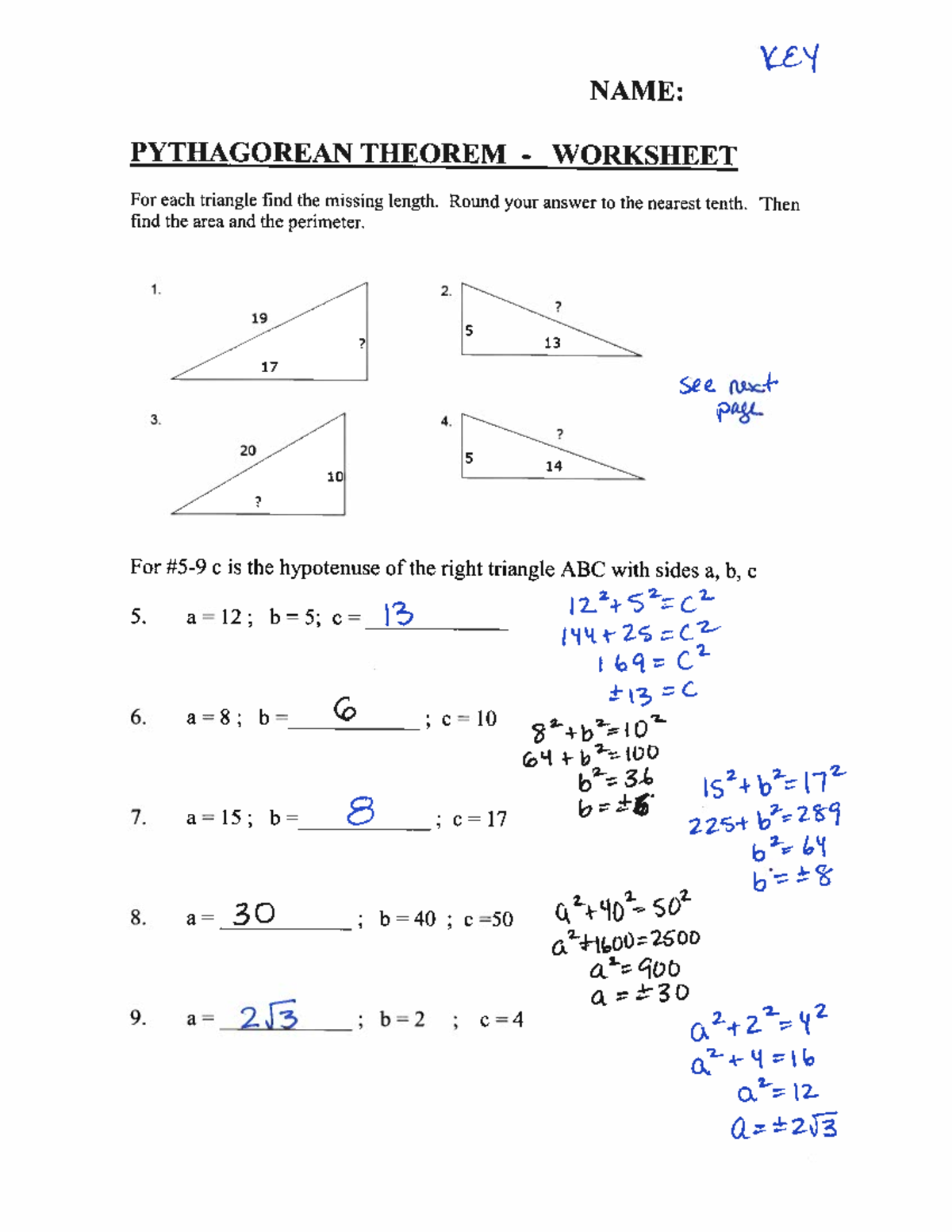
Pythagorean Theorem Worksheet: 5 Answer Key Solutions

Introduction to Pythagorean Theorem

The Pythagorean Theorem is a fundamental principle in geometry that relates the lengths of the sides of a right triangle. It states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides. Here's how you can remember it:
- Formula: c^2 = a^2 + b^2 , where c is the hypotenuse, and a and b are the other two sides.
Examples of Pythagorean Theorem

Let's solve some examples to illustrate how the Pythagorean theorem works:
Example 1: Finding the Hypotenuse
Given:
- Side ( a = 3 ) units
- Side ( b = 4 ) units
Calculate the hypotenuse:
[ c^2 = 3^2 + 4^2 ] [ c^2 = 9 + 16 ] [ c^2 = 25 ] [ c = \sqrt{25} ] [ c = 5 ]
The length of the hypotenuse is 5 units.
Example 2: Finding One Side
Given:
- Side ( b = 7 ) units
- Hypotenuse ( c = 11 ) units
Find side a :
[ 11^2 = a^2 + 7^2 ] [ 121 = a^2 + 49 ] [ a^2 = 121 - 49 ] [ a^2 = 72 ] [ a = \sqrt{72} ] [ a ≈ 8.485 ]
Side a is approximately 8.485 units.
✨ Note: While the value of a is approximately 8.485, in this example, we've given a rounded value for simplicity.
Example 3: Testing for a Right Triangle

