Reading Line Plots Worksheets

Line plots, often referred to as dot plots, are an essential tool in statistics for organizing and visually representing numerical data. They help students and researchers alike to quickly understand the distribution, concentration, and any outliers within a dataset. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore line plots worksheets, their structure, creation, and practical applications, providing insights into how to effectively teach and learn this critical statistical concept.
What is a Line Plot?

A line plot is a graphical representation where each data point is shown as a dot placed over a number line. Here's how to create one:
- Data Collection: Gather the data you wish to analyze.
- Number Line: Draw a horizontal line and mark it with the smallest to the largest values in your dataset, ensuring even intervals.
- Data Points: Plot each piece of data as a dot above its corresponding value on the number line.
- Label: Include a title, label the axes, and if necessary, explain what the dots represent.

Benefits of Line Plots Worksheets

Worksheets centered on line plots offer several educational advantages:
- Visual Learning: They help students visualize data, making it easier to interpret and analyze.
- Statistical Foundation: Line plots provide a foundation for understanding more complex data representations like histograms and box plots.
- Practical Application: Students learn to relate numbers to real-world scenarios, improving their analytical thinking.
- Skill Development: Creating and interpreting line plots enhances mathematical, organizational, and analytical skills.
Creating Line Plots Worksheets

When designing line plots worksheets, consider the following:
- Clarity: Use clear instructions and precise labels.
- Variety: Include diverse datasets to cater to different skill levels and subject areas.
- Progression: Start with basic datasets and gradually increase complexity.
📝 Note: Ensure that the datasets chosen are age-appropriate and align with the curriculum objectives.
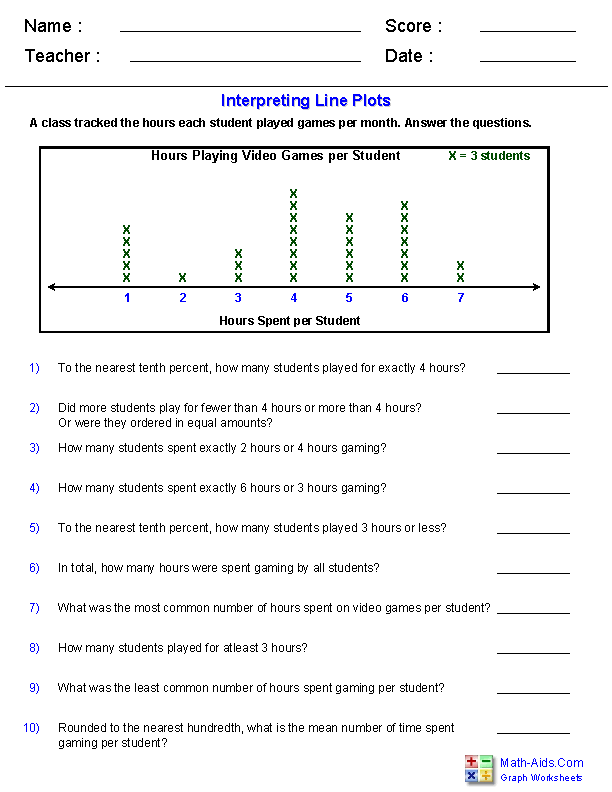
Examples of Line Plots Worksheets

Here are some practical examples of line plots worksheets:
- Weather Tracking: Students can track the daily temperature for a week or month, plotting the data to observe patterns.
- Classroom Survey: Use a survey about favorite snacks, books, or colors and then plot the results to see the most popular choices.
- Math Test Scores: Plot the scores of a math test to understand the distribution of performance.
| Example | Description |
|---|---|
| Number of Pets | Students plot the number of pets each classmate has. |
| Age of Relatives | Plot the ages of extended family members to visualize distribution. |

🌟 Note: For interactive learning, consider using digital tools where students can drag and drop data points onto a virtual number line.
Teaching Strategies for Line Plots

Educators can employ several strategies to teach line plots effectively:
- Hands-On Activity: Use physical items like counters or stickers to represent data points before moving to paper worksheets.
- Real-World Scenarios: Apply line plots to real data sets to engage students with contextual relevance.
- Group Work: Encourage collaboration where students can discuss and verify their plots.
- Critique and Revise: Have students review each other's plots, promoting critical thinking.
Wrapping Up

Line plots are not only a fundamental tool for data visualization but also a stepping stone to more advanced statistical concepts. By incorporating line plots into your educational strategy, you're giving students a visual way to engage with numbers, interpret data, and make informed conclusions. Their simplicity in construction, yet depth in interpretation, makes them a versatile teaching and learning tool. Remember, the key to successful learning with line plots is practice, practical application, and continuous assessment to enhance students' understanding and skills.
What is the difference between a line plot and a bar graph?

+
A line plot shows each data point individually over a number line, whereas a bar graph groups data into bars, showing the frequency or size of each category.
Can you use line plots for categorical data?
+
While line plots are typically used for numerical data, they can represent categories when the categories are assigned numerical values. However, bar graphs or pie charts are more common for categorical data.
How can students benefit from creating line plots?

+
Students develop skills in data collection, analysis, and interpretation. Line plots help in understanding frequency, spread, and outliers, offering a visual way to engage with numerical data and fostering critical thinking.
Are there any digital tools for creating line plots?

+
Yes, there are many digital tools like Google Sheets, Excel, Desmos, and GeoGebra that provide interactive environments for creating and manipulating line plots.
How do you incorporate real-world applications when teaching line plots?

+
Using datasets related to student interests or current events can make learning more engaging. Examples include plotting the daily temperature, test scores, or the frequency of certain words in a book.