5 Essential Answers to Rates of Reaction Worksheet

Understanding the rates of chemical reactions is vital for anyone diving into the fascinating world of chemistry. Whether you're a student trying to solve a chemistry worksheet, or a teacher aiming to elucidate this concept to students, knowing the essentials about reaction rates is indispensable. This post will outline five key answers to common worksheet questions on rates of reaction, helping you navigate this complex topic with clarity and confidence.
The Concept of Rate of Reaction

The rate of reaction refers to the speed at which reactants are converted into products during a chemical reaction. It can be measured by:
- The disappearance of reactants over time.
- The formation of products over time.
📘 Note: Keep in mind, the rate isn't constant over the entire course of a reaction; it generally changes as reactants deplete or conditions change.
How Can We Increase the Rate of Reaction?
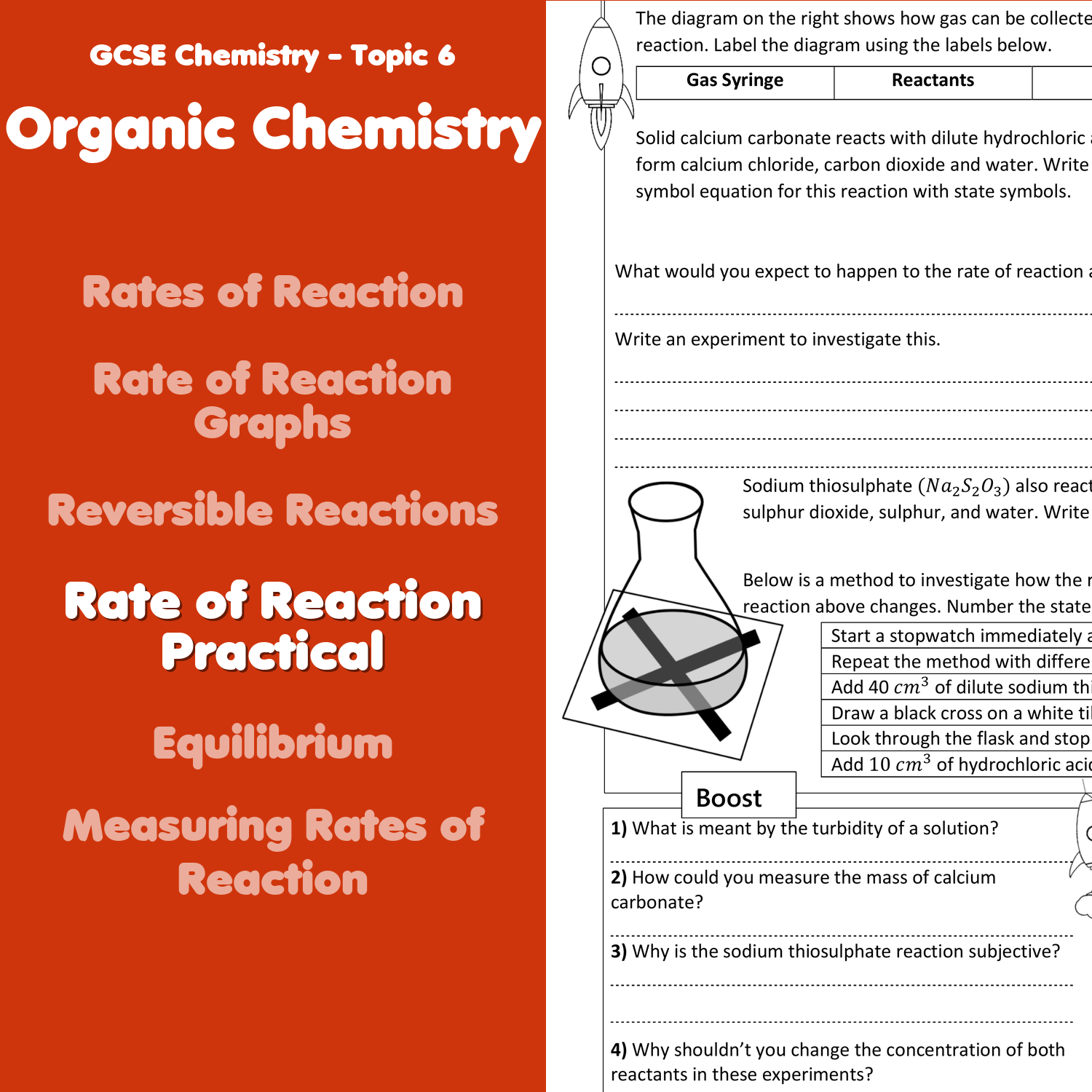
There are several ways to influence how fast a chemical reaction proceeds:
- Concentration: Increasing the concentration of reactants increases the rate of collision, thereby accelerating the reaction rate.
- Temperature: Raising the temperature gives molecules more kinetic energy, leading to more successful collisions.
- Catalyst: A catalyst lowers the activation energy required for the reaction to occur, allowing for faster reactions without being consumed.
- Surface Area: For solid reactants, increasing surface area through grinding or crushing exposes more particles for reaction.
- Pressure: For gases, increasing pressure can force molecules closer together, thus enhancing the rate of reaction.
The Influence of Catalysts on Reaction Rates

Catalysts are essential in many chemical processes, including:
- Reducing the energy required for a reaction to start (activation energy).
- Offering an alternative reaction pathway.
- Speeding up both forward and reverse reactions, but not being consumed.
🧪 Note: Enzymes are biological catalysts crucial for numerous metabolic reactions, demonstrating the real-world significance of catalysts.
Factors Affecting the Rate Equation

The rate equation or rate law expresses how the rate of reaction depends on the concentration of reactants:
[ \text{Rate} = k[A]^m[B]^n ]
Here:
- k is the rate constant, reflecting the intrinsic reactivity of the reaction.
- [A], [B] are concentrations of reactants.
- m and n are the orders of reaction with respect to each reactant.
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| k | Rate constant, unique to each reaction |
| m, n | Reaction orders, must be determined experimentally |

How to Determine the Order of Reaction?

Determining reaction order involves:
- Plotting concentration vs. time data and observing the shape of the curve.
- Using the method of initial rates where different concentrations are used to measure initial rates of reaction.
🔬 Note: Reaction orders can be zero, first, or second with respect to each reactant, but these orders do not necessarily relate directly to the stoichiometric coefficients of the balanced equation.
In summary, the rate of reaction is influenced by several key factors including concentration, temperature, catalysts, surface area, and pressure. Understanding how these variables affect the reaction rate is crucial for predicting how reactions behave under different conditions. By mastering these concepts, students can confidently approach their chemistry worksheets, and chemists can optimize industrial processes.
What is the difference between the rate of reaction and the rate constant?
+
The rate of reaction is how quickly reactants are converted into products, while the rate constant, denoted by k, is a proportionality constant that relates the rate of the reaction to the concentrations of reactants. The rate constant is unique to each reaction and remains constant at a given temperature.
Why doesn’t a catalyst get used up in a reaction?

+
Catalysts lower the activation energy for the reaction, providing an alternative pathway for the reaction to occur. They participate in the reaction by forming an intermediate product, but in the end, the catalyst is regenerated, thus not being consumed.
Can the rate of reaction be negative?

+
Yes, the rate of reaction can be negative if it’s expressed in terms of the disappearance of reactants. This indicates the concentration of reactants is decreasing over time. However, when discussing the rate in terms of product formation, it’s always positive.