Right Triangle Mastery: Ultimate Worksheet Guide for Students
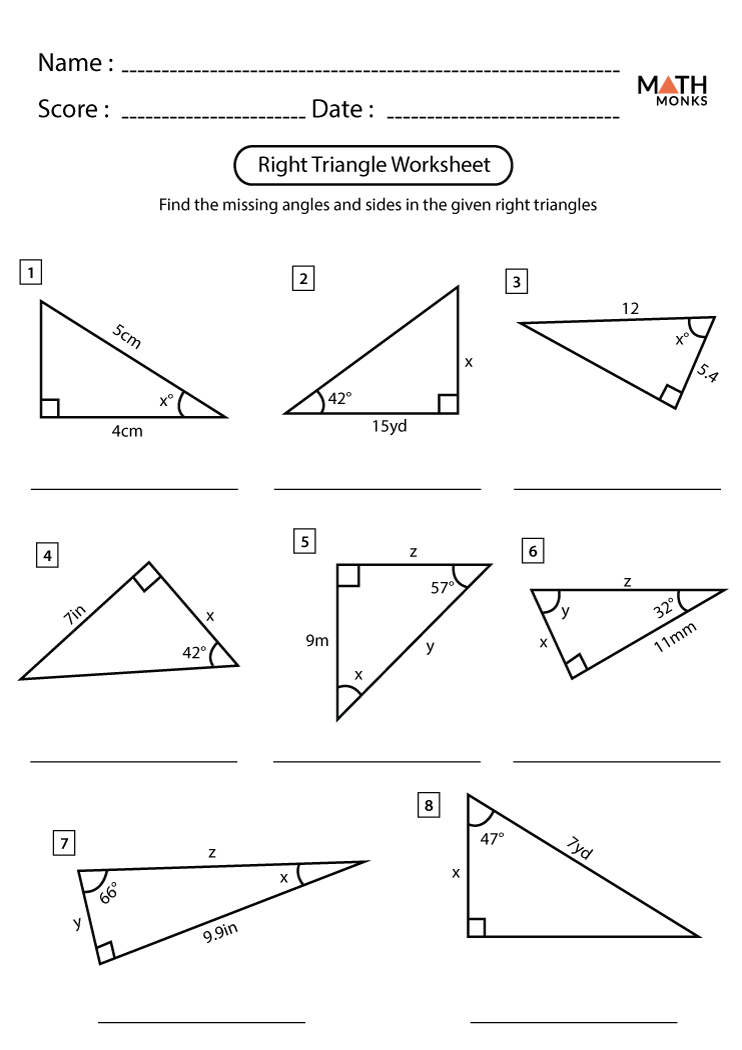
Right triangles, often regarded as one of the fundamental shapes in geometry, are not only crucial in mathematical theory but also in practical applications ranging from architecture to computer graphics. This guide is designed to take students on a journey through the intricacies of right triangles, offering comprehensive insights and practical exercises through an ultimate worksheet tailored for both beginners and advanced learners.
The Basics of Right Triangles
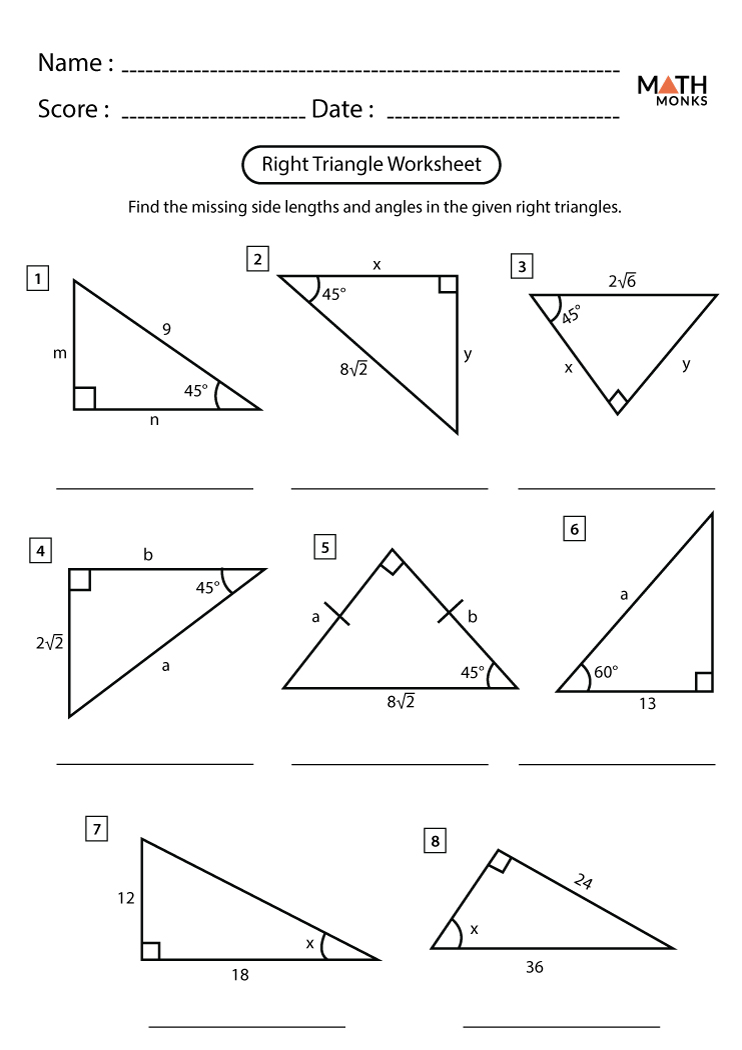
Understanding right triangles starts with their definition and properties:
- Definition: A right triangle has one 90-degree angle, called the right angle, which is marked by a small square in diagrams.
- Hypotenuse: The side opposite to the right angle is the longest side, known as the hypotenuse.
- Legs: The other two sides are called the legs of the triangle.
Pythagorean Theorem: One of the most fundamental relationships in geometry involving right triangles is the Pythagorean Theorem, which states:
a2 + b2 = c2
🔎 Note: Here, a and b represent the legs of the triangle, and c represents the hypotenuse.
Worksheet Section: Understanding the Basics

