Master Rate of Change with Our Engaging Worksheet

What is Rate of Change?

Rate of Change (RoC) is a crucial mathematical concept used to describe how one quantity changes with respect to another. In mathematics and calculus, it's often used to find the slope of a curve or the instantaneous rate at which a function changes at a particular point. Understanding Rate of Change is not only essential in pure mathematics but also has vast applications in physics, economics, engineering, and many other fields.

How to Calculate Rate of Change

Calculating the Rate of Change typically involves finding the slope between two points. Here are the steps:
- Identify the change in the dependent variable, often denoted as 'Δy'.
- Identify the change in the independent variable, denoted as 'Δx'.
- Divide Δy by Δx to get the average rate of change:
| Average Rate of Change Formula | RoC = Δy / Δx |

Here’s an example:
Suppose you have two points on a graph: (2, 5) and (4, 11). The change in y (Δy) is 11 - 5 = 6, and the change in x (Δx) is 4 - 2 = 2.
The average rate of change is:
RoC = 6 / 2 = 3
💡 Note: If you want to find the instantaneous rate of change, you need to take the derivative of the function at a specific point.
Exploring Rate of Change in Real Life

Rate of Change isn't just an abstract mathematical concept; it’s pervasive in our daily lives:
- Speed: How fast a car travels in relation to time.
- Economic Trends: The growth rate of GDP, unemployment, or stock prices over time.
- Physics: Acceleration, velocity, and force all involve rates of change.
- Environmental Science: Changes in temperature or sea level over time.
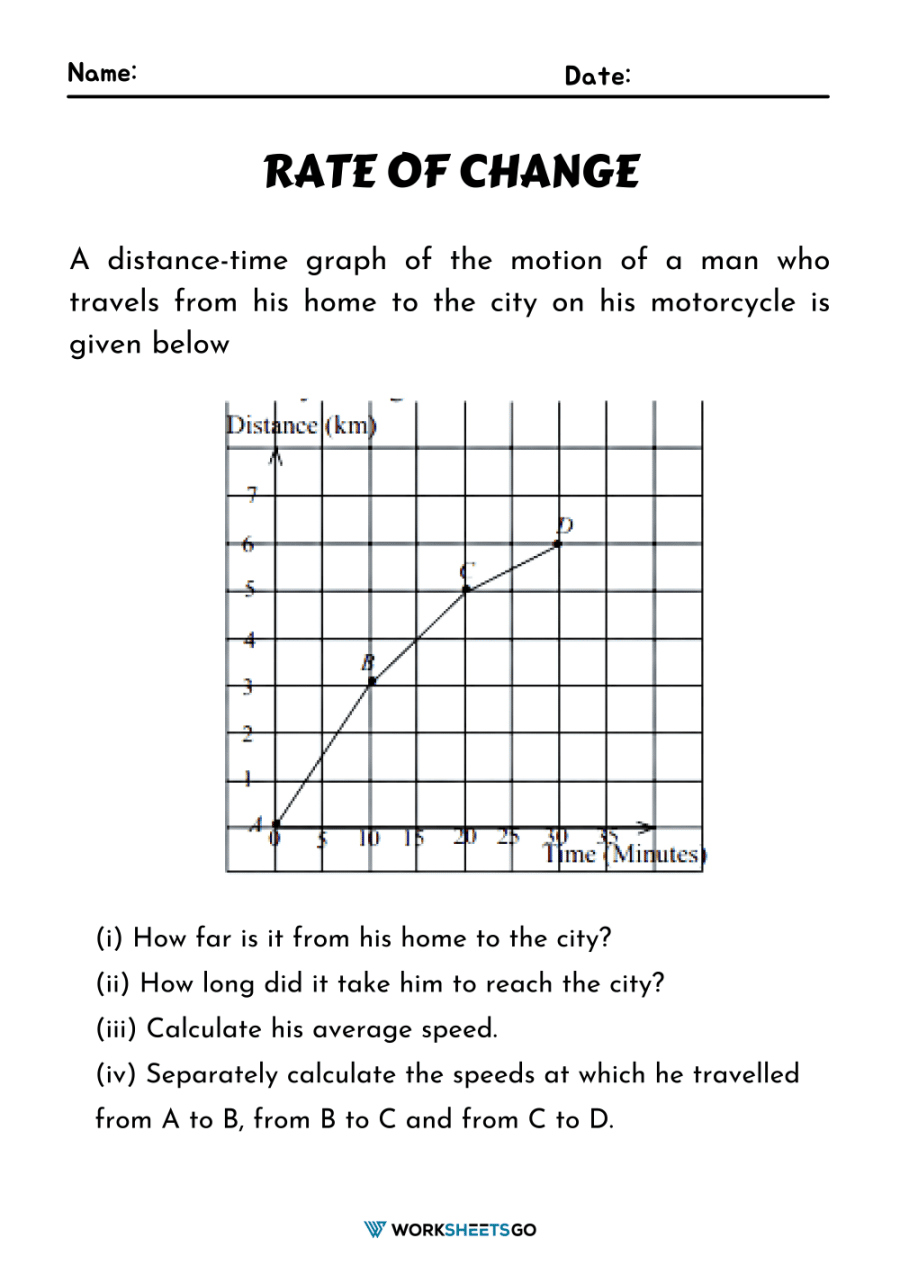
Rate of Change Worksheet