Given sides:
- Side ( a = 6 )
- Side ( b = 8 )
- Side ( c = 10 )
Check if these sides form a right triangle:
[ 10^2 = 6^2 + 8^2 ] [ 100 = 36 + 64 ] [ 100 = 100 ]
Since the equation holds true, these sides do indeed form a right triangle.
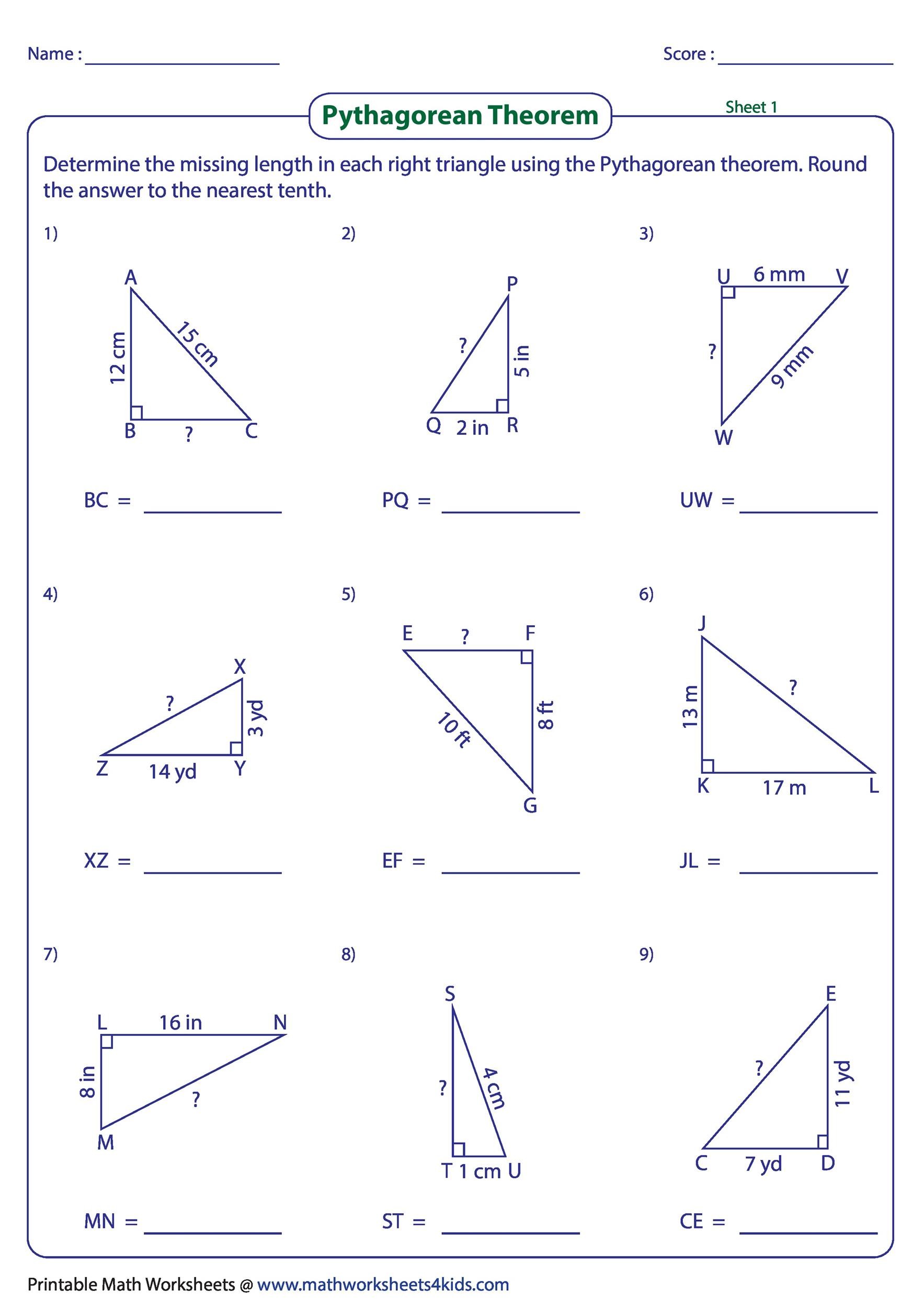
Pythagorean Theorem Worksheet

| Problem | Answer |
|---|---|
| If a = 3 and b = 4 , what is c ? | c = 5 |
| If a = 5 and c = 13 , what is b ? | b = 12 |
| Check if a = 8 , b = 15 , and c = 17 form a right triangle. | Yes, they do. |
| If a = 9 and b = 12 , what is c ? | c = 15 |

More Advanced Applications

Beyond simple problems, the Pythagorean Theorem is also used in:
- Finding the diagonal of a rectangle:
- Determining the distance between two points in a plane (with the distance formula).
- Calculating heights in 3D shapes like pyramids or cones, when you have base dimensions and the slant height.
⚙️ Note: For 3D applications, the Pythagorean theorem can be extended to three dimensions where the square of the diagonal length is the sum of the squares of three sides.
Final Thoughts on Learning with Worksheets

Worksheets are an excellent way to practice and solidify your understanding of the Pythagorean Theorem. Here's why they are beneficial:
- They provide structured problems that help in understanding different types of scenarios where the theorem applies.
- Practice with worksheets allows you to gain speed and confidence in solving Pythagorean theorem-related problems.
- They can serve as a self-check mechanism for your calculations.
Why is the Pythagorean Theorem important?

+
The Pythagorean Theorem is crucial in various fields like architecture, engineering, surveying, and navigation where precise measurements are needed to ensure accuracy in design and construction.
Can the Pythagorean Theorem be used for non-right triangles?
+
The theorem itself is specific to right triangles. However, concepts like the law of cosines, which generalizes the Pythagorean Theorem, can be applied to other types of triangles.
How do you teach the Pythagorean Theorem to students?

+
Start with visual proofs like the tiling method, use real-life examples like finding the diagonal of a TV screen, and then provide practice problems in both abstract and applied contexts.
By mastering the Pythagorean Theorem through worksheets, one can approach real-world problems with confidence, understanding that the foundational geometry will guide the way to accurate solutions.



