5 Essential Polyatomic Ions You Must Know

Polyatomic ions, the charged particles composed of more than one atom, play a crucial role in chemistry, particularly in understanding and predicting the behavior of various compounds. These molecular ions can significantly influence the properties of substances, their reactions, and their interactions with other chemicals. In this blog post, we delve into five of the most essential polyatomic ions that every student of chemistry should know, understand, and recognize. From common compounds found in everyday life to those critical in scientific research, these ions are fundamental for anyone looking to expand their chemical knowledge.
What are Polyatomic Ions?

Polyatomic ions are molecular ions that consist of two or more atoms covalently bonded together, with a net electric charge. This charge results from an imbalance in the number of protons and electrons in the structure. Here are some key points to remember about polyatomic ions:
- Covalent Bonds: The atoms within these ions share electrons through covalent bonds.
- Charge Distribution: The net charge can be positive or negative, influencing how the ion interacts with other molecules or ions.
- Ionic Compounds: Polyatomic ions often form part of ionic compounds where they act as single units, bonding with other ions to balance the charges.
- Reactivity: Their chemical behavior can be quite different from their constituent atoms due to the distribution of charge across the ion.
The Five Essential Polyatomic Ions

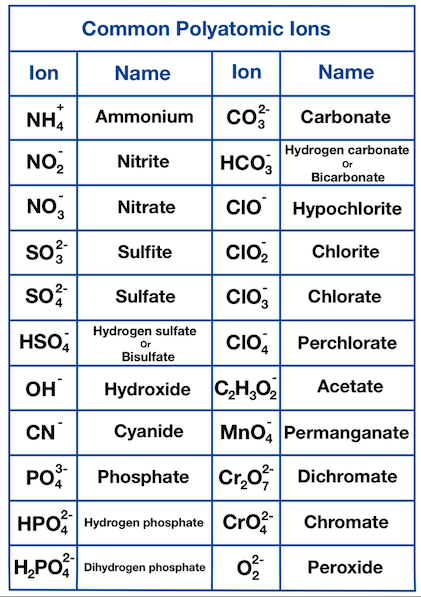
1. Ammonium (NH₄⁺)


The ammonium ion is a common positively charged polyatomic ion formed when an ammonia molecule (NH₃) gains an extra hydrogen atom and becomes positively charged. Here are some vital facts:
- Charge: +1
- Structure: Tetrahedral shape with a nitrogen atom at the center surrounded by four hydrogen atoms.
- Applications: Used in fertilizers (such as ammonium nitrate), cleaning agents, and in many industrial processes.
- Reactivity: It acts as a weak acid, capable of donating a proton (H⁺) in aqueous solutions.
💡 Note: The ammonium ion is vital in biological systems, contributing to the nitrogen cycle by converting ammonia into less toxic forms.
2. Hydroxide (OH⁻)


The hydroxide ion, known for its role in bases and alkaline solutions, is an anion comprising a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to an oxygen atom. Here are its properties:
- Charge: -1
- Structure: Linear, with oxygen sharing electrons with hydrogen in a single covalent bond.
- Applications: Essential in creating soaps, detergents, and many cleaning agents due to its basic properties.
- Reactivity: Hydroxide ions can accept protons (H⁺), making solutions basic or alkaline.
3. Nitrate (NO₃⁻)

The nitrate ion is a common anion found in fertilizers and plays a critical role in plant nutrition. Key details include:
- Charge: -1
- Structure: Trigonal planar with a nitrogen atom at the center surrounded by three oxygen atoms.
- Applications: Used in fertilizers, explosives, and as preservatives in cured meats.
- Reactivity: It's an oxidizing agent and can undergo reduction to form nitrogen gas.
🌱 Note: Nitrates are integral for plant growth, converting to ammonium and then to amino acids.
4. Sulfate (SO₄²⁻)


Sulfate is a widely encountered polyatomic ion, particularly in environmental chemistry due to its role in acid rain formation. Here's what you need to know:
- Charge: -2
- Structure: Tetrahedral with a sulfur atom in the center surrounded by four oxygen atoms.
- Applications: Present in detergents, paper, dyes, and pharmaceuticals.
- Reactivity: Can form salts when combined with cations or protons, making sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄).
5. Phosphate (PO₄³⁻)

