters differ.
🎨 Note: Encourage students to use different colors to draw each shape to make the lesson visually appealing.
Worksheet 2: The Grid Challenge

Here, students are presented with a grid:
- Task: Students draw several shapes on the grid, each with an area of 15 square units.
- Twist: They then have to shade in or color the grid to demonstrate that all shapes cover the same amount of space but have different outlines.
- Discussion: Students are prompted to discuss how the placement of grid lines affects the perimeter of the shapes.
📝 Note: This worksheet helps in visualizing how small changes in shape can significantly affect the perimeter.
Worksheet 3: Perimeter Puzzle

This worksheet introduces puzzles:
- Setup: Students are given shapes with missing pieces. Each piece has a defined area but unknown perimeter.
- Activity: Students solve the puzzles by figuring out where the missing piece fits, ensuring that the shape retains the same area but has a new, unique perimeter.
- Bonus: After solving, they measure the perimeter of the new shape to compare with their hypothesis.
Worksheet 4: Design Your Own

Encouraging creativity:
- Task: Students design a room layout with furniture, ensuring the total area is consistent between designs but the layout and perimeter vary.
- Goals: Understand practical applications of area and perimeter in real-life scenarios.
🛋️ Note: This worksheet can be linked to interior design or architectural applications, making math relevant and engaging.
Worksheet 5: The Farmyard Fiasco

Here's a story-based activity:
- Scenario: A farmer wants to fence in a certain area of his land, but he's not sure which shape would give him the least amount of fencing material.
- Activity: Students design different layouts for the farmyard, calculate the area to ensure it meets the requirement, and then figure out the perimeter.
- Learning: This worksheet demonstrates the real-world implications of perimeter in cost management and efficiency.
Throughout these worksheets, we can see how engaging with shapes, their areas, and perimeters can be an exciting journey. Each activity has been crafted to not only teach mathematical concepts but also to foster creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills. The interplay between area and perimeter often goes unnoticed in everyday life, but through these exercises, students learn to recognize the practical applications and subtle differences that make mathematics not just a subject but a tool for life.
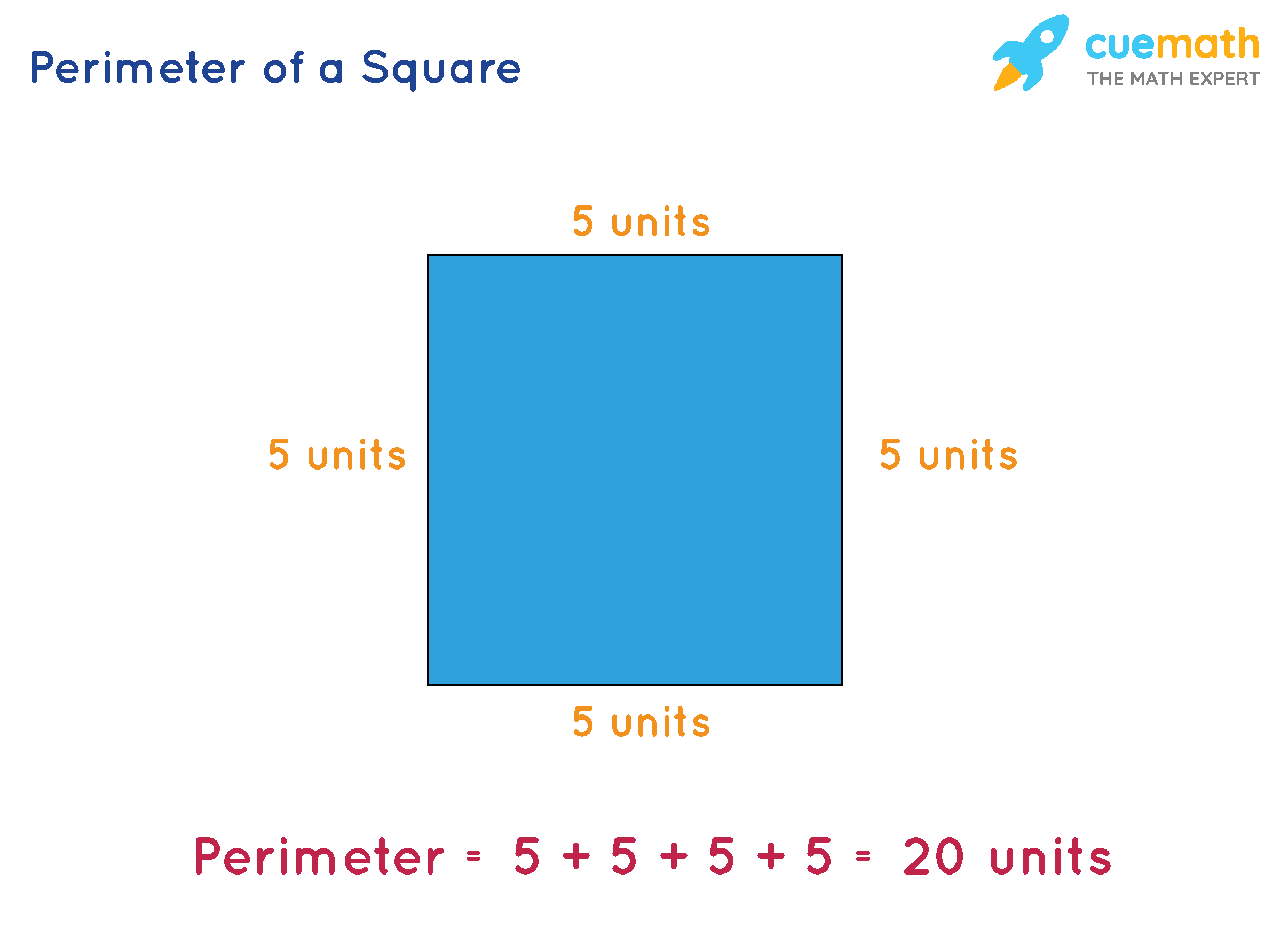
Why do shapes with the same area have different perimeters?

+
Shapes with the same area can have different perimeters because the perimeter depends on the shape’s configuration. For example, a square with an area of 16 square units has a perimeter of 16 units, while a rectangle with the same area could have a perimeter of 20 units if its sides are not equal.
Can a circle and a square ever have the same perimeter?

+
Yes, but only if the side of the square equals the circumference of the circle divided by 4. The circle’s circumference is 2πr (where r is the radius), while the square’s perimeter would be 4s, where s is the side length. For equality, s must be πr/2.
How can understanding area and perimeter help in real life?
+
Understanding area and perimeter can be useful in numerous real-life scenarios, from home decoration to land management, where optimizing space while minimizing material costs is crucial. For example, in agriculture or fencing, knowing how to get the least amount of fencing for a given area saves money.



