Punnett Square Worksheet 1 Answers: Simplified Guide
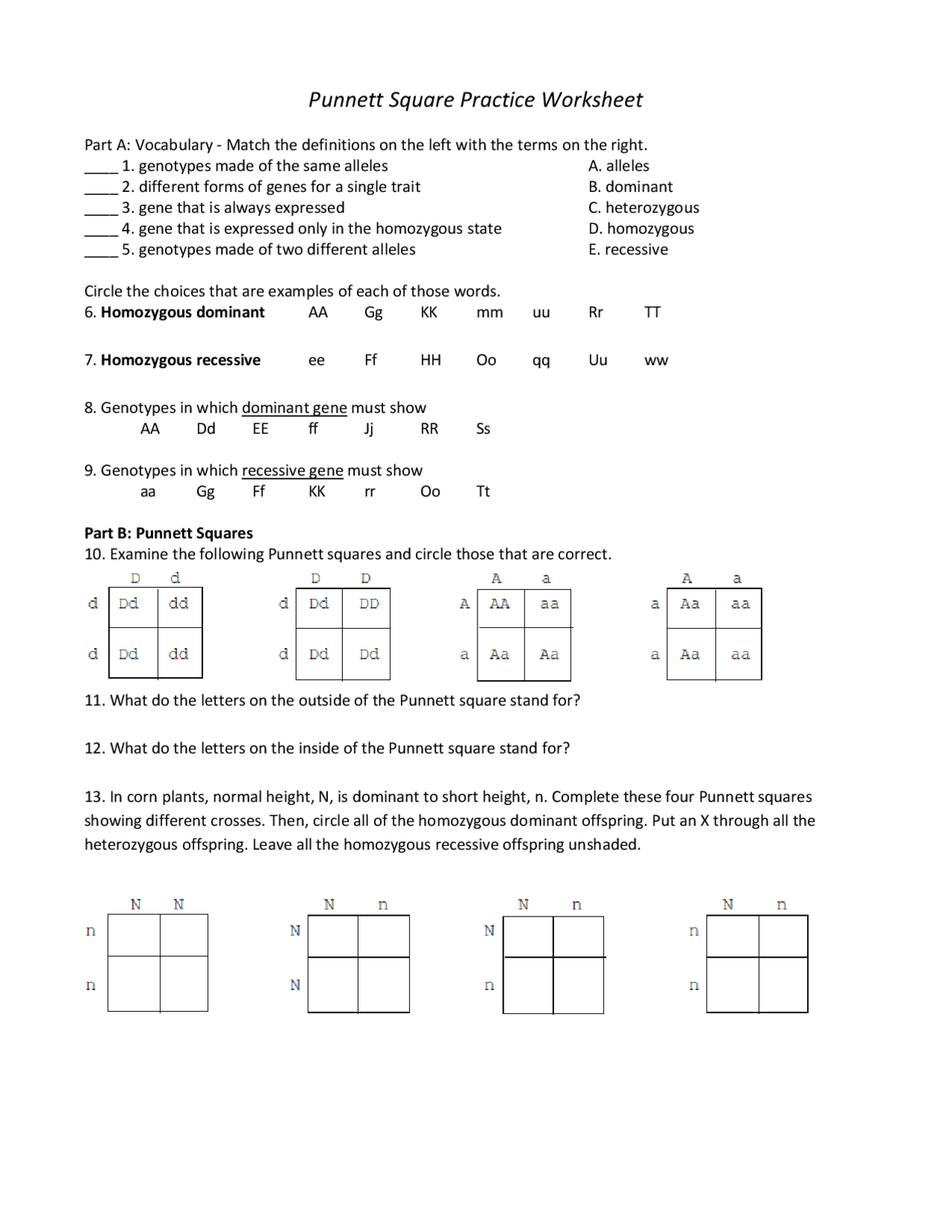
In the vast realm of genetics, Punnett squares are a fundamental tool for predicting the outcomes of genetic crosses. Whether you're a student learning about heredity, an enthusiast trying to understand genetics, or someone simply curious about how traits pass down from parents to offspring, mastering the use of Punnett squares can be immensely rewarding. This guide will simplify your journey by providing a clear and concise walkthrough of Punnett Square Worksheet 1, where we'll solve the answers step-by-step.
