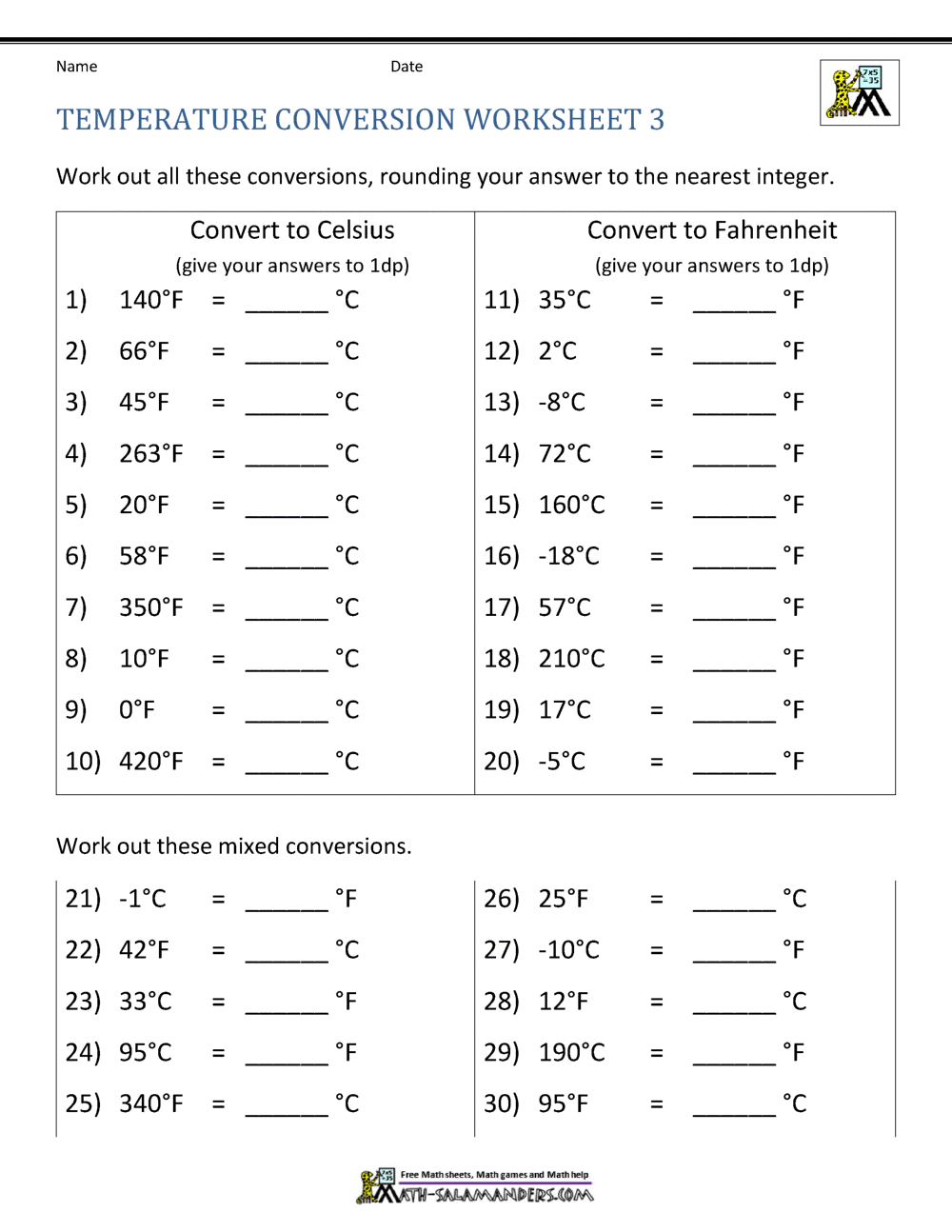
