5 Tips to Master Solubility Curves Easily
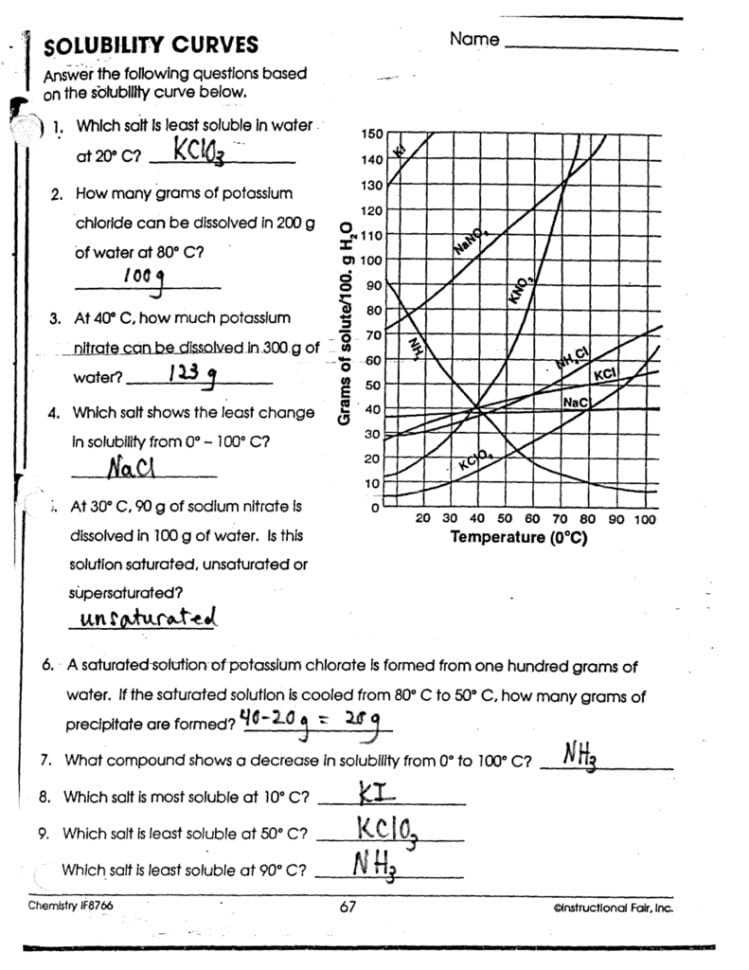
Understanding solubility curves can be daunting for many students, yet it's an essential aspect of chemistry that can unlock fascinating insights into the behavior of substances in different solutions. Whether you're preparing for an exam, aiming to understand the fundamentals of solubility for experimental work, or simply looking to refresh your knowledge, mastering these curves can significantly boost your comprehension. Here are five strategic tips to help you master solubility curves with ease.
Understand the Basics of Solubility

Before delving into the complexities of solubility curves, grasp the basics:
- Solubility is the ability of a solute to dissolve in a solvent at a given temperature.
- A solubility curve is a graphical representation that shows how the solubility of a solute changes with temperature.
- The axes on a solubility curve typically represent temperature (°C) on the x-axis and grams of solute per 100 grams of solvent (g/100g) on the y-axis.
🔍 Note: Remember, solubility can also be influenced by factors like pressure, but the primary focus for solubility curves is temperature.
Recognize the Trends