Understanding Punnett Squares


Before diving into the worksheet, let’s briefly review what Punnett squares are:
- Punnett Squares are diagrammatic representations used to determine the probability of offspring possessing specific genotypes based on the genetics of their parents.
- They allow for an organized approach to visualize possible combinations of alleles from both parents.
Breaking Down Punnett Square Worksheet 1

Let’s analyze the questions from Punnett Square Worksheet 1 one by one:
Question 1: Flower Color
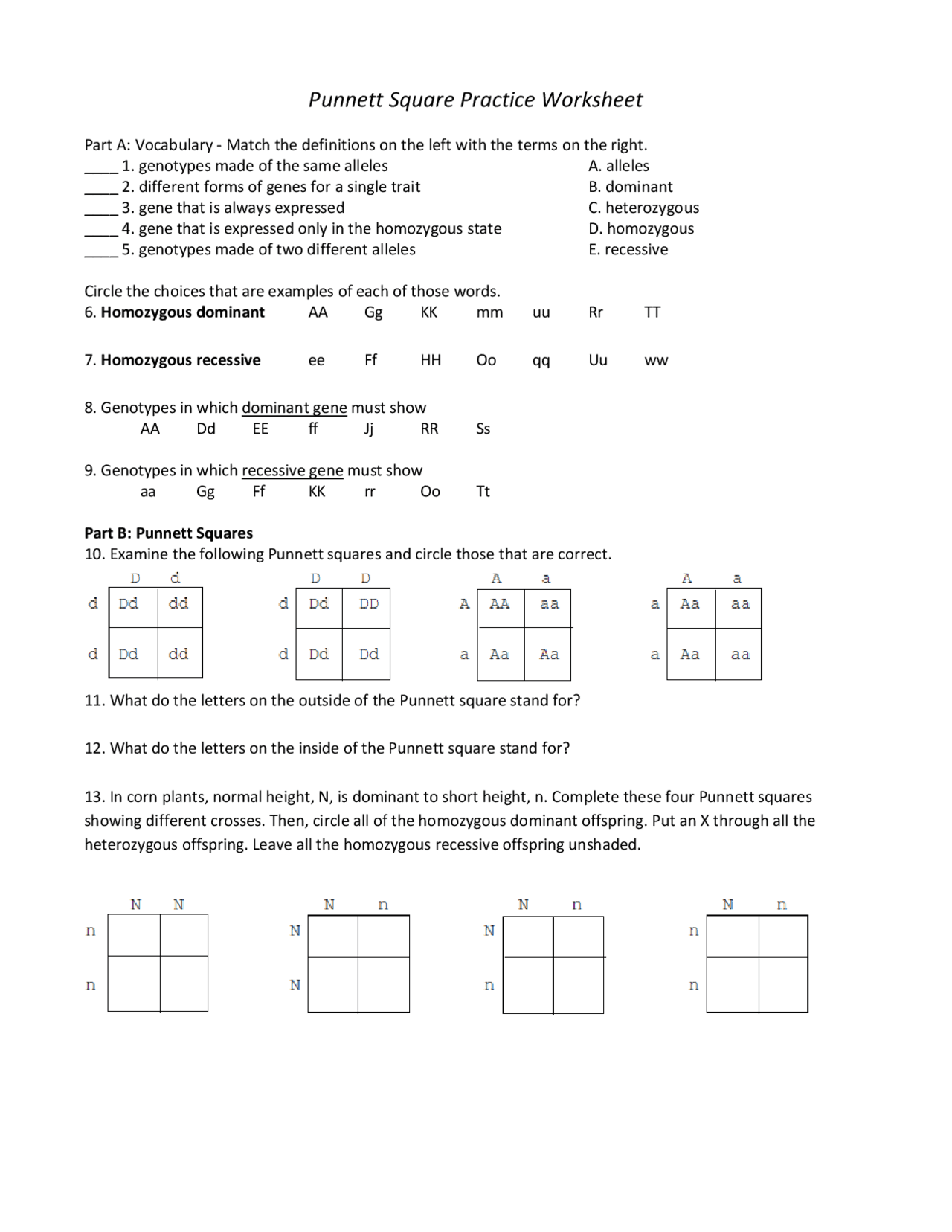
Suppose two plants, both heterozygous for the flower color gene (Bb), are crossed. Predict the possible genotypes and phenotypes of their offspring.
