5 Tips to Master Position-Time Graphs Easily
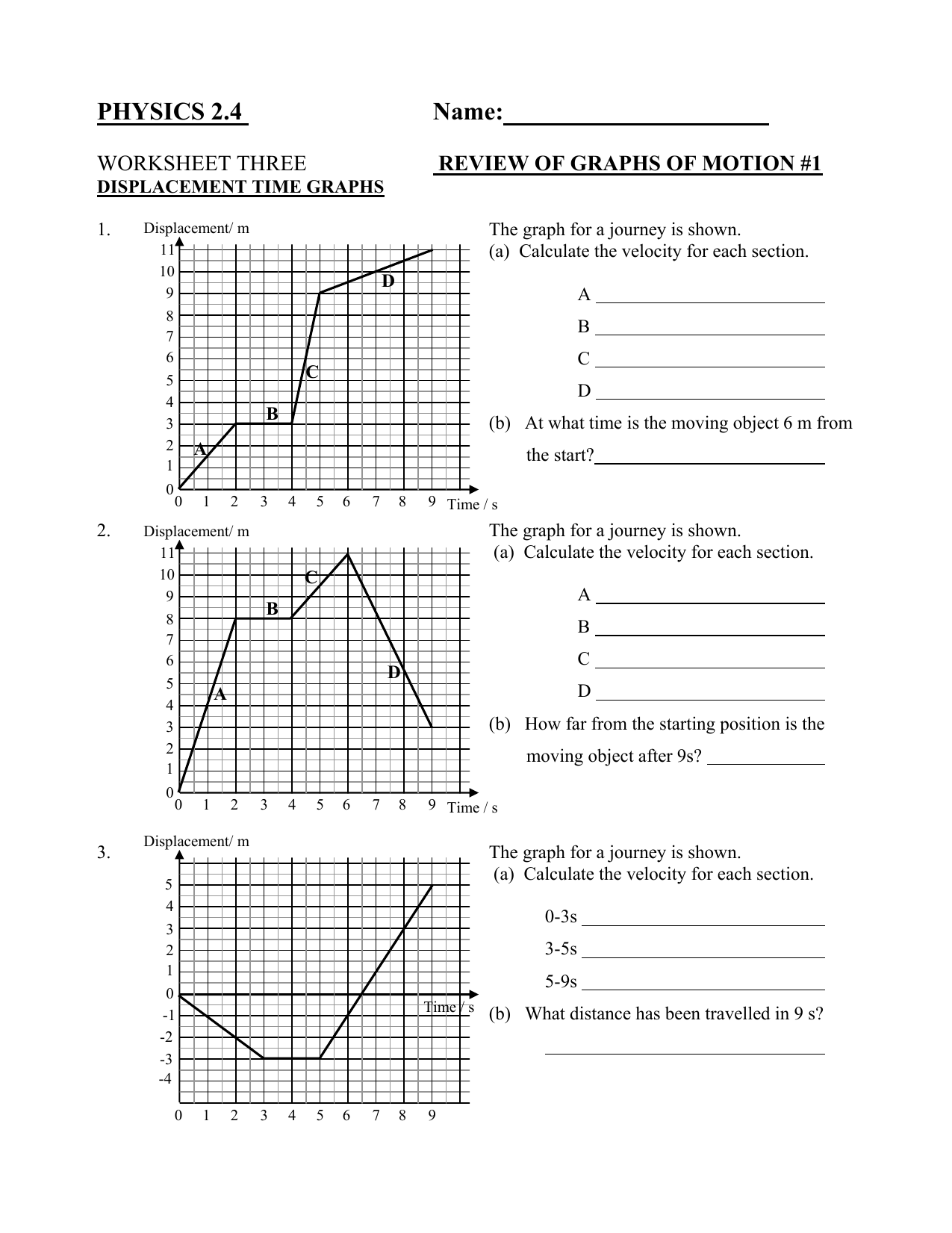
Understanding position-time graphs is crucial for any student or enthusiast of physics. These graphs provide a visual representation of how an object's position changes over time, offering insights into velocity, acceleration, and distance traveled. Here are five essential tips to not only understand but also master position-time graphs with ease:
1. Know Your Axes