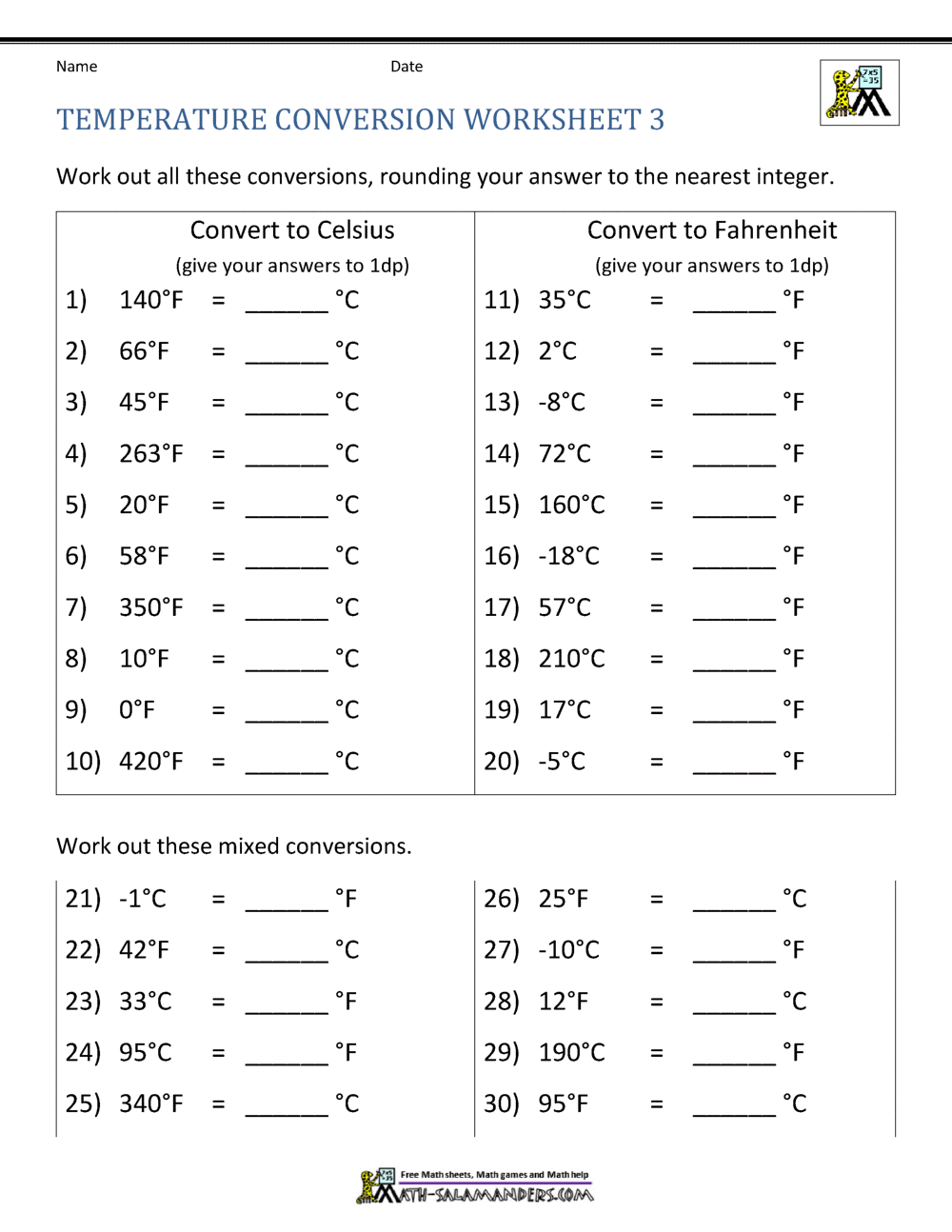
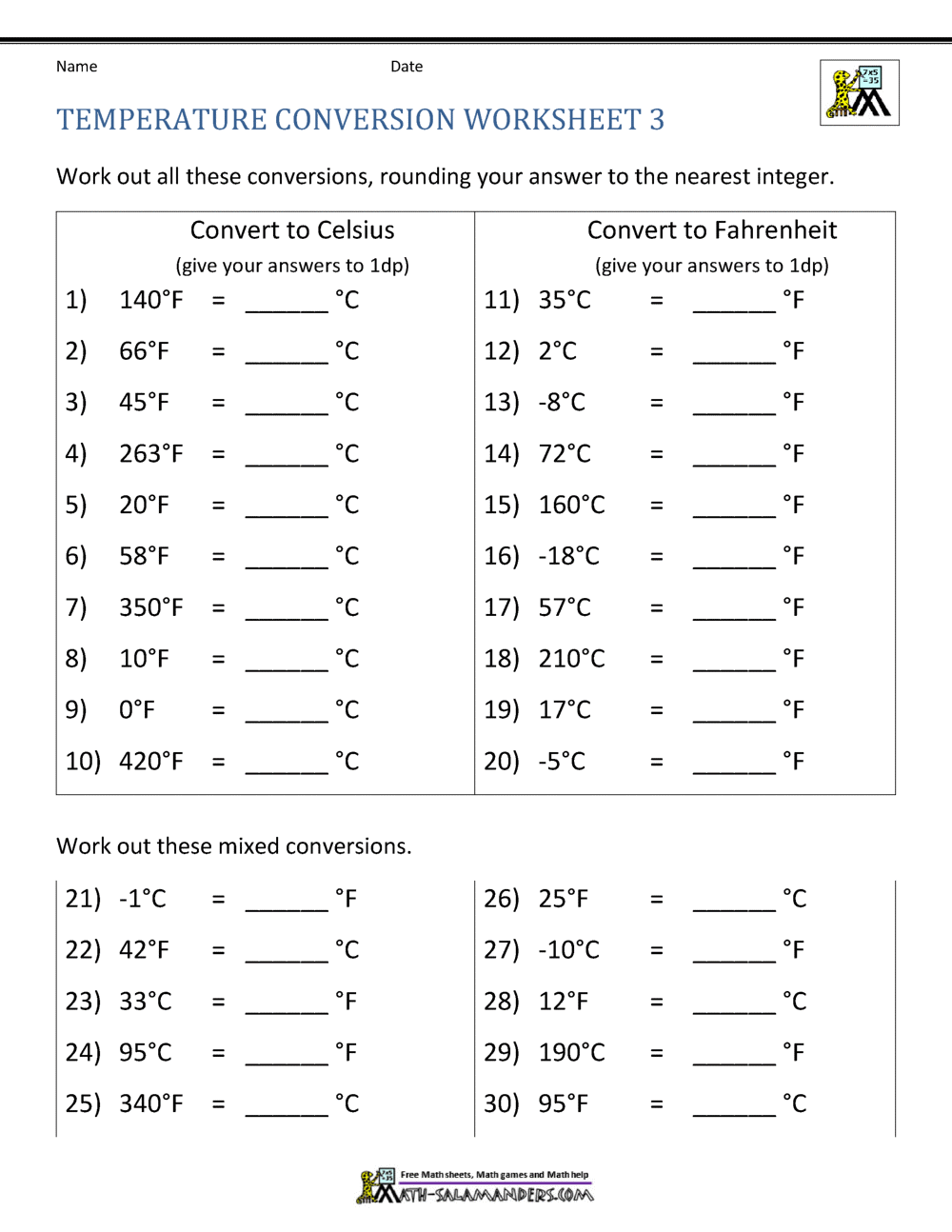
Practice Temperature Conversion Worksheet

