Monohybrid Punnett Squares Practice: Answer Key Revealed

Are you intrigued by the fundamentals of genetics? Perhaps you've been delving into the science of inheritance and stumbled upon the fascinating world of Punnett squares. If you're looking to test your understanding of monohybrid crosses or simply seeking clarity on how to solve them, you're in the right place. Here, we will reveal the answer key to our monohybrid Punnett squares practice, providing insights that deepen your grasp of basic genetic principles.
What is a Monohybrid Punnett Square?


Monohybrid Punnett squares are graphical tools used to predict the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring from a genetic cross involving one trait. This simple, yet powerful method allows us to predict the probability of inheriting specific traits.
To understand the Punnett square:
- Identify the alleles - Each trait is controlled by two alleles, one from each parent.
- Set up the square - Create a 2x2 grid where each row and column represent the possible alleles from each parent.
- Predict the offspring - Fill in the squares with the possible combinations of alleles from the parents.
The Practice Questions
Here are some sample questions we’ve covered in our practice:
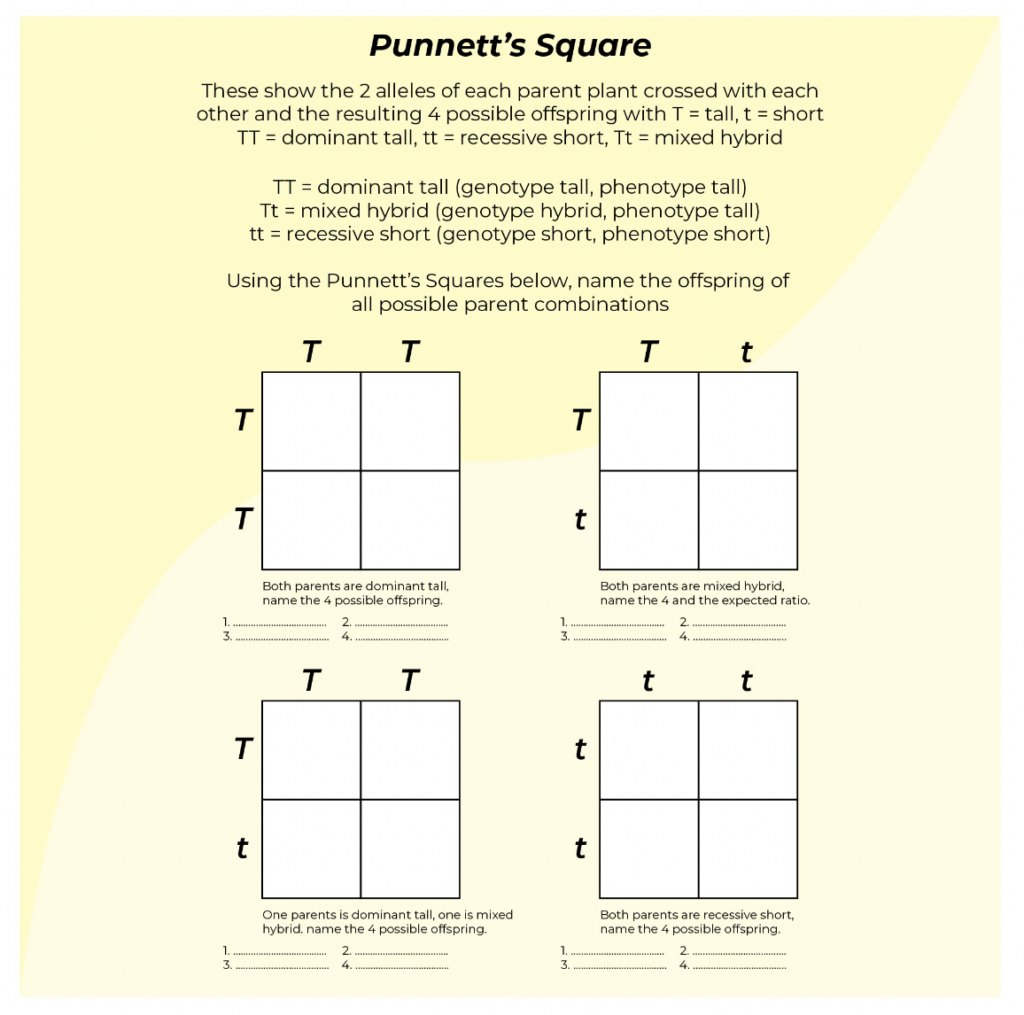
- In a cross between two heterozygous pea plants (Yy), what are the expected genotypes and ratios of the offspring?
- What would be the probability of an offspring being homozygous recessive if one parent is homozygous dominant (YY) and the other is heterozygous (Yy)?
- Suppose a homozygous dominant pea plant (YY) is crossed with a homozygous recessive pea plant (yy). What is the phenotype ratio in the F1 generation?
Answer Key
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| In a cross between two heterozygous pea plants (Yy), what are the expected genotypes and ratios of the offspring? |
|
| What would be the probability of an offspring being homozygous recessive if one parent is homozygous dominant (YY) and the other is heterozygous (Yy)? | There is a 0% chance since the homozygous dominant parent can only provide a dominant allele. |
| Suppose a homozygous dominant pea plant (YY) is crossed with a homozygous recessive pea plant (yy). What is the phenotype ratio in the F1 generation? | The phenotype ratio would be 100% yellow peas. |

💡 Note: Always verify Punnett squares by calculating the expected ratios through probability; each square should represent a possible combination of alleles.
Detailed Explanation of Each Answer
1. Cross between Two Heterozygous Pea Plants (Yy)

Let’s break down this Punnett square:
| Y | y | |
|---|---|---|
| Y | YY | Yy |
| y | Yy | yy |
- The genotypes YY, Yy, yy occur in a 1:2:1 ratio.
- All individuals with at least one Y allele (YY or Yy) will have a yellow phenotype.
- Only the yy genotype will result in a green phenotype.
2. Probability of Homozygous Recessive Offspring from Heterozygous and Homozygous Dominant Parents

Using the Punnett square:
| Y | y | |
|---|---|---|
| Y | YY | Yy |
| Y | YY | Yy |
No yy combination is possible; therefore, there’s a 0% chance of homozygous recessive offspring.
3. Crossing Homozygous Dominant with Homozygous Recessive Pea Plants

The Punnett square for this cross:
| y | y | |
|---|---|---|
| Y | Yy | Yy |
| Y | Yy | Yy |
- All offspring will inherit one Y allele from the homozygous dominant parent, resulting in the phenotype of yellow peas.
💡 Note: Mendelian inheritance patterns are simplifications of more complex genetic interactions. Punnett squares are excellent for basic predictions but remember that genetic inheritance can be influenced by many factors.
By delving into the answer key, we've not only practiced using Punnett squares but also understood the underlying principles of Mendelian genetics. These insights enable us to better predict genetic outcomes, understand the probability of inherited traits, and appreciate the complexity of genetic diversity. We've learned how to apply this knowledge to everyday scenarios, like predicting the color of pea plants or the probability of certain human genetic conditions.
What is the difference between a monohybrid and dihybrid cross?

+
A monohybrid cross deals with the inheritance of a single trait, while a dihybrid cross involves two traits.
Why are Punnett squares useful in genetics?

+
Punnett squares help predict the probability of different genotypes and phenotypes in offspring from known parental genotypes.
Can Punnett squares predict inheritance for traits affected by multiple genes?
+
They are limited in complex polygenic traits but are very effective for traits controlled by one or two genes.