- Create the Punnett Square:
B b B BB Bb b Bb bb 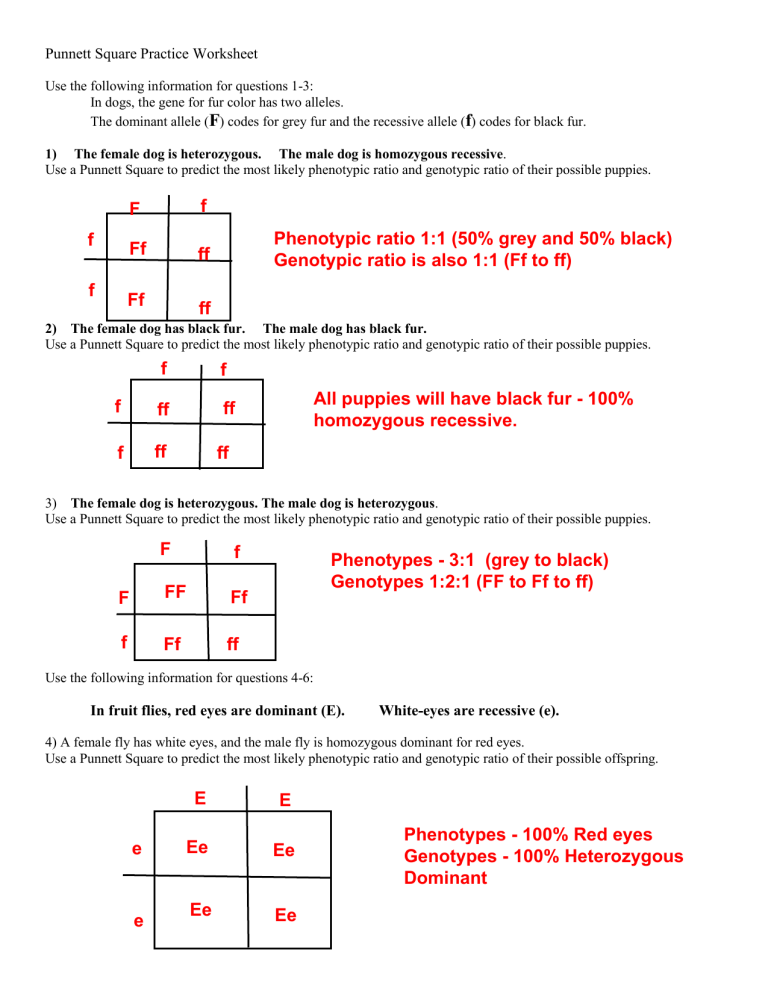
- Interpret Results:
- Genotypes: 25% BB, 50% Bb, 25% bb
- Phenotypes:
- 75% of the offspring will have purple flowers (BB and Bb).
- 25% will have white flowers (bb).
💡 Note: In this case, the gene for purple flowers (B) is dominant over the white gene (b).
Question 2: Fur Pattern

Consider a cross between a homozygous dominant (HH) and heterozygous (Hh) rabbit for fur pattern. Determine the potential offspring:
- Set up the Punnett Square:
H h H HH Hh H HH Hh - Analyze:
- Genotypes: 50% HH, 50% Hh
- Phenotypes: All offspring will exhibit dominant trait fur pattern since it’s dominant.
Question 3: Eye Color

A blue-eyed (bb) individual mates with a heterozygous individual (Bb) for eye color. What will the offspring likely look like?
- Construct the Punnett Square:
B b b Bb bb b Bb bb - Determine:
- Genotypes: 50% Bb, 50% bb
- Phenotypes:
- 50% will have brown eyes (Bb).
- 50% will have blue eyes (bb).