Understanding Temperature Conversions

Temperature conversion is an essential skill for students, scientists, and anyone dealing with measurements across different scales. Whether you’re working in a lab, traveling, or just checking the weather forecast, understanding how to convert between degrees Celsius (°C), Fahrenheit (°F), and Kelvin (K) can be very useful. In this blog post, we’ll explore how these scales work, their histories, and practical tips for converting between them.
What Are the Temperature Scales?

- Celsius (°C): Also known as the centigrade scale, Celsius is widely used around the world. It defines the freezing point of water as 0°C and the boiling point as 100°C at standard atmospheric pressure.
- Fahrenheit (°F): Predominantly used in the United States and a few other places, Fahrenheit sets the freezing point of water at 32°F and the boiling point at 212°F.
- Kelvin (K): This is the International System of Units (SI) base unit of thermodynamic temperature. It is absolute zero where molecular motion theoretically stops, making it 0 K. Water freezes at 273.15 K, and boils at 373.15 K.
History Behind Temperature Scales
Each temperature scale has its own origin story:
- Celsius: Created by the Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius in 1742, it originally had 100 degrees between the freezing and boiling points of water, but was later inverted by Carl Linnaeus to make 0°C the freezing point.
- Fahrenheit: Developed by the German physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in 1724, his scale initially set 0°F as the temperature of an ice/salt mixture and 96°F as the average human body temperature.
- Kelvin: Proposed by William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin, in 1848, this scale starts from absolute zero where entropy approaches a minimum.
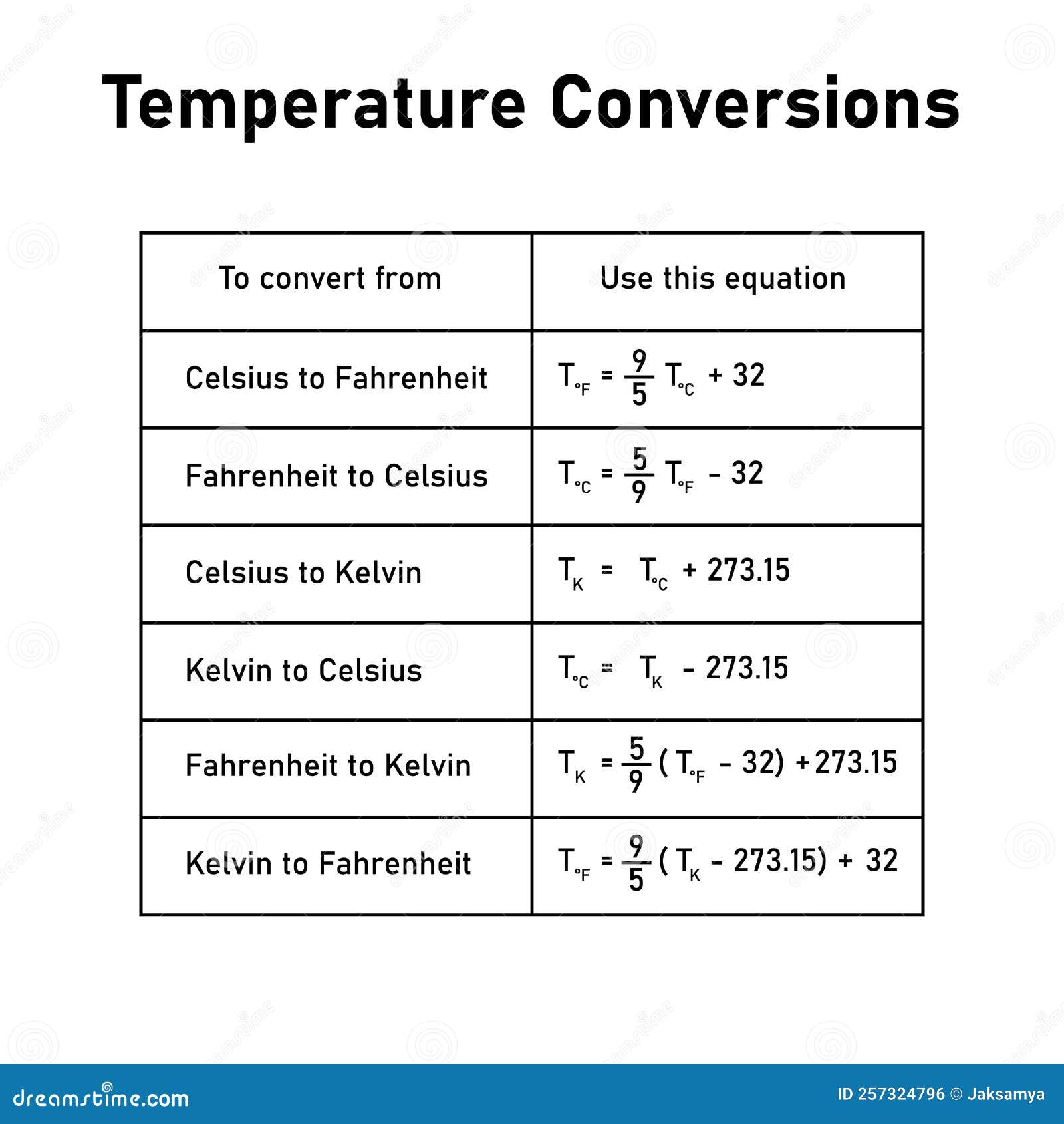
Conversion Formulas

