5 Tips to Master Angle Bisectors on Practice Sheet 1.5a

Mastering angle bisectors in geometry can significantly elevate your understanding and proficiency in mathematical concepts. Whether you're studying for an upcoming exam or just want to brush up on your geometry skills, focusing on the nuances of angle bisectors can make a substantial difference. Here are five detailed tips to help you master angle bisectors, using Practice Sheet 1.5a as your tool.
1. Understand the Definition
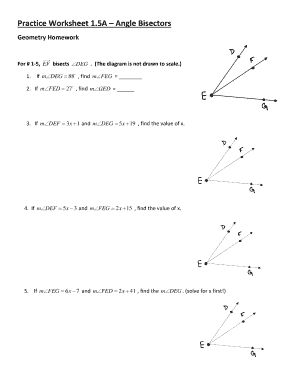
Before diving into practice, it’s essential to understand what an angle bisector is. An angle bisector is a line or line segment that divides an angle into two equal angles. Remember:
- The sum of the two angles created by the bisector must be equal to the original angle.
- An angle bisector can only divide an angle into two equal parts; not more, not less.
Practice Sheet 1.5a might have problems where you’re asked to either find the angle bisector or construct one, so ensure you know these basics well.
2. Use Geometry Software

To get a real-time understanding of how angle bisectors work, use geometry software like GeoGebra or Sketchpad. Here’s how:
- Draw any angle, and use the software tools to construct its bisector.
- Manipulate the vertices of the angle to see how the bisector changes.
- Explore properties like the Angle Bisector Theorem, which states that the angle bisector of an angle in a triangle divides the opposite side into segments that are proportional to the adjacent sides.
This visual approach can help in visualizing what’s happening in Practice Sheet 1.5a.
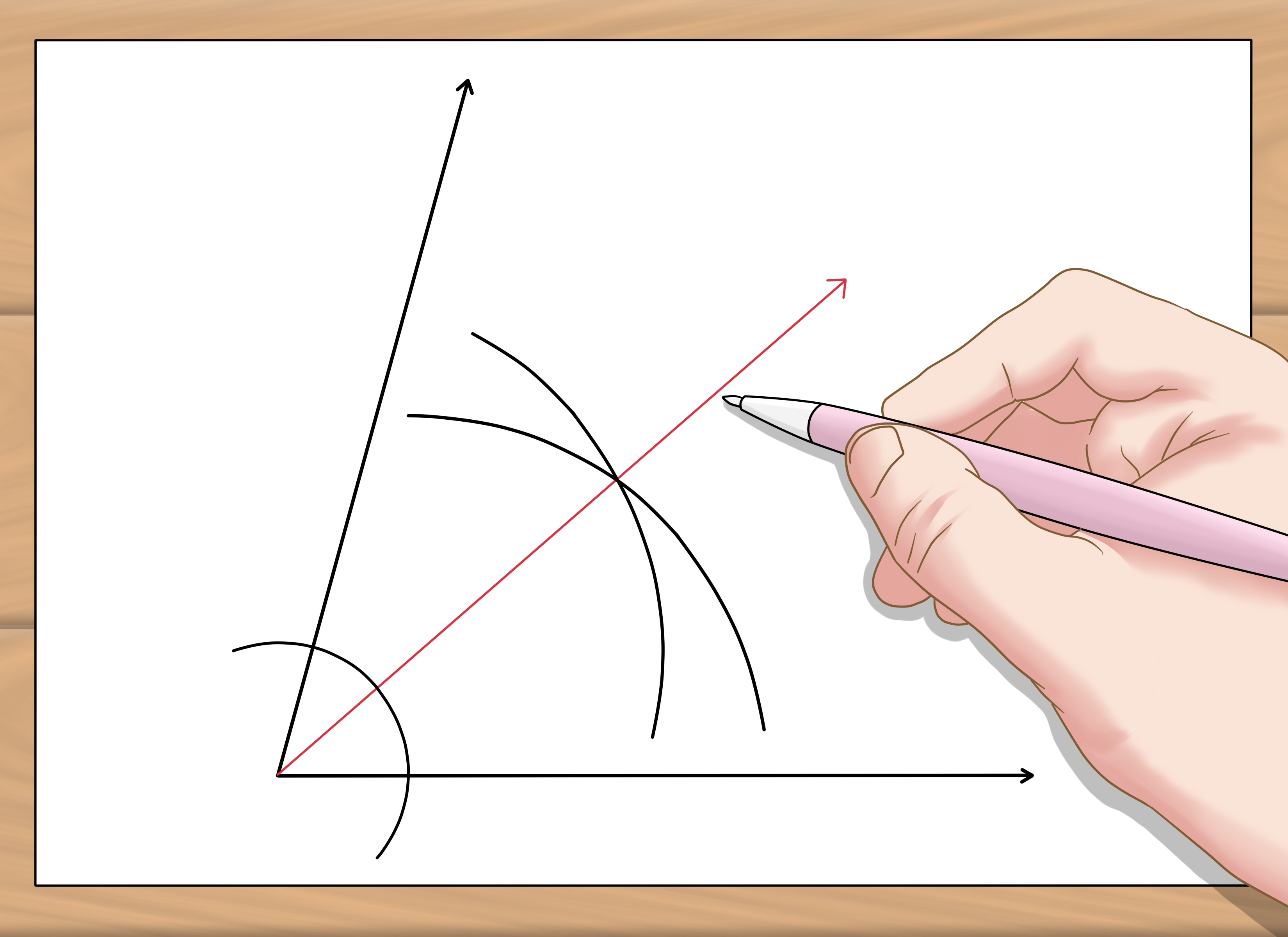
3. Practice Construction

