Remagen Bridge History

Introduction to the Remagen Bridge

The Remagen Bridge, also known as the Ludendorff Bridge, is a significant historical landmark located in Remagen, Germany. The bridge played a crucial role in World War II, particularly during the Allied forces’ advancement into Germany. The bridge’s strategic importance made it a key target for both the German and Allied forces. In this blog post, we will delve into the history of the Remagen Bridge, its construction, and its significance in the context of World War II.
Construction and Early History

The Remagen Bridge was constructed between 1916 and 1919 by the German Empire. The bridge was designed to facilitate the transportation of troops and supplies across the Rhine River. The bridge’s construction was a significant engineering feat, with a total length of 335 meters and a height of 12 meters above the river. The bridge was named after General Erich Ludendorff, a prominent German military leader during World War I.
World War II and the Bridge’s Significance

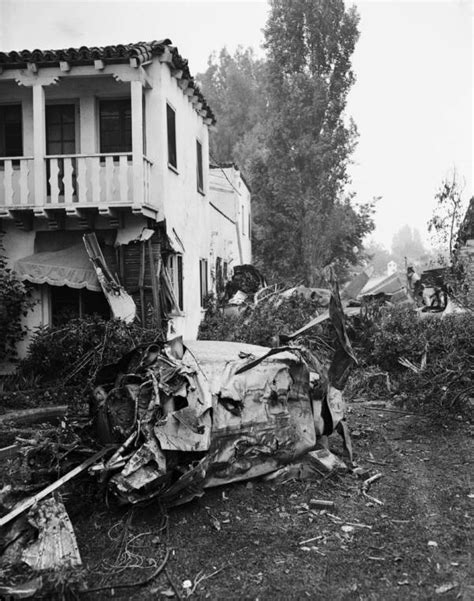
During World War II, the Remagen Bridge became a critical target for the Allied forces. In March 1945, the Allied forces, led by the United States Army, launched an operation to capture the bridge. The bridge’s capture would provide a crucial crossing point over the Rhine River, allowing the Allied forces to advance deeper into Germany. The German forces, aware of the bridge’s importance, attempted to destroy it. However, the Allied forces were able to capture the bridge intact on March 7, 1945.
The Battle for the Remagen Bridge

The battle for the Remagen Bridge was intense and chaotic. The German forces had planted explosives on the bridge, but they failed to detonate. The Allied forces, led by the 9th Armored Division, launched a surprise attack on the bridge, catching the German forces off guard. The bravery and quick thinking of the Allied forces allowed them to capture the bridge, despite being outnumbered and outgunned.
Aftermath and Legacy

The capture of the Remagen Bridge marked a significant turning point in the war. The Allied forces were able to establish a foothold on the eastern bank of the Rhine River, paving the way for their advance into Germany. The bridge’s capture also marked a significant psychological blow to the German forces, who had considered the Rhine River a natural barrier against the Allied advance. Today, the Remagen Bridge is a museum and a memorial to the soldiers who fought and died during the battle.
📚 Note: The Remagen Bridge was eventually destroyed by the German forces on March 17, 1945, but not before the Allied forces had established a secure foothold on the eastern bank of the Rhine River.
Preservation and Tourism

After the war, the Remagen Bridge was rebuilt, and it now serves as a museum and a memorial to the soldiers who fought and died during the battle. The bridge’s preservation is a testament to the significance of the event and the importance of remembering the past. Today, the Remagen Bridge is a popular tourist destination, attracting visitors from all over the world.
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 1916-1919 | Construction of the Remagen Bridge |
| 1945 | Capture of the Remagen Bridge by Allied forces |
| 1945 | Destruction of the Remagen Bridge by German forces |
| Present day | Remagen Bridge serves as a museum and memorial |

In summary, the Remagen Bridge played a significant role in World War II, and its capture marked a crucial turning point in the war. The bridge’s history and legacy continue to fascinate people today, and it serves as a reminder of the importance of remembering and learning from the past.
What was the significance of the Remagen Bridge during World War II?

+
The Remagen Bridge was a crucial crossing point over the Rhine River, allowing the Allied forces to advance deeper into Germany.
Who captured the Remagen Bridge during World War II?

+
The Remagen Bridge was captured by the Allied forces, led by the United States Army, on March 7, 1945.
What is the current status of the Remagen Bridge?

+
The Remagen Bridge was rebuilt after the war and now serves as a museum and memorial to the soldiers who fought and died during the battle.