Let’s start with some exercises to grasp the basics:
- Identify the right triangle in a set of shapes.
- Label the legs and hypotenuse in given triangles.
- Find the length of one leg when given the hypotenuse and the other leg.
- Use the Pythagorean Theorem to calculate the hypotenuse when the legs are known.
Special Right Triangles
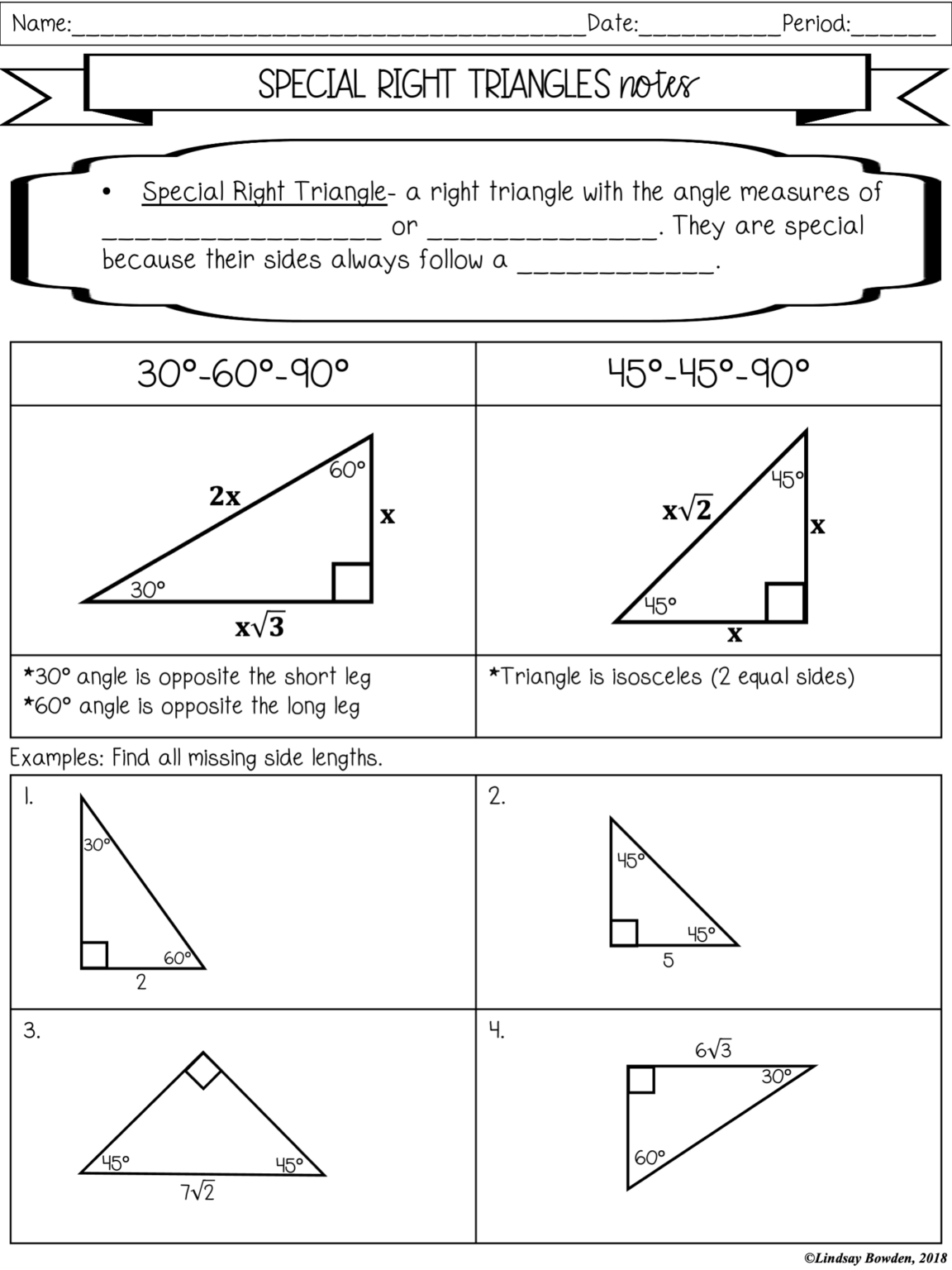
Right triangles come in two special forms that have specific side ratios:
- 45-45-90 Triangle: Known as an isosceles right triangle, it has two legs equal in length. The ratio of the sides is 1:1:√2.
- 30-60-90 Triangle: The sides opposite to the angles of 30°, 60°, and 90° are in the ratio 1:√3:2.
💡 Note: Memorizing these ratios can greatly simplify many geometric problems!
Worksheet Section: Special Right Triangles

