Restriction Enzyme Worksheet Answers: Master Your Knowledge

In the field of molecular biology, understanding the tools at our disposal is key to unlocking the vast potential of genetic manipulation. One such tool, which has revolutionized the way we approach the study of DNA, is restriction enzymes. Often hailed as the molecular scissors, restriction enzymes allow us to cut DNA at specific sites, enabling us to manipulate and analyze genetic material with unprecedented precision. This comprehensive guide will delve into restriction enzymes, offering you answers to a worksheet, and expanding on the knowledge you need to master this essential molecular biology technique.
Understanding Restriction Enzymes


Restriction enzymes, also known as restriction endonucleases, are enzymes naturally produced by bacteria to defend themselves against bacteriophages or viruses. Their main function is to cut DNA at specific sequences, known as recognition sites or restriction sites, thereby preventing the viral DNA from replicating inside the bacterium.
Here are some key points to understand about restriction enzymes:
- Specificity: Each restriction enzyme recognizes a particular DNA sequence, usually 4-8 base pairs long. For instance, EcoRI recognizes the sequence GAATTC.
- Cutting Pattern: Restriction enzymes can leave staggered (sticky ends) or blunt ends after cutting. Sticky ends are useful in DNA cloning as they can be matched with complementary ends of another DNA fragment.
- Nomenclature: The enzymes are named after the organism from which they were isolated, followed by a Roman numeral. For example, HindIII comes from Haemophilus influenzae serotype d.
How to Use Restriction Enzymes

Using restriction enzymes involves several steps:
- Selection of Enzyme: Choose an enzyme that matches your target DNA sequence. There are databases like REBASE where you can find this information.
- Preparation of DNA: The DNA should be in high quality and concentration. A plasmid or genomic DNA can be used.
- Digestion Reaction: Mix the DNA with the enzyme in a buffer that optimizes the enzyme's activity. Incubate at the appropriate temperature, usually around 37°C.
- Analysis: After digestion, analyze the DNA fragments through techniques like gel electrophoresis.
💡 Note: Always keep your reagents and DNA samples on ice or at the recommended temperature to prevent degradation or unintended reactions.
Restriction Enzyme Worksheet Answers
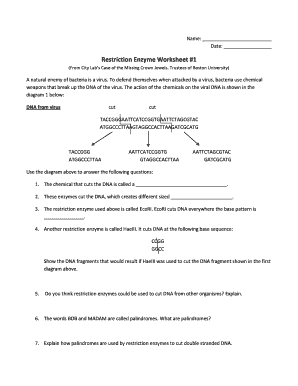
Here are detailed answers to common restriction enzyme worksheet questions:
Question 1: What is the function of restriction enzymes?

Restriction enzymes are used to cut DNA at specific sequences. This function is pivotal in gene cloning, DNA mapping, and various molecular biology techniques.
Question 2: Explain how EcoRI cuts DNA.

EcoRI recognizes the sequence GAATTC and cuts between the G and the following A, leaving a 5’ overhang or sticky end. The cut site looks like:
| 5’ - G | AATTC - 3’ |
|---|---|
| 3’ - CTTAA | G - 5’ |

Question 3: Why are sticky ends useful?
Sticky ends created by some restriction enzymes can form hydrogen bonds with their complementary sequences on other DNA fragments. This is particularly useful in:
- Cloning: Facilitating the joining of vectors and inserts.
- Recombinant DNA Technology: Allowing for the directed assembly of DNA constructs.
Question 4: What are isoschizomers?

Isoschizomers are pairs of restriction enzymes specific to the same recognition sequence. For example, EcoRI and EcoRI-HF both recognize GAATTC but might have different optimal conditions or cutting efficiencies.
Question 5: List three considerations when selecting a restriction enzyme for an experiment.

- Sequence recognition site in your DNA of interest.
- The enzyme’s activity at your working temperature and buffer conditions.
- The type of end it produces (sticky vs. blunt).
🧬 Note: When choosing a restriction enzyme, consider the downstream applications as the type of ends produced can influence cloning strategies and results.
Conclusion Paragraph

Through this detailed exploration of restriction enzymes, we've unraveled their vital role in molecular biology, from understanding their specificity to the practical applications in DNA manipulation. Each step in using these enzymes has been outlined, providing a comprehensive guide to mastering this technique. Remember, the precision of restriction enzymes allows scientists to delve deep into genetic engineering, paving the way for advancements in medical, agricultural, and ecological sciences. By understanding and applying this knowledge, you not only comprehend the essence of DNA manipulation but also position yourself to contribute to the ongoing revolution in biotechnology.
What is the difference between Type I and Type II restriction enzymes?

+
Type I restriction enzymes require ATP, recognize a specific sequence, but cleave the DNA randomly at a distance from the recognition site, often outside the site itself. Type II enzymes, conversely, cleave within their recognition site, do not require ATP, and are the most commonly used in biotechnology for their precision.
Can restriction enzymes cut DNA at any temperature?

+
Most enzymes have optimal temperatures for activity, typically around 37°C. However, some enzymes can function at lower temperatures for more controlled reactions, or higher temperatures might be used to inactivate the enzyme after the reaction.
How can you prevent DNA from being cut by restriction enzymes?

+
To prevent unwanted cutting, you can use:
- Methylation of the recognition site to protect the DNA from digestion.
- Using buffers that are not optimal for enzyme activity.
- Heating the sample after digestion to inactivate the enzyme.