Master Chem 10 Stoichiometry: Reaction Worksheet Guide

The realm of chemistry is vast and intricate, particularly when it comes to understanding reactions through stoichiometry. This pivotal area of study in chemistry involves not just identifying the reactants and products but also calculating their quantities involved in chemical reactions, a concept crucial for fields ranging from pharmaceuticals to environmental science. In this post, we'll explore how to effectively utilize the Chem 10 Stoichiometry Reaction Worksheet, which serves as a tool for mastering these foundational concepts. From deciphering mole-mole relationships to applying real-world applications, this guide will ensure you grasp the nuances of stoichiometry through practical exercises.
Understanding the Basics of Stoichiometry

Stoichiometry is the calculation of reactants and products in chemical reactions. Here's a brief overview of what you need to know:
- Mole Concept: Understanding that 1 mole equals Avogadro's number of particles is fundamental.
- Molar Mass: This is the mass of one mole of a substance and plays a crucial role in stoichiometry.
- Balanced Chemical Equations: For accurate stoichiometry, reactions must be balanced; this ensures the law of conservation of mass is upheld.
Navigating the Stoichiometry Reaction Worksheet
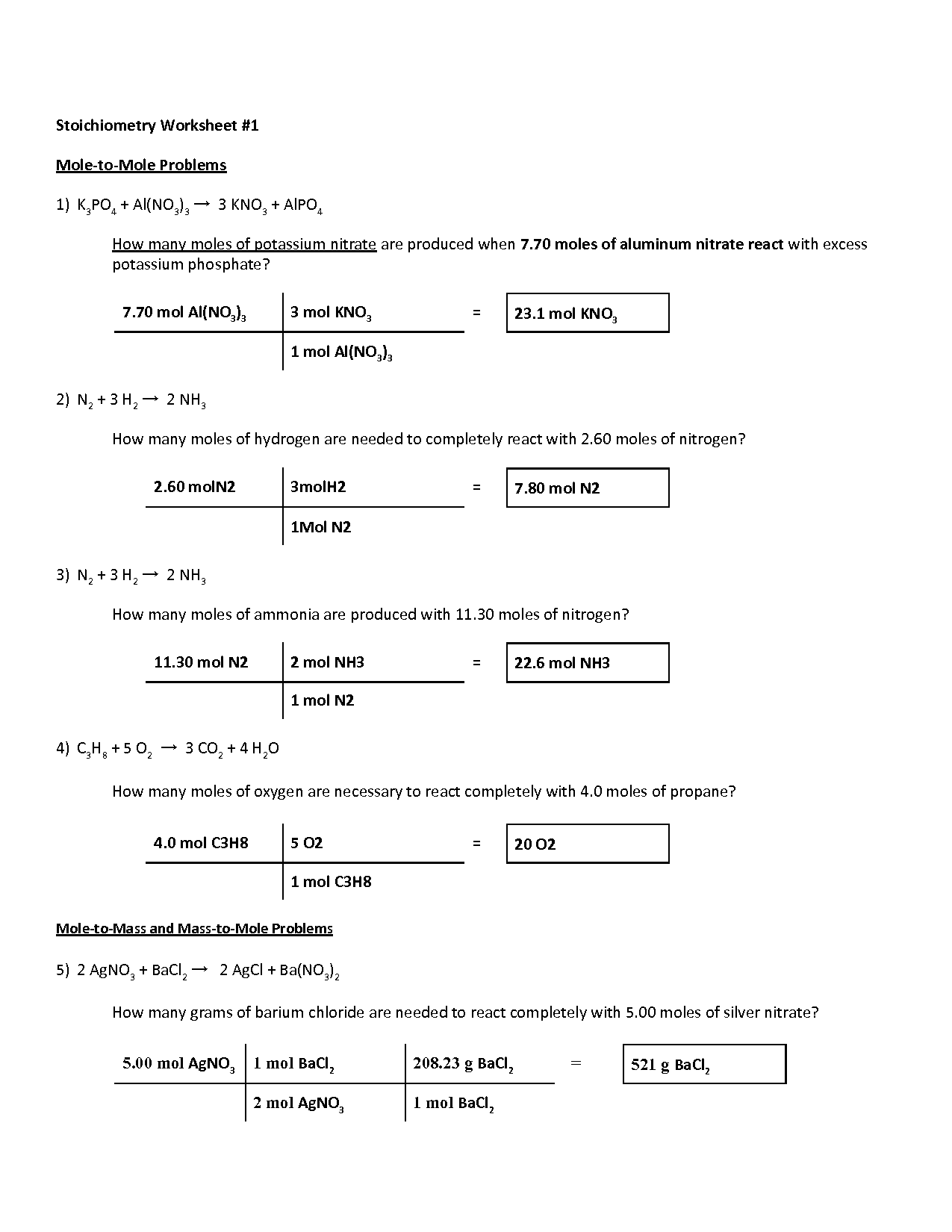
The Chem 10 Stoichiometry Reaction Worksheet is designed to guide you through different stoichiometry problems. Here's how to navigate it effectively:
Step-by-Step Problem Solving