Construction of angle bisectors is a critical skill in geometry. Here’s how to go about it:
- Start with a given angle.
- From the vertex, draw an arc intersecting both sides of the angle.
- Without changing the compass width, draw two more arcs from these intersection points, inside the angle, such that they intersect.
- Draw a line from the vertex to this intersection point. This line is the angle bisector.
🔎 Note: Always check your construction with a protractor to ensure the angles are indeed equal.
4. Solve Problems Systematically
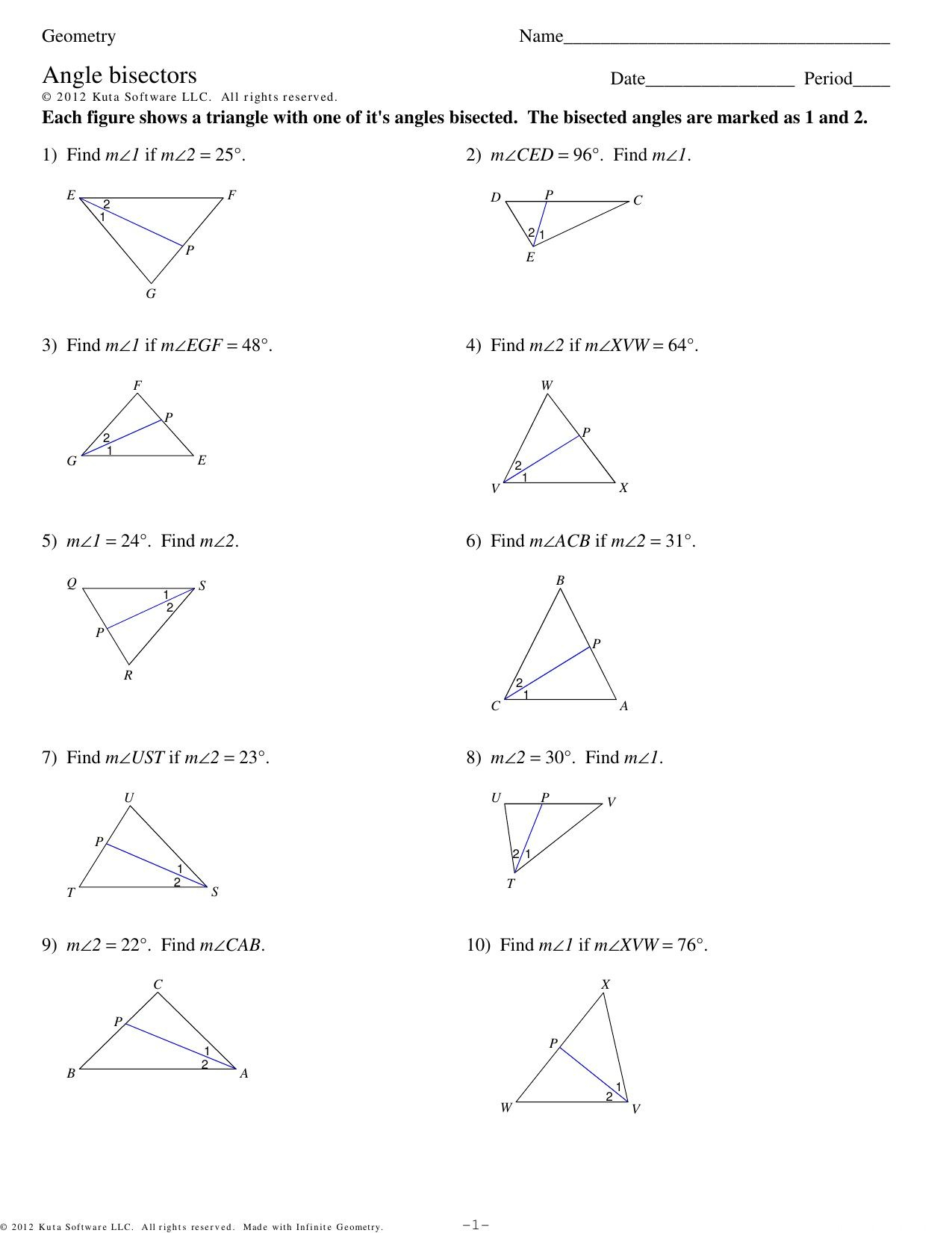
When tackling problems in Practice Sheet 1.5a, follow this systematic approach:
- Identify what type of problem you’re dealing with (construction, finding measures, etc.).
- Sketch the given angle or triangle if not provided, and label all known information.
- Apply the appropriate geometric properties or theorems. For example, if the problem involves a triangle, remember the Angle Bisector Theorem.
- Work through the problem step-by-step, noting each relevant geometric rule you use.
This method will help you understand the why behind each step, enhancing your problem-solving skills.
5. Review and Reflect

