Discover the Basics: Protons, Electrons, and Neutrons Worksheet

In the intricate universe of chemistry, understanding the very building blocks of matter is crucial. These fundamental particles, known as protons, electrons, and neutrons, shape our understanding of everything from simple chemical reactions to the complex functionalities of the world around us. Today, we delve deep into these elementary particles through our comprehensive worksheet, designed to enhance learning and retention about atomic structure.
What Are Protons, Electrons, and Neutrons?
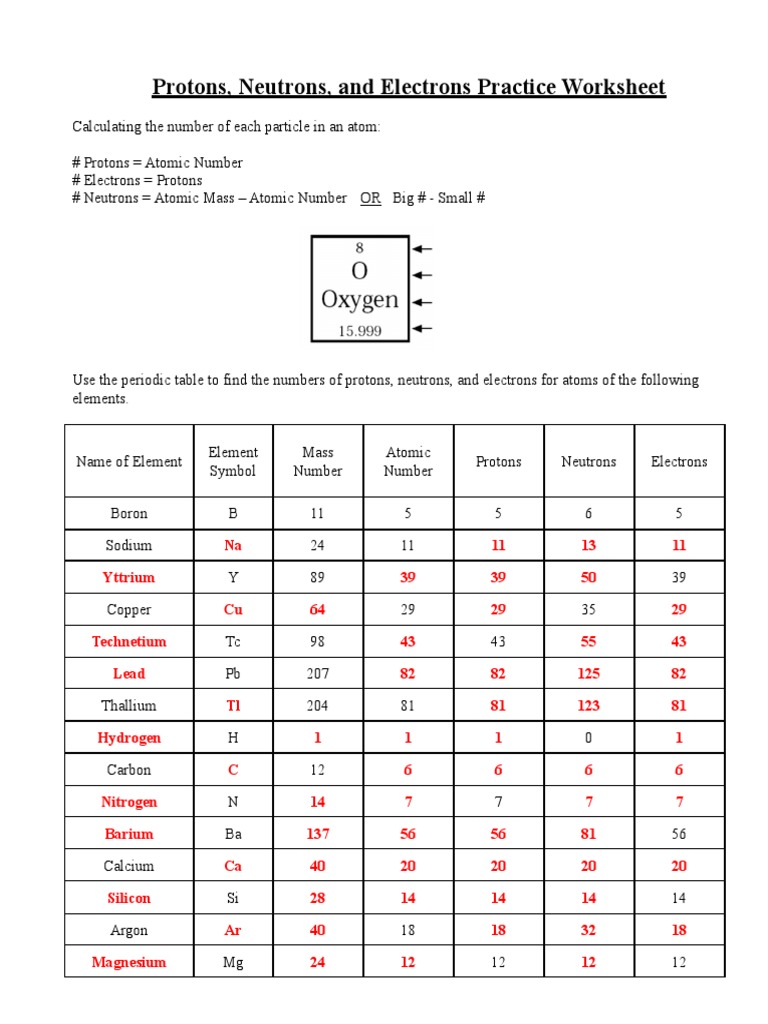