Try these exercises to master special right triangles:
- Identify if given triangles are 45-45-90 or 30-60-90 triangles.
- Calculate unknown sides when one side is given in these special triangles.
- Use the special triangle ratios to solve word problems.
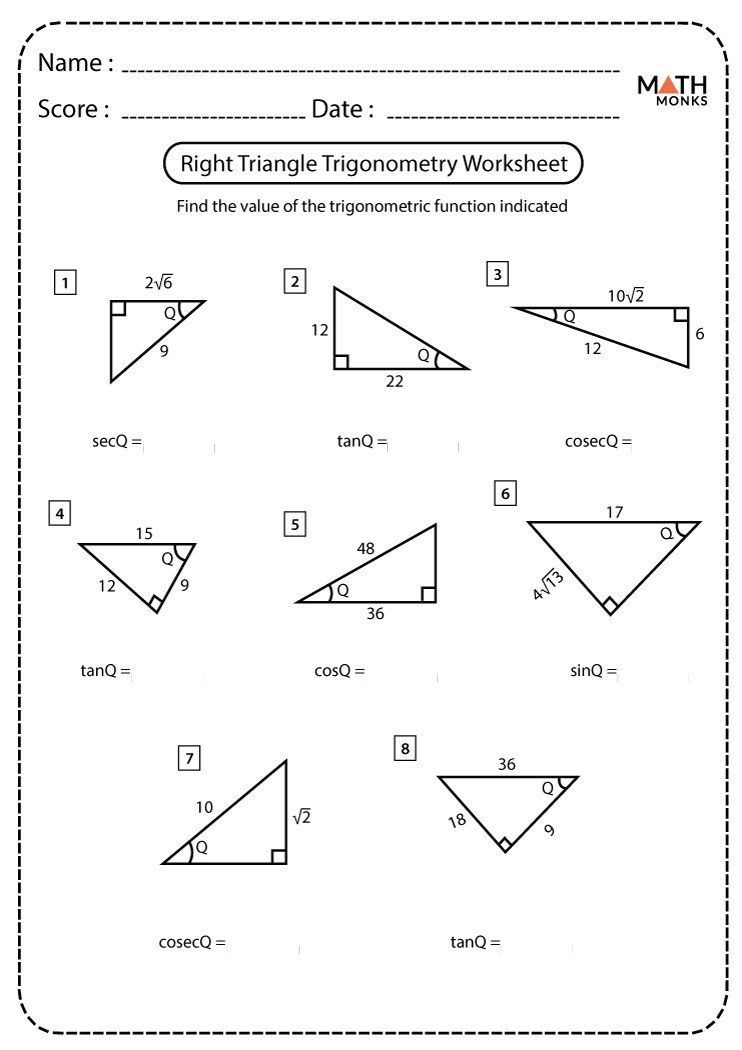
Trigonometry in Right Triangles