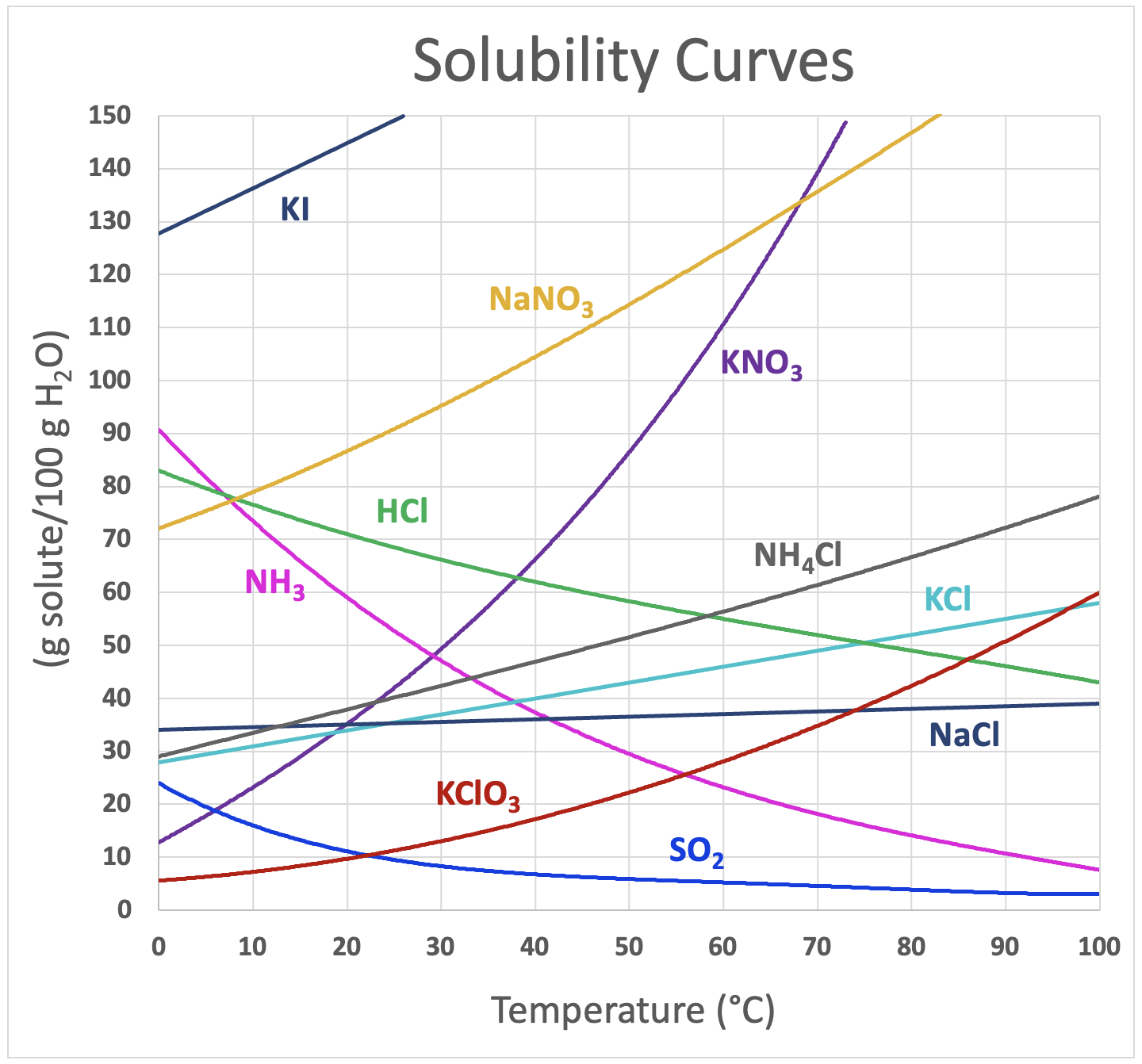
Most solubility curves follow certain trends:
- Positive Slope: For many substances like salts, solubility increases as temperature rises.
- Negative Slope: Some substances (like Ce2(SO4)3) have decreasing solubility with increasing temperature.
- Horizontal Line: For some compounds, solubility does not significantly change with temperature, indicating a constant solubility at varying temperatures.
By recognizing these trends, you’ll be able to predict solubility behaviors and identify anomalies in solubility data more effectively.
Learn the Common Solutes

Familiarize yourself with the solubility behavior of common solutes:
| Solute | Typical Solubility Behavior |
|---|---|
| NaCl (Sodium chloride) | Gradual increase with temperature |
| KNO3 (Potassium nitrate) | Steep increase with temperature |
| LiCl (Lithium chloride) | Increase, but with a curve that can plateau at high temperatures |
| CuSO4 (Copper(II) sulfate) | Moderate increase with temperature |