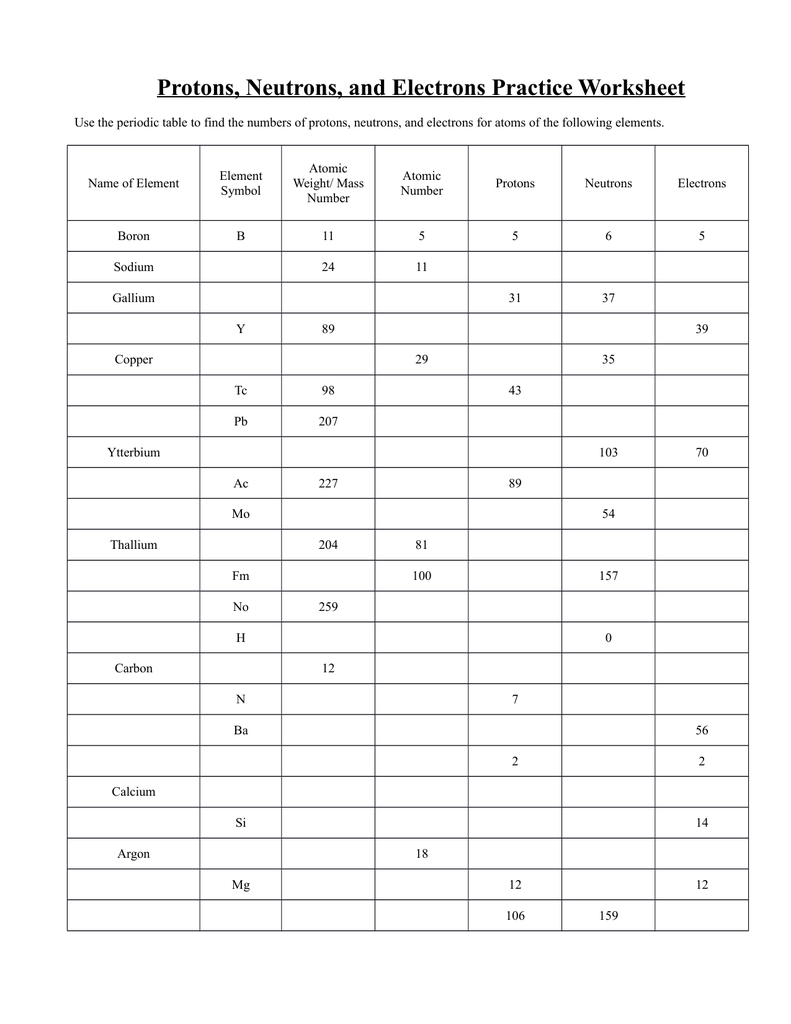
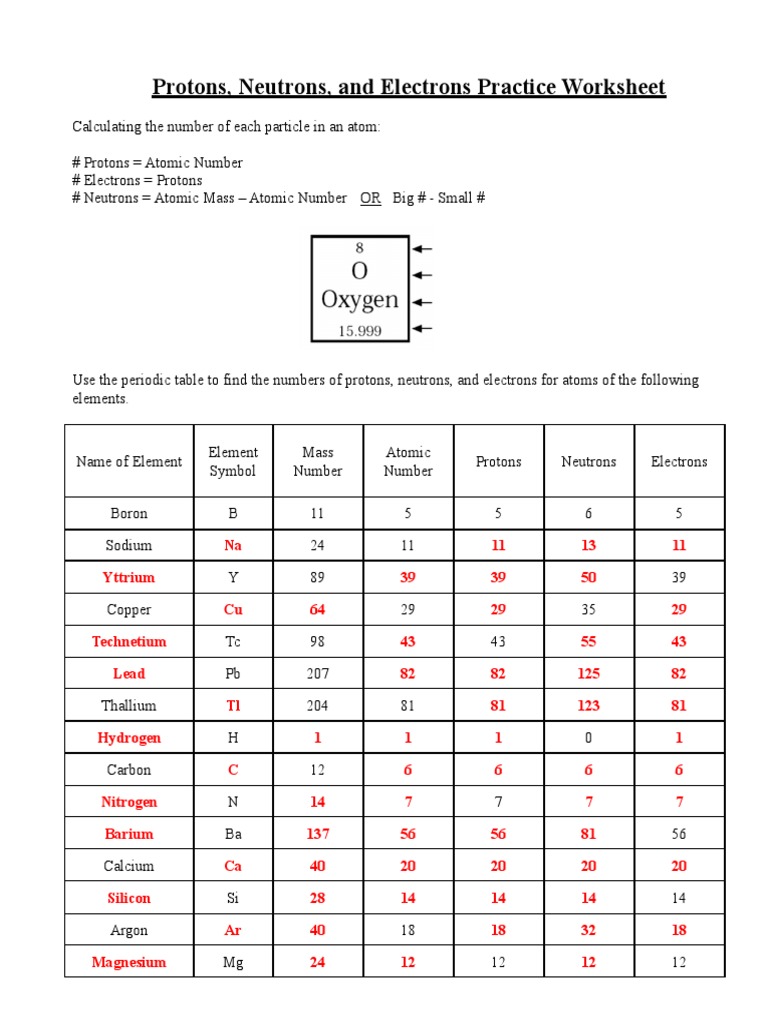
Protons, electrons, and neutrons are subatomic particles that are essential in constructing atoms, the smallest unit of an element that maintains its chemical identity:
- Protons: Positively charged particles found in the nucleus of an atom. They give the atom its atomic number, which identifies the element. For instance, hydrogen has one proton, making its atomic number 1.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus in shells or energy levels. Their number equals that of protons in a neutral atom, creating an electrostatic balance.
- Neutrons: Neutral particles in the nucleus, contributing to the mass of the atom without affecting its charge. Neutrons stabilize the nucleus; their count can vary, leading to isotopes of the same element.
Worksheet for Understanding

Let's engage with our understanding through a structured worksheet:
| Element | Protons | Electrons | Neutrons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Helium | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Oxygen | 8 | 8 | 8 or 9 or 10 |

💡 Note: Neutrons can vary in number for the same element due to isotopes.
Interactive Exercises

Interactive exercises help in solidifying the knowledge:
Quiz Time

Test your knowledge by answering:
- What is the charge of an electron?
- What determines the atomic mass?
- What is an isotope?
Notes on Learning

Education in subatomic particles is not just about memorizing facts; it’s about understanding the underpinnings of chemistry:
- The number of protons uniquely identifies an element, showcasing its position in the periodic table.
- Electrons are involved in chemical reactions, bonding, and electrical conductivity.
- Neutrons play a role in nuclear reactions and can affect the stability of an atom's nucleus.
⚗️ Note: While learning, always relate the properties of these particles to real-world applications to deepen your understanding.
The Role in Real World
Protons, electrons, and neutrons are not just theoretical entities:
- Medical: Understanding isotopes helps in medical imaging and treatments like radiation therapy.
- Electronics: The behavior of electrons is pivotal in the functioning of electronic devices.
- Energy: Nuclear power plants rely on reactions involving protons and neutrons.
Conclusion

By breaking down the complexity of matter into protons, electrons, and neutrons, we've explored the very essence of our universe. Through practical exercises and quizzes, you've now gained a foundational understanding of these particles, their interactions, and their real-world implications. Remember, this knowledge is not static but continually evolving as we discover more about the subatomic world.
Why are protons, electrons, and neutrons important?
+
These particles determine the properties of atoms, which in turn shape the behavior of all elements, their chemical reactions, and their role in various scientific and industrial applications.
What’s the difference between an ion and an atom?

+
An atom has an equal number of protons and electrons, making it neutral. An ion occurs when an atom gains or loses electrons, creating a net positive or negative charge.
Can you find an element’s atomic weight knowing only its protons and neutrons?

+
Yes, atomic mass can be approximately calculated by adding the number of protons to the number of neutrons. However, this is a simplification, as electrons have negligible mass compared to protons and neutrons.
Why don’t electrons crash into the nucleus?
+
Electrons exist in discrete energy levels or shells around the nucleus. Their movement is quantized, preventing them from spiraling into the nucleus due to quantum mechanics principles.
What would happen if an atom had more protons than electrons?

+
It would become a positively charged ion, called a cation. This imbalance would influence its chemical behavior, making it more likely to attract electrons from other atoms or compounds.