Trigonometry introduces students to the sine, cosine, and tangent functions:
- Sine (sin): opposite/hypotenuse
- Cosine (cos): adjacent/hypotenuse
- Tangent (tan): opposite/adjacent
📝 Note: Remember SOHCAHTOA: Sine = Opposite/Hypotenuse, Cosine = Adjacent/Hypotenuse, Tangent = Opposite/Adjacent.
Worksheet Section: Trigonometry

Here are some trigonometry exercises:
- Calculate the sine, cosine, or tangent of angles in given right triangles.
- Find missing sides or angles using trigonometric identities.
- Solve real-world problems involving angles of elevation or depression.
Applications in Real Life

The principles of right triangles are widely applied:
- Construction: Architects use right triangles to ensure perpendicular walls.
- Navigation: Trigonometry helps pilots and sailors calculate their path relative to land or other ships.
- Surveying: Surveyors often measure distances indirectly using right triangle geometry.
To wrap up, this guide has provided a comprehensive overview of right triangles, from basic understanding to advanced trigonometry applications. By mastering these concepts through the accompanying worksheet, students can develop both theoretical knowledge and practical skills. This understanding will not only excel in geometry class but also in many real-world scenarios where accurate measurement and calculation are essential.
Why is the Pythagorean Theorem Important?
+
The Pythagorean Theorem is crucial because it provides a relationship between the sides of a right triangle, allowing us to solve for unknown sides. It’s not only foundational for trigonometry but also has countless applications in physics, engineering, and architecture.
How Can I Remember the Side Ratios of Special Right Triangles?

+
One mnemonic is ‘45-45-90 gives you √2, 30-60-90 gives you √3.’ This reminds you that for 45-45-90 triangles, the hypotenuse is √2 times the legs, and for 30-60-90 triangles, the longest leg is √3 times the shortest leg.
What Real-Life Applications Use Right Triangles?

+
Right triangles are integral in GPS technology to calculate distances, in building construction for ensuring right angles, in architecture for roof designs, and in calculating the heights of unreachable objects through indirect measurement.