Here are the key formulas for converting between temperature scales:
Celsius to Fahrenheit
°F = (°C × 9⁄5) + 32
Fahrenheit to Celsius

°C = (°F - 32) × 5⁄9
Celsius to Kelvin

K = °C + 273.15
Kelvin to Celsius
°C = K - 273.15
Fahrenheit to Kelvin

K = (°F + 459.67) × 5⁄9
Kelvin to Fahrenheit

°F = K × 9⁄5 - 459.67
📝 Note: When converting between Celsius and Fahrenheit, remember that the freezing point of water is 32°F, which is subtracted or added in the formulas.
Practical Temperature Conversion Steps

Let’s break down the steps for converting temperatures:
Converting Celsius to Fahrenheit
- Multiply the temperature in Celsius by 9⁄5.
- Add 32 to the result to get the Fahrenheit temperature.
Converting Fahrenheit to Celsius

- Subtract 32 from the Fahrenheit temperature.
- Multiply the result by 5⁄9 to get the Celsius temperature.
Converting between Kelvin and Celsius

- To convert from Celsius to Kelvin, add 273.15.
- To convert from Kelvin to Celsius, subtract 273.15.
Converting between Kelvin and Fahrenheit

- To convert from Kelvin to Fahrenheit, subtract 273.15 from K, then multiply the result by 9⁄5 and add 32.
- To convert from Fahrenheit to Kelvin, first convert to Celsius and then to Kelvin.
🔍 Note: When dealing with fractional values, it's best to round off to two decimal places for practical purposes.
Common Temperature Conversions
Here are some common temperatures and their equivalents:
| Condition | Celsius (°C) | Fahrenheit (°F) | Kelvin (K) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Absolute Zero | -273.15 | -459.67 | 0 |
| Freezing Point of Water | 0 | 32 | 273.15 |
| Boiling Point of Water | 100 | 212 | 373.15 |
| Room Temperature | 25 | 77 | 298.15 |

Tips for Quick Mental Conversions

- For approximating Fahrenheit from Celsius: Double the Celsius value, subtract 10% (or 5% for more precision), then add 32. This won’t be exact, but it’s good for a quick estimate.
- For Celsius from Fahrenheit: Subtract 32, then multiply by 5⁄9 or roughly by 0.5556. Remember, this is an approximation.
In wrapping up our journey through temperature conversions, we've learned that while the scales may differ, the principles of conversion are straightforward. Knowing how to switch between Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin not only helps in academic or professional settings but also enriches your understanding of global temperature reports, scientific experiments, and daily weather updates. With these formulas and tips in hand, you're now equipped to tackle any temperature conversion task with confidence.
Why is Kelvin useful in scientific contexts?
+Kelvin is useful because it’s an absolute temperature scale where 0 K represents absolute zero, the theoretical minimum temperature. It’s used in thermodynamics and other scientific fields where the concept of absolute zero is essential.
Can I convert directly from Fahrenheit to Kelvin?
+Yes, you can convert directly using the formula: K = (°F + 459.67) × 5⁄9.
What’s the easiest way to remember temperature conversion?
+The easiest way might be to use mnemonics or quick conversion rules, like “add 32 and multiply by 9⁄5” for °C to °F, or vice versa, “subtract 32 and multiply by 5⁄9” for °F to °C.
Is room temperature the same in all countries?
+No, what is considered “room temperature” can vary by location, building standards, and season. Generally, it ranges from 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) in many places.
How can I quickly estimate Celsius from Fahrenheit?
+Subtract 32, then roughly divide by 2 to get a quick estimate. This isn’t accurate but can give you a ballpark figure.