Master Pressure Conversions with Chem Worksheet 13-1

In the vast and intricate world of chemistry, understanding the different units of pressure is essential for students and professionals alike. The Chem Worksheet 13-1 focuses on mastering these conversions, offering a structured way to navigate through various pressure measurements. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of pressure conversion, making it a valuable resource for anyone seeking to excel in chemistry.
Introduction to Pressure Conversions

Pressure is a measure of force per unit area, and in chemistry, it plays a critical role in various calculations and experiments. Here are some common units of pressure:
- Atmosphere (atm) - Commonly used in atmospheric pressure discussions.
- Bar (bar) - A metric unit of pressure.
- Pascal (Pa) - The SI unit of pressure.
- Torr (Torr) - Equivalent to 1⁄760 of an atmosphere, commonly used in vacuum physics.
- mmHg (Millimeters of Mercury) - Frequently used in medical and physiological pressure measurements.
- Pounds per square inch (psi) - Predominantly used in American engineering.
Understanding how to convert between these units not only helps in solving chemical problems but also in understanding the application of physical principles across different fields.

The Basics of Pressure Conversion
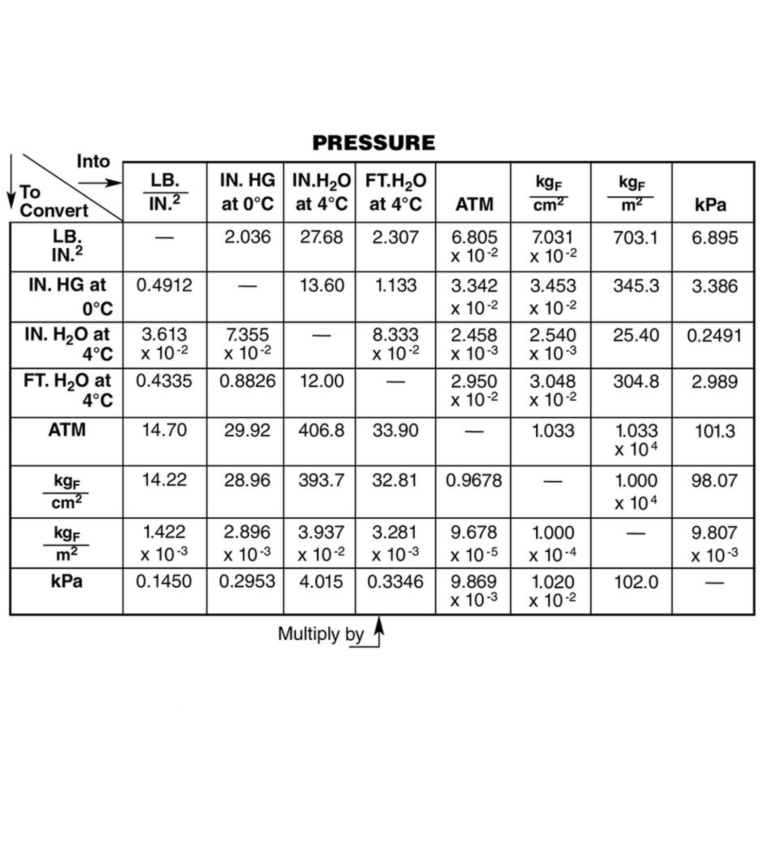
To master pressure conversion, one must understand the basic conversion factors:
| From | To | Conversion Factor |
|---|---|---|
| atm | Pa | 1 atm = 101,325 Pa |
| atm | Torr | 1 atm = 760 Torr |
| bar | atm | 1 bar = 0.986923 atm |
| Pa | psi | 1 Pa ≈ 0.000145 psi |
| Torr | mmHg | 1 Torr = 1 mmHg |

Conversion Steps

Here are the steps for converting pressure from one unit to another:
- Identify the given pressure and its unit: Start by noting down what you have.
- Find the conversion factor: Use the table provided above to identify the appropriate conversion.
- Set up the conversion: Multiply or divide the given pressure by the conversion factor depending on what is needed.
- Calculate the result: Perform the calculation to obtain the pressure in the desired unit.
📌 Note: Always double-check your conversion factor to avoid errors.
Practical Examples

Let’s apply these steps with some practical examples:
Example 1: Convert 5 atm to Pascal.
Using the conversion factor:
5 atm * 101,325 Pa/atm = 506,625 Pa
Example 2: Convert 250 Torr to mmHg.
Since 1 Torr = 1 mmHg:
250 Torr = 250 mmHg
⚠️ Note: Conversion between Torr and mmHg is straightforward as they are equivalent, but not all units share such a direct conversion.
Important Considerations

- Significant Figures: Keep in mind the rules of significant figures when performing conversions to maintain accuracy in your calculations.
- Units Compatibility: Ensure that your units are compatible with the conversion factor you are using.
- Rounding: Depending on the application, rounding might be necessary, but be cautious not to lose precision unnecessarily.
Mastering pressure conversion is not just about memorizing conversion factors; it involves understanding the context in which different units are used and appreciating the nuances of various pressure measurements.
🎓 Note: Practical application through experiments or real-world scenarios can solidify your understanding of pressure units and their conversions.
Wrapping Up

Having explored the foundational aspects of pressure conversions through Chem Worksheet 13-1, we’ve uncovered the importance of these conversions in chemistry and beyond. This guide has provided a structured approach to understand and apply various conversion factors, ensuring accuracy and efficiency in pressure-related calculations. From the significance of units like atm, bar, Pascal, to the practicalities of converting between them, this knowledge is invaluable for students, researchers, and professionals alike, ensuring they are well-equipped to handle pressure-related challenges in their respective fields.
Why is it important to convert pressure units?

+
Pressure conversions are critical because different fields and regions might use different units for the same physical property. Understanding these conversions allows for communication and calculation across these fields, ensuring accuracy and consistency in scientific work.
Can I convert pressure units using online calculators?

+
Yes, there are many online tools available that can perform pressure conversions. However, understanding the process manually is beneficial for educational purposes and in situations where online access is not possible.
How often should I practice pressure conversions?

+
Practice should be regular, especially when you are actively involved in chemical or physical calculations. Periodic review or tackling real-world problems can help maintain proficiency.



