Polyatomic Ions Worksheet: Answer Key & 5 Essential Tips
Welcome to our in-depth exploration of polyatomic ions, a fundamental concept in chemistry that can be both challenging and intriguing. Polyatomic ions are ions composed of two or more atoms covalently bonded together, which carry a net charge. Understanding these ions is crucial for students at various levels of education due to their pivotal role in chemical reactions, molecular composition, and overall understanding of chemistry. This blog post will delve into the key points regarding polyatomic ions, offer a comprehensive worksheet answer key, and provide essential tips for mastering this topic.
What Are Polyatomic Ions?

Polyatomic ions, as the name suggests, are collections of atoms bonded together that carry a collective charge. Here are some basic points:
- They act as a single unit in chemical reactions despite containing multiple atoms.
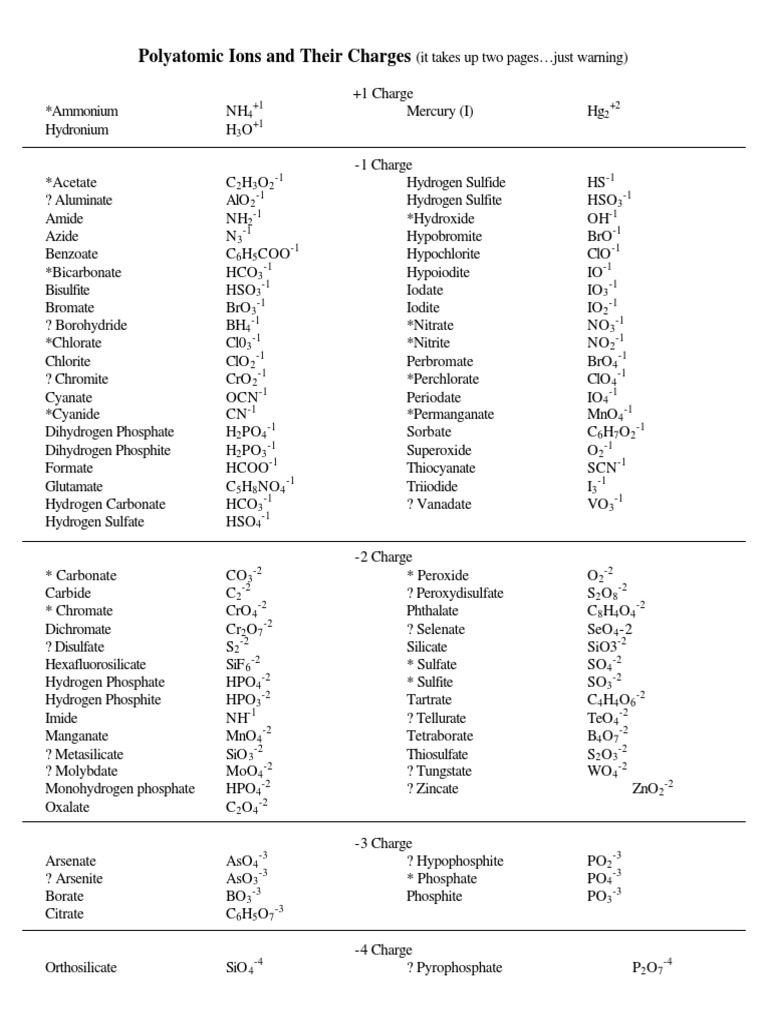
- Common examples include ammonium (NH4+), nitrate (NO3-), and sulfate (SO42-).
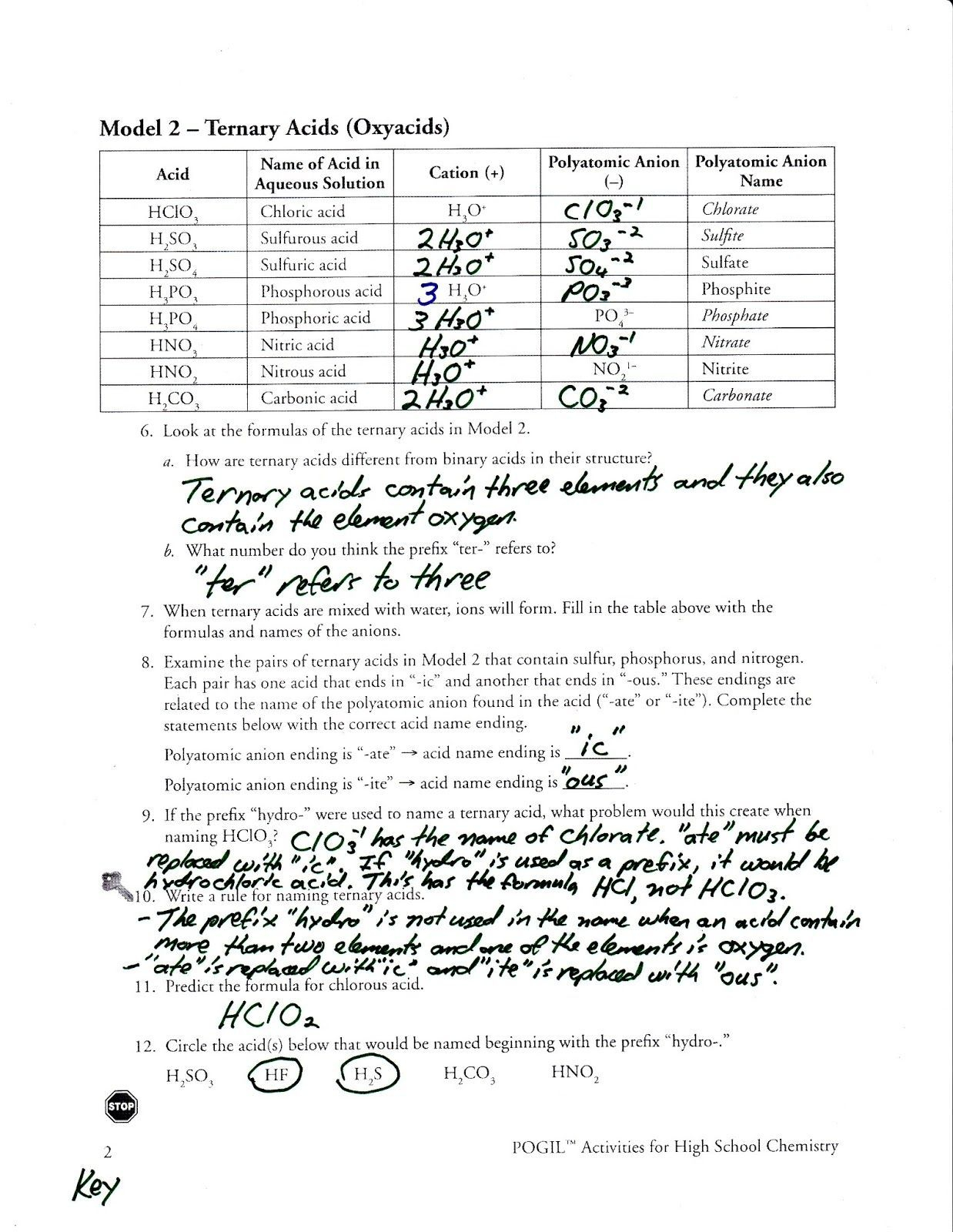
- Unlike monatomic ions like Na+ or Cl-, they have complex structures that require you to memorize or derive their names, formulas, and charges.

