5 Fascinating Facts About Rock Pocket Mice
The rock pocket mouse (Chaetodipus intermedius) is a small, nocturnal rodent native to the deserts of the southwestern United States and Mexico. While at first glance this creature might seem unremarkable, its survival tactics and adaptations are nothing short of fascinating. In this long-form exploration, we'll delve into five intriguing aspects of rock pocket mice that showcase their evolutionary brilliance.
Genetic Adaptations for Camouflage

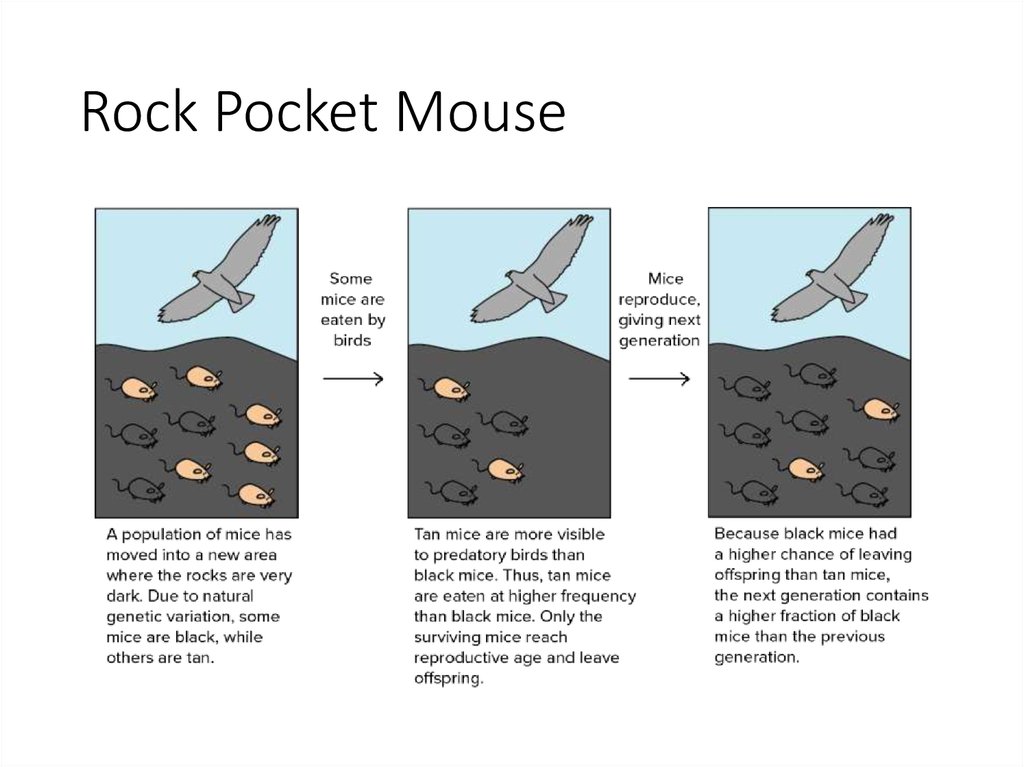
The rock pocket mice exhibit one of the most visually striking examples of natural selection. These mice have adapted to their environment in a way that showcases the very essence of survival of the fittest.
- Camouflage Variability: In areas with light-colored sandy soil, rock pocket mice are generally light in color. However, in regions where dark, basaltic volcanic rock dominates, the population exhibits a darker pigmentation. This darker fur helps the mice blend in with their surroundings, providing a survival advantage against predation.
- Genetic Basis: The difference in coloration is primarily due to a single gene, the Mc1r (melanocortin 1 receptor) gene, which controls fur color. Mutation in this gene leads to the dark fur essential for camouflage in environments with dark substrate.
🧬 Note: Natural selection's impact can be witnessed when observing the varied mouse populations on different substrates. Mice with fur colors that match their surroundings are less likely to be spotted by predators, illustrating a clear survival advantage.
Behavioral Adaptations for Survival

Apart from their physical characteristics, rock pocket mice have evolved several behavioral traits:
- Nocturnal Lifestyle: They avoid diurnal predators by being active at night, reducing the risk of being caught out in the open.
- Burrowing: These mice are skilled diggers, creating complex burrow systems for shelter from extreme temperatures and predators. Their burrows also serve as safe spots for storing food.
- Energy Conservation: Living in the desert, where food can be scarce, these mice have adapted to enter torpor, a state of decreased physiological activity, to conserve energy.
Reproduction and Life Cycle

The life cycle of rock pocket mice is tailored to ensure species survival under harsh conditions:
- Breeding Season: Mating season typically coincides with the periods when food availability is at its peak, ensuring better chances for offspring survival.
- Short Gestation Period: With a gestation period of about 23-24 days, female mice can give birth to multiple litters in a year. This rapid reproductive cycle allows for population growth when conditions are favorable.
- Mother’s Bond: Females form strong bonds with their young, providing care until they are weaned and able to fend for themselves. This nurturing helps increase the young's survival rate in their early life stages.
Environmental Impact and Role in Ecosystem

Rock pocket mice, though small, play significant roles in their ecosystems:
- Seed Dispersal: They contribute to plant dispersal by eating seeds and excreting them in different locations. This helps in maintaining plant diversity.
- Predator-Prey Dynamics: They are part of the food chain, being prey for a variety of predators like owls, snakes, and coyotes, influencing population dynamics.
- Ecosystem Engineers: Their burrowing activity aerates the soil, enhancing microbial activity and soil fertility, aiding in desert ecosystem stability.
Research Significance

The study of rock pocket mice has profound implications:
- Ecological Model: These mice serve as an ideal model for ecological and evolutionary studies due to their rapid reproductive cycle and observable adaptation through coloration.
- Genetics: Research into the Mc1r gene not only helps understand camouflage but also explores how single gene mutations can lead to significant evolutionary changes.
- Climate Change Indicator: Their responses to environmental changes can inform scientists about how species might adapt or fail to adapt to climate shifts, providing critical data for conservation efforts.
In summary, rock pocket mice offer a captivating look into the complexities of adaptation and survival in harsh desert environments. Their genetic, behavioral, and ecological significance paints a broader picture of nature's adaptability and the intricate web of life in which all species, big or small, play a part. Observing these tiny creatures provides profound insights into how life adapts, survives, and thrives against the odds.
What environmental factors influence the fur color of rock pocket mice?

+
The primary environmental factor influencing fur color in rock pocket mice is the substrate color of their habitat. Natural selection favors mice whose fur color matches the substrate, providing them with better camouflage against predators.
How do rock pocket mice manage to survive in such extreme conditions?

+
Rock pocket mice have evolved various survival strategies like nocturnal activity, burrowing to regulate temperature, and entering torpor to conserve energy during food scarcity. Their adaptations allow them to thrive in arid environments.
Why are rock pocket mice important for genetic research?

+
They provide a clear example of how a single gene mutation can lead to observable evolutionary changes, making them valuable for studying genetics, adaptation, and population dynamics.
Can rock pocket mice serve as indicators for climate change?

+
Yes, their response to environmental changes can act as an indicator for how species might adapt or fail to adapt to shifting climates, informing conservation strategies.
What predators do rock pocket mice have?

+
Rock pocket mice face predation from a variety of predators including owls, snakes, coyotes, and various small carnivores, all of which influence their population dynamics in the desert ecosystem.