To help you master this concept, we've crafted an engaging Rate of Change worksheet. Below are some problems to get you started:
- Calculate the rate of change for points (1, 3) and (5, 19).
- A car accelerates from 20 mph to 60 mph in 5 seconds. What is the average acceleration?
- The function f(x) = x2 - 2x + 3 changes from x = 0 to x = 3. Determine the average rate of change.
📝 Note: These problems are designed to illustrate both the theoretical application and practical problem-solving skills.
Understanding the Slope and RoC Connection

In calculus, the derivative of a function gives us the instantaneous rate of change. Here's how:
- The slope of the tangent to the curve at any point represents the derivative at that point.
- This slope is the rate of change of the function with respect to its variable.

Mastering Advanced Concepts in RoC
Here are some more advanced applications and nuances of Rate of Change:
- Second Order Derivatives: Rate of change of the rate of change, acceleration in physics, concavity in economics.
- Partial Derivatives: Multivariate calculus, where functions have multiple inputs affecting the output.
- Numerical Differentiation: Approximating the derivative when functions or data are not easily differentiable analytically.
🧪 Note: Higher-level rate of change concepts require a deep understanding of calculus. However, practical applications can still be comprehended with basic knowledge.
In summary, the Rate of Change is a vital mathematical tool with widespread applications. Whether it’s understanding motion, analyzing economic trends, or solving engineering problems, mastering RoC opens up a world of insights into how the universe functions. By using our engaging worksheet, you’ll not only grasp the foundational principles but also develop the confidence to tackle more complex problems in various fields. Remember, the rate of change is not just about numbers; it’s about understanding the essence of change itself.
What does “instantaneous rate of change” mean?

+
Instantaneous rate of change represents how fast something is changing at a specific point in time or at a specific point on a curve. It is the derivative of the function at that point, essentially the slope of the tangent line.
How can Rate of Change be applied in business?

+
In business, RoC can help analyze sales trends, profit margins, or the performance of investments over time. For example, understanding the growth rate of a company’s revenue helps in forecasting and decision-making.
Are there tools or software to calculate Rate of Change?

+
Yes, many software packages like Microsoft Excel, MATLAB, and various online calculators can compute rates of change for data sets or specific functions. These tools often include functions for both numerical and symbolic differentiation.
How does Rate of Change differ from derivatives?

+
While both terms relate to the change in a function’s value, the derivative is a more specific mathematical operation that gives the instantaneous rate of change at any point. Rate of Change, in general, could refer to average changes or changes over specific intervals.
What is an example of a negative Rate of Change?

+
A negative RoC would be observed when a quantity decreases over time. For instance, a company experiencing a decline in revenue over consecutive months would exhibit a negative rate of change in its income.