Why Polyatomic Ions Matter in Chemistry

- Chemical Bonding: Polyatomic ions play a crucial role in ionic bonding where they often bond with monatomic ions to form compounds.
- Chemical Equations: They are key players in balancing equations, as they must be considered as whole units.
- Reactivity: Their charge distribution influences how they interact with other ions or molecules.

Answer Key for Polyatomic Ions Worksheet

Here’s a brief answer key for a typical polyatomic ions worksheet, focusing on identification, naming, and charge:
| Name | Formula | Charge |
|---|---|---|
| Ammonium | NH4 | +1 |
| Nitrate | NO3 | -1 |
| Sulfate | SO4 | -2 |

📌 Note: This answer key provides a simplified example. Actual worksheets might include more complex polyatomic ions or require different exercises.
5 Essential Tips for Mastering Polyatomic Ions

- Memorize the Basics: Start with common ions, their formulas, and charges. Use flashcards or mnemonic devices to aid memory.
- Visualize Structures: Understand the molecular structure. This can help in deducing charges and naming conventions.
- Practice Naming: Regularly practice naming compounds with polyatomic ions to become familiar with their patterns.
- Balance Equations: Polyatomic ions often need to be treated as a single entity when balancing chemical equations. This skill is essential for chemistry problems.
- Utilize Patterns: Many polyatomic ions follow similar naming patterns or have recognizable suffixes (-ate, -ite, -ide). Recognizing these patterns can aid in learning new ions.
In summary, polyatomic ions are a complex yet fascinating part of chemistry that connects atomic structure, bonding, and reaction behavior. By understanding their nature, memorizing key examples, and applying the tips provided, you'll be well on your way to mastering this essential topic. Remember, consistent practice, pattern recognition, and understanding the fundamental reasons behind their properties are your best tools for success in chemistry.
What makes a polyatomic ion different from a monatomic ion?

+
A polyatomic ion contains multiple atoms bonded together with a collective charge, while a monatomic ion consists of a single atom with a charge. Polyatomic ions maintain their structural integrity in chemical reactions.
Can polyatomic ions change their charge?

+
Yes, under certain conditions like redox reactions, polyatomic ions can gain or lose electrons, thereby changing their charge. However, this is less common than with monatomic ions due to their covalent bonding.
How do I memorize polyatomic ions effectively?
+
Flashcards, pattern recognition in naming conventions, and associating names with their charges or uses can help in memorizing polyatomic ions. Also, understanding the logic behind their formation aids in retention.
Why are polyatomic ions important in environmental chemistry?

+
They are crucial in processes like the nitrogen and sulfur cycles, affecting soil acidity, water quality, and air pollution. Understanding their behavior helps in managing environmental impacts and pollution.