Phosphate ions are crucial in biological systems for energy transfer and structural components. Key points include:
- Charge: -3
- Structure: Tetrahedral with a phosphorus atom at the center surrounded by four oxygen atoms.
- Applications: Found in DNA, RNA, ATP (adenosine triphosphate), and as a fertilizer component.
- Reactivity: Forms multiple bonds, often with metals or hydrogen, playing key roles in biochemistry.
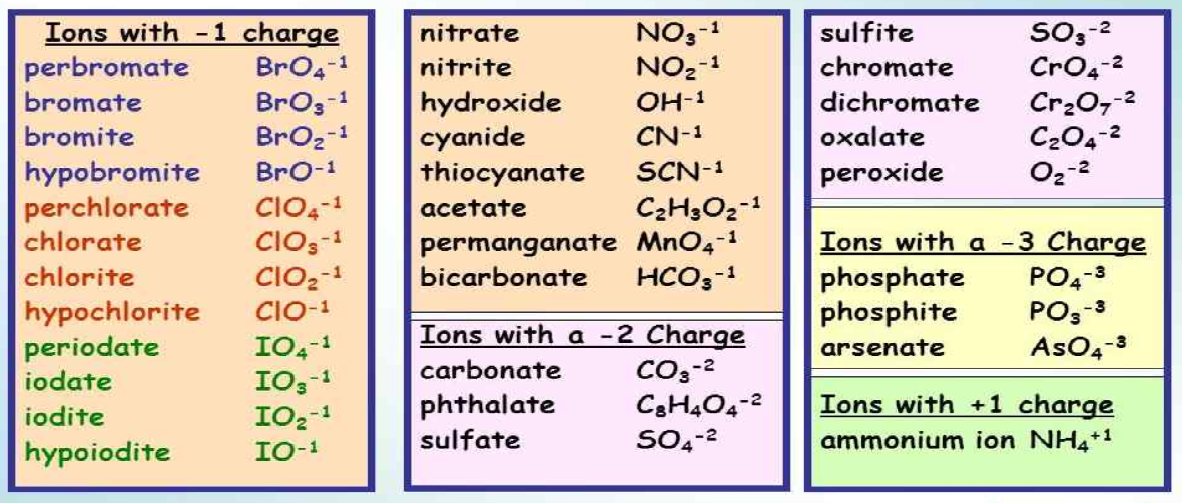
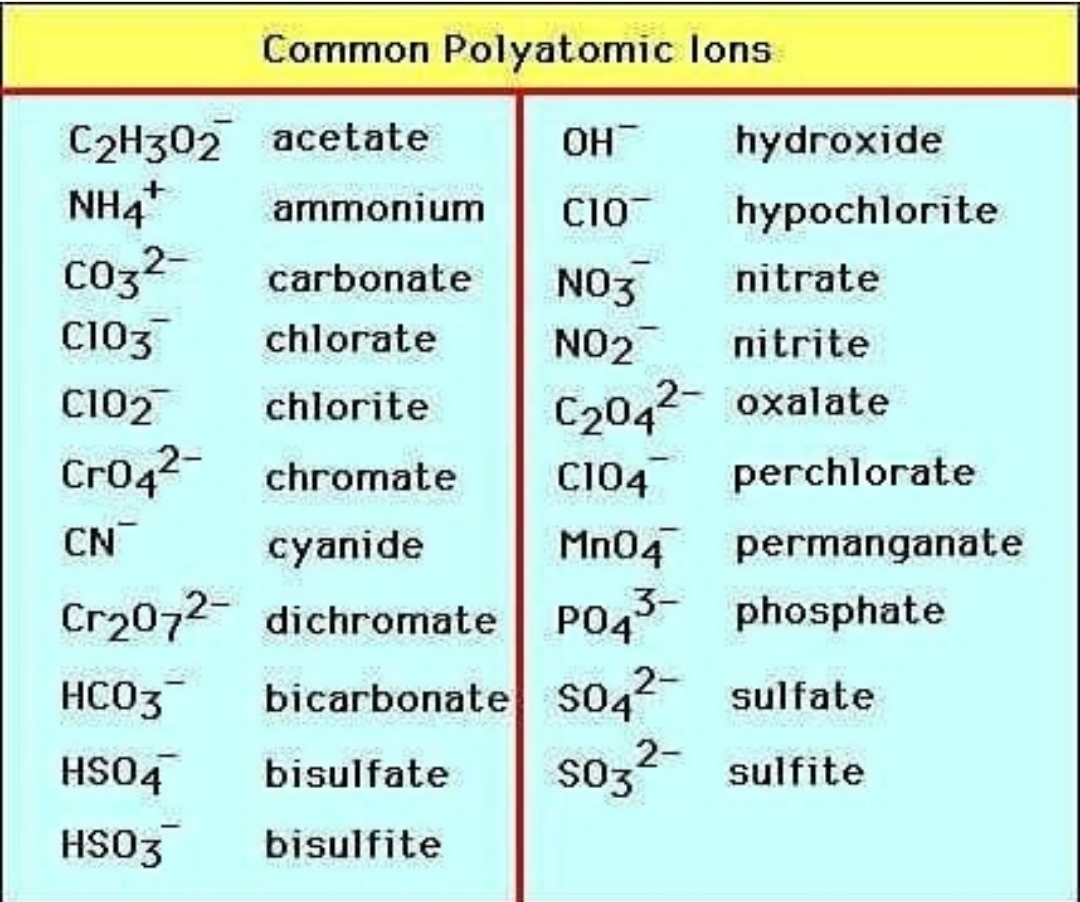
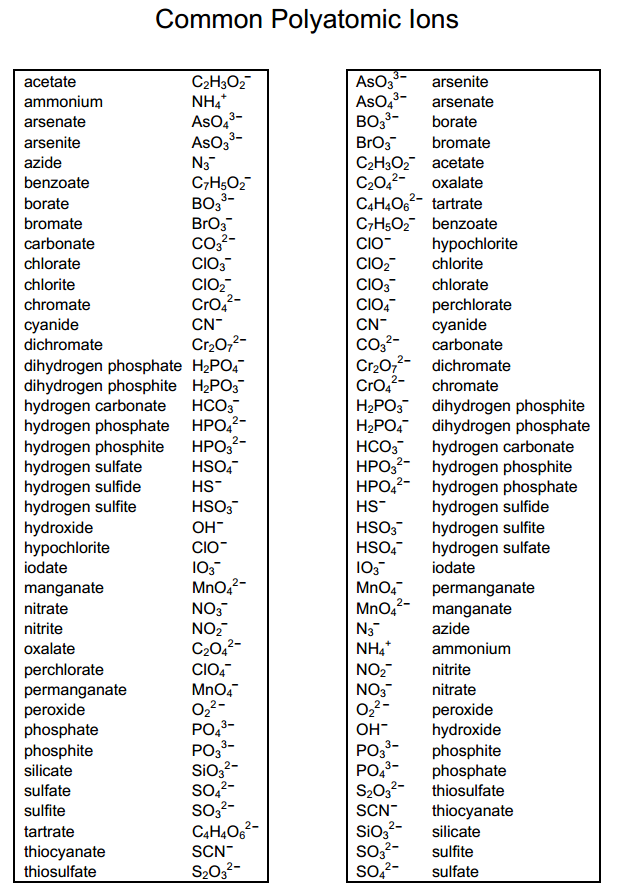
| Polyatomic Ion | Formula | Charge | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ammonium | NH₄⁺ | +1 | Fertilizers, cleaning agents |
| Hydroxide | OH⁻ | -1 | Soaps, bases, detergents |
| Nitrate | NO₃⁻ | -1 | Fertilizers, explosives |
| Sulfate | SO₄²⁻ | -2 | Detergents, pharmaceuticals |
| Phosphate | PO₄³⁻ | -3 | Biological systems, fertilizers |

