Pure Substances vs. Mixtures: Essential Worksheet Guide

Understanding the distinction between pure substances and mixtures is crucial in chemistry, where the nature of materials can significantly affect their properties, reactions, and applications. This guide provides an in-depth look into how to differentiate these types of matter, making it easier for students, educators, and anyone interested in chemistry to grasp these foundational concepts.
Understanding Pure Substances

Pure substances are materials that consist of only one type of particle. These particles could either be atoms or molecules. Here’s what defines a pure substance:
- They have a fixed composition, meaning the ratio of their constituents does not change.
- They exhibit consistent properties regardless of the amount of substance present.
- They can be either elements or compounds:
- Elements: Consist of only one kind of atom. Examples include hydrogen (H) or gold (Au).
- Compounds: Made up of atoms from two or more different elements bonded together. For example, water (H2O) or sodium chloride (NaCl).
Identifying Pure Substances

To identify if a material is a pure substance, consider the following:
- Look for uniformity in composition.
- Check for consistency in melting point or boiling point.
- Observe for single-phase under given conditions.
Understanding Mixtures

Mixtures, on the other hand, are materials composed of two or more substances that are physically combined. Here’s what you need to know:
- Mixtures do not have a fixed composition; the proportions of their components can vary.
- They retain the properties of their individual substances, although physical characteristics like color or boiling point might be influenced.
- Mixtures can be further classified as:
- Homogeneous Mixtures: These have a uniform composition throughout; examples include solutions like salt water.
- Heterogeneous Mixtures: Where composition is not uniform, such as in a sand and sugar mixture.
Identifying Mixtures

To identify mixtures, you can look out for:
- Variability in properties like color, density, or other physical attributes.
- The ability to physically separate the components.
- Multiple phases can be observed in some cases.
Essential Worksheet Guide

Here are steps to design and utilize a worksheet that aids in understanding pure substances and mixtures:
1. Introduction

Begin with definitions and key differences between pure substances and mixtures. Use bullet points for clarity:
- Pure Substances: Only one type of matter throughout. Examples?
- Mixtures: Two or more substances combined. Examples?
2. Classify Substances

Provide a list of common substances and ask students to classify them into pure substances or mixtures:
| Substance | Type |
|---|---|
| Water | Pure Substance (compound) |
| Air | Mixture (homogeneous) |
| Salt Water | Mixture (solution) |
| Gold | Pure Substance (element) |
| Trail Mix | Mixture (heterogeneous) |

📚 Note: Ensure students understand that classifying substances as pure or mixtures often requires more than just observing physical properties; sometimes, chemical tests or phase separation is necessary.
3. Separation Techniques

Explain different methods for separating mixtures:
- Filtration: Used for separating solid from liquid mixtures.
- Distillation: For separating liquid mixtures with different boiling points.
- Chromatography: To separate mixtures based on the differential movement of components through a medium.
4. Diagram and Label

Include diagrams or flowcharts to visually depict the differences or separation processes:

5. Application Exercises

Provide scenarios or real-life applications where understanding pure substances and mixtures is crucial, like:
- Discussing the purification of drinking water.
- Analyzing air quality.
🧪 Note: Real-world applications can enhance student engagement, making abstract concepts more tangible.
In wrapping up, the distinction between pure substances and mixtures is not only a foundational aspect of chemistry but also has practical implications in daily life and industry. By understanding these principles, one can better appreciate how substances interact, how they are purified, and the specific applications they are suited for. This guide offers a structured approach to teaching and learning these concepts, ensuring that students and enthusiasts alike can confidently navigate the nuances of chemistry with clarity and precision.
What is the difference between a compound and a mixture?

+
A compound is a pure substance formed when two or more elements are chemically bonded, with a fixed composition and new properties distinct from its constituents. A mixture, however, combines substances without a chemical bond, retaining the properties of the individual substances, and its composition can vary.
Can a pure substance be separated into simpler substances?
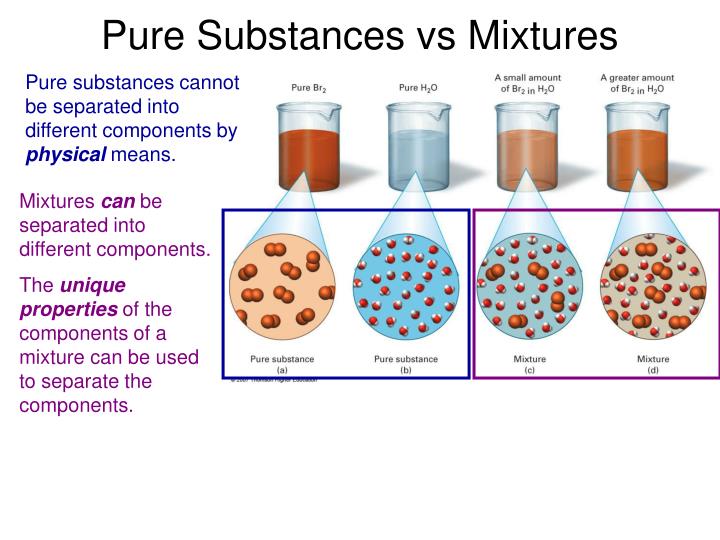
+
Pure substances, like elements, cannot be broken down into simpler substances by physical means. Compounds, however, can be separated into elements or simpler compounds through chemical reactions, not by physical separation techniques.
Why is it important to understand pure substances and mixtures in chemistry?

+
Understanding pure substances and mixtures helps in identifying the nature of materials, predicting their behavior in reactions, and applying appropriate separation techniques in both scientific research and industrial processes.
How can you tell if something is a mixture just by looking at it?
+Mixtures often show signs like visible separation of components, lack of uniformity in appearance, or changes in properties like color, texture, or taste as you move through different parts of the sample.
Is air considered a pure substance or a mixture?
+Air is a mixture of gases, predominantly nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%), with smaller amounts of other gases like argon, carbon dioxide, and water vapor. Thus, it is not a pure substance but a homogeneous mixture.