Knowing these will help you quickly interpret solubility curves and make predictions based on experimental data or theoretical analysis.
Practice Interpolation and Extrapolation
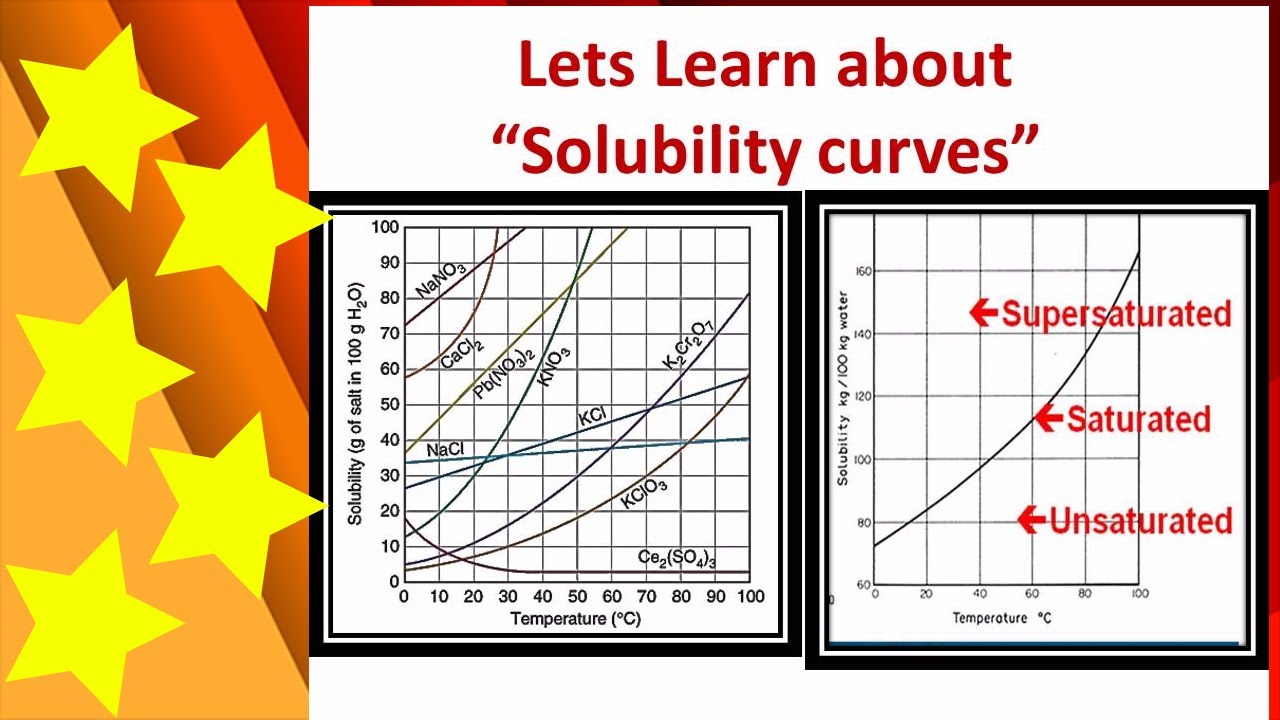
Mastering solubility curves involves understanding how to read, interpret, and extrapolate data:
- Interpolation: Estimate the solubility at a temperature that falls between known data points.
- Extrapolation: Predict the solubility at temperatures beyond the available data.
Here’s how you might approach these skills:
- Start by plotting known solubility points on a graph.
- Use these points to draw a curve that best represents the trend.
- For interpolation, use the curve to estimate solubility at temperatures between the plotted points.
- For extrapolation, extend the curve beyond your data, keeping in mind that this is less reliable due to potential changes in solubility behavior at extreme temperatures.
Utilize Practical Applications
Solubility curves are not just academic exercises; they have real-world applications:
- Crystallization: In the pharmaceutical industry, solubility curves help in determining conditions for crystal formation.
- Water Purification: Understanding how solubility changes with temperature is crucial for removing impurities from water.
- Environmental Science: Analyzing solubility aids in predicting the distribution of chemicals in water systems.
Engaging with these applications can make the study of solubility curves more engaging and relevant, enhancing your retention of the concepts.
By implementing these five tips, you'll find that solubility curves become less of an enigma and more of a tool in your chemistry toolkit. Solubility is not just about numbers and graphs; it's about understanding the interaction between molecules in solutions. From predicting the outcomes of chemical processes to designing experiments, a firm grasp of solubility will serve you well in various scientific endeavors.
What is the significance of the temperature in solubility curves?

+
Temperature plays a crucial role in solubility because it changes the kinetic energy of the solvent and solute particles. As temperature increases, the solubility of most salts increases due to increased molecular movement, allowing more solute to dissolve.
Can solubility curves predict how much solute will dissolve at any temperature?

+
While solubility curves provide a general trend, they are most accurate within the range of data points provided. Extrapolation beyond this range can lead to less reliable predictions as solubility behaviors can change unexpectedly at extreme temperatures.
How do solubility curves help in industrial applications?

+
In industries like pharmaceuticals or water treatment, solubility curves are used to optimize processes like crystallization, where knowing at what temperature a substance starts to crystallize from solution is vital for controlling product purity and yield.