Understanding these polyatomic ions helps in comprehending chemical reactions, predicting the behavior of compounds, and applying chemical knowledge practically. Each of these ions has unique properties and uses, illustrating the diversity and complexity of chemical species.
The Importance of Polyatomic Ions in Chemistry

Polyatomic ions are more than just theoretical constructs; they are key players in both industrial processes and biological systems. They influence:
- Solubility: Polyatomic ions can alter the solubility of salts, affecting how these compounds dissolve in water.
- Reaction Pathways: Their charge and structure can direct the course of chemical reactions, influencing reaction rates and products.
- Electrical Conductivity: In solutions, polyatomic ions facilitate the movement of electric charges, making them vital for battery technology.
- Environmental Impact: From acid rain (sulfates) to nutrient overloads (nitrates), polyatomic ions affect the environment in profound ways.
Knowing these ions is not just academic; it's practical for:
- Engineers who work with materials and reactions
- Biologists studying metabolic pathways
- Environmental scientists tackling pollution
- Pharmacologists developing new drugs
These polyatomic ions are building blocks in the vast and intricate world of chemistry, bridging simple atoms into complex compounds, shaping our understanding of nature, and even influencing technological advancements.
By mastering the properties, structures, and applications of these five essential polyatomic ions, chemists and students alike gain invaluable insights into the world of chemistry, enabling them to better understand, manipulate, and predict chemical reactions.
What are polyatomic ions?

+
Polyatomic ions are charged particles made up of more than one atom, where the charge is not equal to zero. These ions often form part of larger molecular compounds and are essential in understanding chemical behavior.
Why are polyatomic ions important in everyday life?

+
Polyatomic ions appear in various forms of daily life: from cleaning agents, fertilizers, to even our own biochemical processes. Understanding them helps us in handling chemicals safely and utilizing them effectively for daily needs.
Can polyatomic ions react with each other?
+
Yes, polyatomic ions can indeed react with each other or with other substances. These reactions can lead to the formation of salts, acids, or bases, significantly altering the properties and behaviors of the compounds involved.
How do I remember the charges of polyatomic ions?
+
Using mnemonic devices, flashcards, or practice problems can help. Also, understanding the oxidation states of common elements and how they combine to form polyatomic ions can make remembering charges easier.
What role do polyatomic ions play in environmental chemistry?

+
Polyatomic ions like sulfates, nitrates, and phosphates influence environmental chemistry significantly. They can contribute to problems like acid rain, nutrient overload in ecosystems, and help in geochemical cycles like nitrogen and sulfur cycles.