Before diving into the specifics of the graph, it’s imperative to understand the axes. The horizontal axis, or x-axis, typically represents time, while the vertical axis, or y-axis, represents the position of the object.
- Time: Measured in seconds (s), minutes, or any other time units.
- Position: Measured in meters (m), kilometers (km), or other units of distance.
The origin of the graph is usually where time and position are both zero. The scale of the graph should be consistent to ensure accurate interpretation.
2. Identify Key Points

Position-time graphs are not just about drawing lines; they are about interpreting the shape of the graph. Here are crucial points to identify:
- Starting Point: Where the object begins its journey.
- End Point: Where the object’s journey ends.
- Intersections: Points where the graph crosses the x-axis or any other significant point.
- Slope: The steepness of the line, which indicates velocity.
- Curve: Changes in the slope, which indicate changes in velocity or acceleration.
By pinpointing these key features, you can quickly grasp the story the graph is telling.
3. Interpret the Slope

One of the most valuable pieces of information provided by a position-time graph is the slope. Here’s how to interpret it:
- A steep slope signifies high velocity.
- A gentle slope means the object is moving slowly.
- A zero slope indicates the object is at rest or not changing its position.
- A positive slope means the object is moving forward.
- A negative slope signifies backward movement.
📝 Note: The slope of the line at any given point equals the instantaneous velocity at that time.
4. Visualize Motion

To truly master position-time graphs, visualization is key. As you look at the graph:
- Imagine the object’s motion: Is it speeding up, slowing down, or maintaining a constant speed?
- Consider the nature of the motion: Is it linear, parabolic, or more complex?
- Draw small scenes or diagrams next to the graph to depict the object’s position at various times.
Visualizing the motion helps you understand the graph’s implications beyond mere numbers and lines.
5. Practice, Practice, Practice

Mastery comes with practice. Here’s how to reinforce your understanding:
- Draw your own graphs: Based on motion descriptions or given data.
- Analyze provided graphs: Try to narrate the object’s journey from the graph.
- Use simulations: Many online tools and apps allow you to simulate motion and see how graphs change.
- Solve problems: Quantitative problems help solidify your understanding of the relationship between time, position, and velocity.
In summary, mastering position-time graphs involves understanding their basic structure, key points, and the significance of the slope. By visualizing the motion and dedicating time to practice, you can deepen your grasp of this fundamental concept in physics. Remember that each graph tells a story of motion, and with these tips, you're well on your way to deciphering any position-time narrative with ease.
Why is understanding position-time graphs important?

+
Understanding position-time graphs is essential as they visually depict how an object moves over time, providing insights into its velocity, acceleration, and overall motion. This knowledge is not only crucial for academic pursuits in physics but also practical applications in engineering, sports science, and technology.
Can an object have a negative position on the graph?

+
Yes, an object can have a negative position on a position-time graph. This indicates that the object is positioned in a direction opposite to the positive axis established by the reference point or coordinate system.
What does a curve in the graph signify?

+
A curve in a position-time graph signifies changing velocity, which could indicate acceleration or deceleration. The curvature of the line reflects the rate at which the velocity is changing.
How can I quickly find the object’s velocity on a position-time graph?

+
To find the object’s velocity on a position-time graph, calculate the slope at any point. If the graph is a straight line, velocity is constant; if it curves, you’ll need to find the instantaneous slope at the desired point using calculus or approximations.
Are position-time graphs useful in real-world applications?

+
Absolutely! Position-time graphs are used in real-world applications such as analyzing traffic flow, GPS tracking, ballistics, and sports analytics to understand player movements. They provide essential information on how objects or people move through space over time.