The worksheet usually begins with straightforward mole-to-mole conversions, progressing to more complex calculations:
- Identify the Balanced Equation: The first step involves ensuring you have a balanced chemical equation. This is crucial for all stoichiometric calculations.
- Find the Moles of Known Substance: You'll need to convert the given mass or volume into moles using the molar mass or density. For gases, use the Ideal Gas Law if needed.
- Use the Mole Ratio: Apply the mole ratio from the balanced equation to convert moles of the known substance to moles of the unknown substance.
- Convert Moles to Desired Units: Finally, convert the moles back to grams or any other desired units like volume or particles.
Types of Stoichiometry Problems

The worksheet categorizes problems into different types, each providing a distinct learning opportunity:
- Mass-Mass Stoichiometry: Where you convert the mass of a reactant to the mass of a product.
- Volume-Volume Stoichiometry: Involving gases where volumes of reactants and products are given or required.
- Molarity and Titration Problems: These involve solutions where molarity is used to find the amount of solute.
Sample Problem

Let's work through a sample problem from the worksheet:
Given:

- 15 grams of hydrogen gas
- Balance the equation: 3 H2 + N2 → 2 NH3
Find:

- Mass of NH3 produced
Steps:

- Calculate moles of H2 used:
- 15 g / 2 g/mol = 7.5 mol of H2
- Using the mole ratio, 7.5 mol of H2 will produce (7.5 * (2/3) = 5 mol) of NH3.
- Convert moles of NH3 to grams:
- 5 mol * 17 g/mol = 85 g of NH3
Real-World Applications
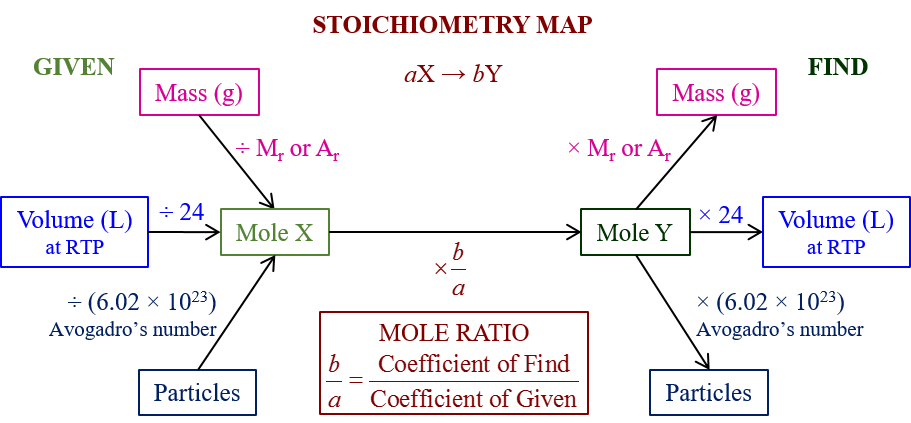
Stoichiometry isn't just an academic exercise; it has profound real-world implications:
- Pharmaceutical Chemistry: Precise calculations are necessary for the synthesis of drugs.
- Environmental Science: Quantifying pollutants in air or water involves stoichiometry.
- Industrial Processes: From fertilizer production to steel manufacturing, stoichiometry optimizes resource use.
🔍 Note: Always ensure your calculations reflect realistic conditions as stoichiometry assumes ideal scenarios which might not occur in real-world settings.
Practical Tips for Solving Stoichiometry Problems

Here are some practical strategies to tackle stoichiometry problems efficiently:
- Use dimensional analysis to set up your calculations correctly.
- Keep track of your units; they act as guides for your stoichiometric journey.
- Double-check your mole ratios from the balanced equation.
- Use tables or diagrams for complex problems to visualize the stoichiometric relationships.
📌 Note: When working with gases, remember that the Ideal Gas Law might come into play to relate moles to volume or temperature conditions.
Concluding Thoughts

As we've seen, the Chem 10 Stoichiometry Reaction Worksheet is more than just a collection of problems; it's a structured approach to mastering chemical reaction calculations. By engaging with this worksheet, students learn not only to solve for the unknown in chemical reactions but also understand the quantitative relationships within chemistry. From converting masses to moles to exploring the implications of stoichiometry in real-world scenarios, this guide provides the necessary steps to excel in understanding chemical reactions at a deeper level.
Why is stoichiometry important?

+
Stoichiometry provides the mathematical basis for predicting the amounts of reactants needed and products formed in chemical reactions, which is crucial for various industries like pharmaceuticals, food production, and environmental science.
What are common mistakes in stoichiometry calculations?

+
Common errors include using incorrect molar masses, misinterpreting balanced equations, neglecting units, and failing to account for the stoichiometric coefficients properly.
Can stoichiometry be applied outside of a laboratory setting?

+
Yes, stoichiometry principles are used in cooking recipes, automotive industry emissions control, and in understanding biological processes like metabolism and photosynthesis.