Army Officer Ranks Explained

Understanding Army Officer Ranks: A Comprehensive Guide
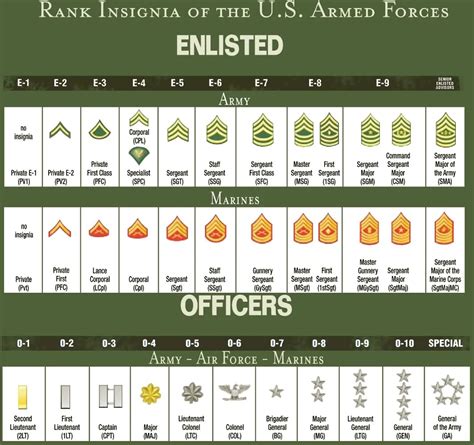
The army is a hierarchical organization with a well-defined rank structure. Officer ranks are used to denote the level of responsibility, authority, and expertise of an officer. In this article, we will delve into the world of army officer ranks, exploring the different types of ranks, their responsibilities, and the paths to advancement.
The Commissioned Officer Ranks
Commissioned officers are leaders who have completed a commissioning program, such as a service academy, ROTC, or Officer Candidate School. They hold positions of authority and are responsible for leading and managing units. The commissioned officer ranks are:
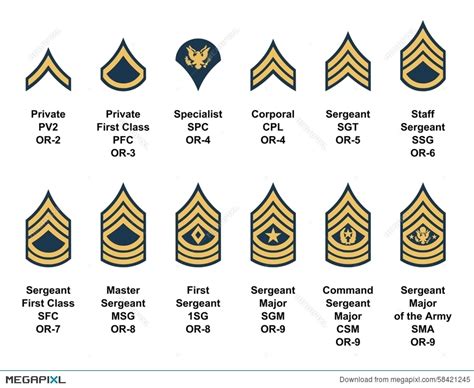
- Second Lieutenant (2LT): The most junior commissioned officer rank, typically held by new officers. 2LTs serve as platoon leaders or executive officers.
- First Lieutenant (1LT): A higher rank than 2LT, 1LTs serve as platoon leaders, executive officers, or staff officers.
- Captain (CPT): A company-grade officer, CPTs serve as company commanders, executive officers, or staff officers.
- Major (MAJ): A field-grade officer, MAJs serve as battalion or brigade executive officers, staff officers, or as commanders of smaller units.
- Lieutenant Colonel (LTC): A higher field-grade officer, LTCs serve as battalion or brigade commanders, executive officers, or staff officers.
- Colonel (COL): A senior field-grade officer, COLs serve as brigade commanders, executive officers, or staff officers.
- Brigadier General (BG): A one-star general officer, BGs serve as deputy commanders or as commanders of brigades.
- Major General (MG): A two-star general officer, MGs serve as division commanders or as deputy commanders.
- Lieutenant General (LTG): A three-star general officer, LTGs serve as corps commanders or as deputy commanders.
- General (GEN): The highest rank in the army, GENs serve as commanders of armies or as the Chief of Staff of the Army.
The Warrant Officer Ranks
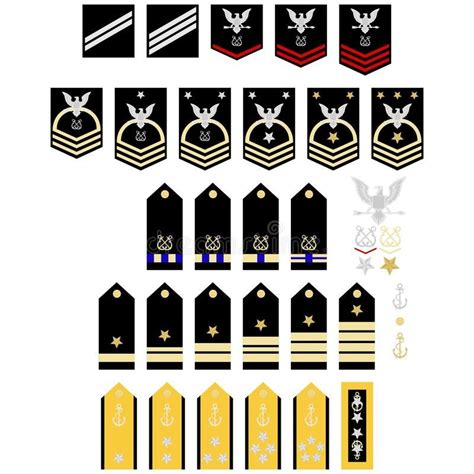
Warrant officers are technical experts who specialize in a specific area, such as aviation, communications, or intelligence. They are appointed by a warrant, rather than a commission, and hold a unique position in the army hierarchy. The warrant officer ranks are:
- Warrant Officer 1 (WO1): The most junior warrant officer rank, WO1s serve as technical experts or as instructors.
- Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CW2): A higher rank than WO1, CW2s serve as technical experts or as instructors.
- Chief Warrant Officer 3 (CW3): A senior warrant officer, CW3s serve as technical experts or as advisors.
- Chief Warrant Officer 4 (CW4): A higher senior warrant officer, CW4s serve as technical experts or as advisors.
- Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CW5): The highest warrant officer rank, CW5s serve as technical experts or as advisors.
Specialized Officer Ranks
The army also has several specialized officer ranks, including:
- Judge Advocate General (JAG): JAG officers are lawyers who serve as military judges, prosecutors, or defense attorneys.
- Chaplain: Chaplains are clergy members who serve as spiritual advisors to soldiers.
- Medical Officer: Medical officers are physicians or other medical professionals who serve as doctors or medical administrators.
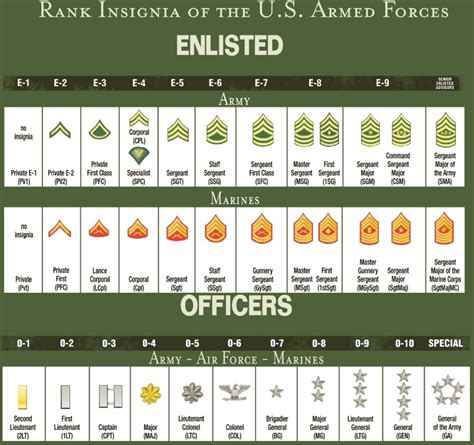
Officer Rank Insignia

Each officer rank has its own unique insignia, which is worn on the uniform to denote rank. The insignia typically consist of bars, leaves, or stars, and are worn on the shoulder or collar.
| Rank | Insignia |
|---|---|
| Second Lieutenant | Gold bar |
| First Lieutenant | Silver bar |
| Captain | Two silver bars |
| Major | Gold oak leaf |
| Lieutenant Colonel | Silver oak leaf |
| Colonel | Eagle |
| Brigadier General | One-star |
| Major General | Two-star |
| Lieutenant General | Three-star |
| General | Four-star |

📝 Note: Officer rank insignia may vary depending on the country or branch of service.
Conclusion
Understanding army officer ranks is essential for anyone interested in the military or seeking to advance their career as an officer. By knowing the different types of ranks, their responsibilities, and the paths to advancement, individuals can make informed decisions about their career goals. Whether you’re a seasoned officer or just starting out, this guide provides a comprehensive overview of the army officer ranks and their insignia.
What is the highest rank in the army?
+
The highest rank in the army is General (GEN), which is a four-star general officer rank.
What is the difference between a commissioned officer and a warrant officer?

+
A commissioned officer is a leader who has completed a commissioning program, while a warrant officer is a technical expert who specializes in a specific area.
How do I advance in rank as an officer?

+
To advance in rank, officers must meet certain requirements, such as completing professional military education, gaining experience, and demonstrating leadership and technical skills.
Related Terms:
- Military rank list
- Military rank in the world
- Military rank 1960
- Highest rank in military
- Sergeant major of the army
- U S Army rank