Summing Up
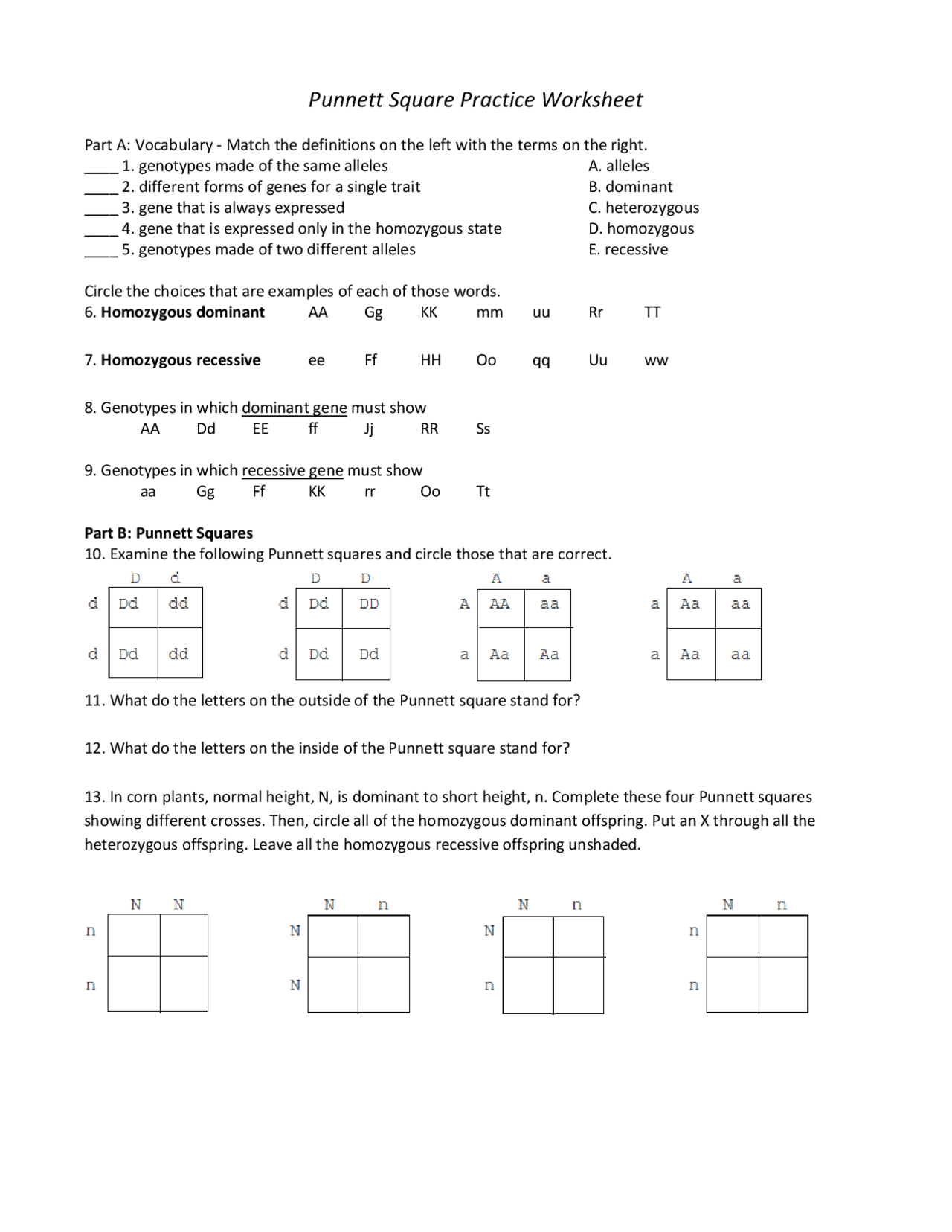
By working through these examples from Punnett Square Worksheet 1, you’ve seen how to determine the probabilities of different genotypes and phenotypes in offspring. Understanding these principles allows us to appreciate the predictability and variation in genetic inheritance. Remember, these outcomes are based on Mendelian genetics and can be affected by various other genetic phenomena like codominance or incomplete dominance.
What is a Punnett Square?
+
A Punnett Square is a simple graphical method for predicting the possible genotypes of offspring, given the genotypes of their parents.
How do I know which allele is dominant or recessive?
+
Typically, uppercase letters represent dominant alleles, while lowercase letters represent recessive alleles. The dominance can often be inferred from observations or known genetic principles.
Can a Punnett Square predict with certainty the exact offspring?

+
No, Punnett Squares show probability distributions for offspring outcomes, not definitive results. Actual genetic crosses can yield any of the possible combinations or phenotypes.