After completing Practice Sheet 1.5a, take the time to review your work:
- Go back through each problem to understand where mistakes were made, if any.
- Reflect on what made some problems easier or more challenging than others.
- Note down any common patterns or issues you face in understanding angle bisectors and revise those areas specifically.
Reflection is key to mastering any skill. It not only helps in reinforcing your knowledge but also prepares you for similar problems in future exams or practice sheets.
In wrapping up, mastering angle bisectors requires a combination of understanding the basic principles, using technological aids, practicing construction, approaching problems systematically, and reflective learning. With the Practice Sheet 1.5a as your guide, these tips will not only help you excel in geometry but also develop a deeper appreciation for the beauty of mathematical reasoning.
What is the Angle Bisector Theorem?
+
The Angle Bisector Theorem states that the angle bisector of an angle in a triangle divides the opposite side into two segments that are proportional to the adjacent sides.
Can I use a protractor to find an angle bisector?

+
Yes, you can use a protractor to find the approximate measure of an angle bisector by bisecting the angle manually, but for precise construction, traditional geometry tools like a compass and straightedge are preferred.
How can I practice finding angle bisectors at home?

+
At home, you can practice by drawing angles on a piece of paper and using a compass and straightedge to construct their bisectors. Alternatively, using geometry software can provide a more interactive learning experience.



