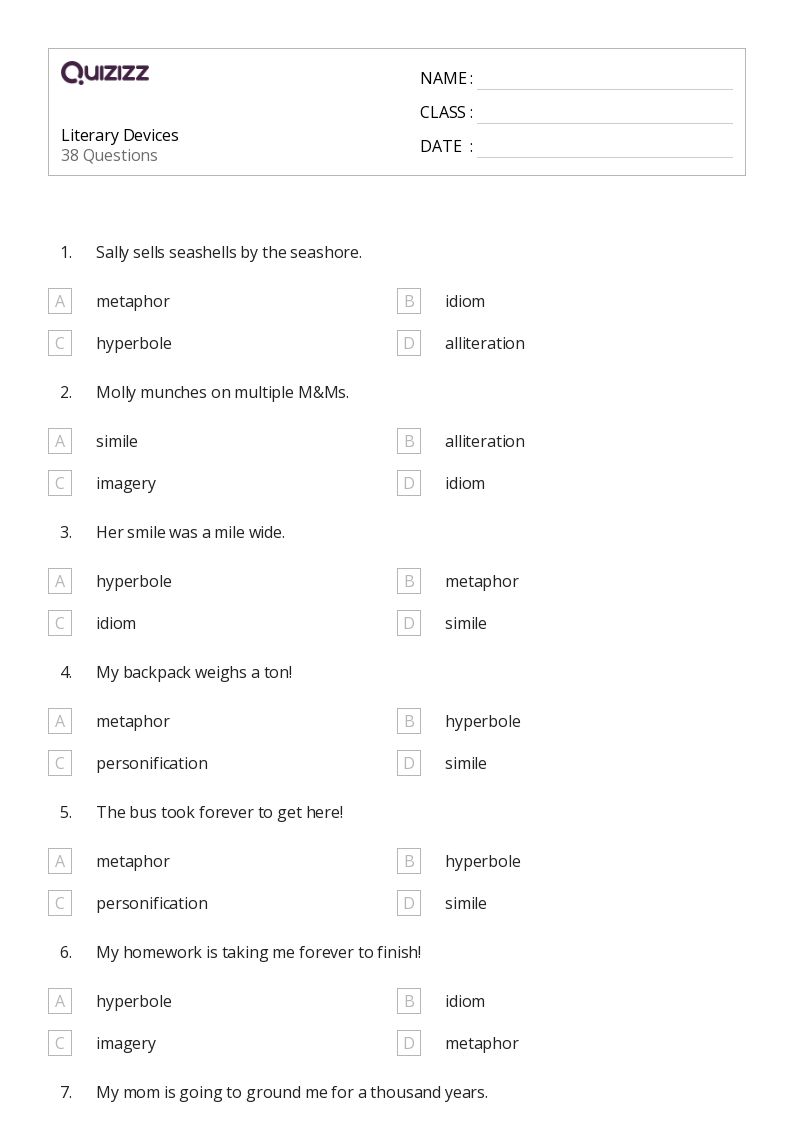
Poetic Devices Worksheet 2: Unveiling the Answers

Poetry, with its rhythmic cadence and unique structure, often employs a variety of poetic devices to enrich meaning and offer a deeper experience for the reader. Today, we're exploring these devices through a dedicated worksheet, aiming to not only demystify them but also to illustrate their importance in understanding poetry at a deeper level. Let's embark on this enlightening journey together.
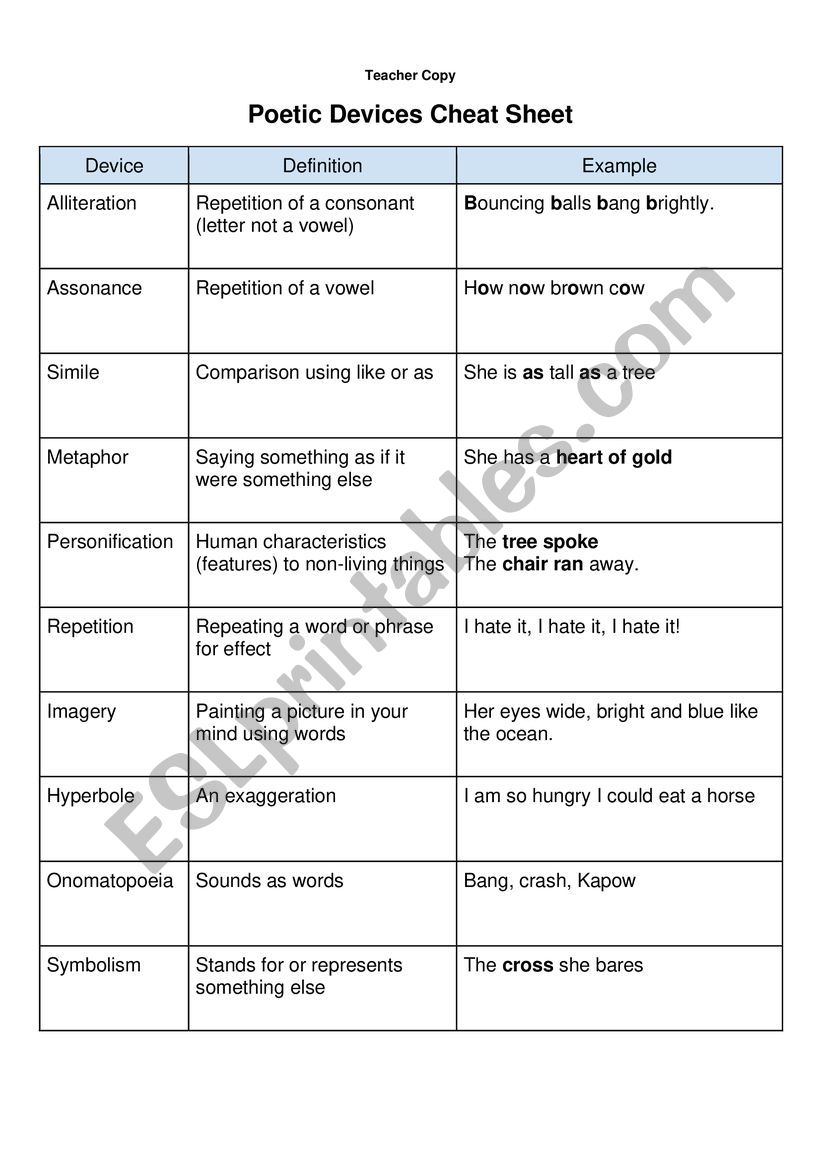
Understanding Poetic Devices

Poetic devices are tools poets use to craft their work, giving it texture, depth, and a distinct voice. Here are some common devices:
- Simile: A comparison between two distinct things using “like” or “as.”
- Metaphor: Direct comparison without “like” or “as.”
- Personification: Giving human qualities to inanimate objects or non-human entities.
- Alliteration: The repetition of initial consonant sounds in consecutive or closely positioned words.
- Assonance: Repetition of vowel sounds within words.
- Consonance: The repetition of consonant sounds, typically within or at the end of words.
Worksheet Analysis

We’re diving into a worksheet designed to hone your understanding of these devices. Here are some examples to work through:
Example 1: Simile

Her eyes sparkled like diamonds in the sun.
This line uses a simile to compare the sparkle of someone’s eyes to diamonds. This device helps the reader visualize the intensity and beauty of the eyes, making the description more vivid.
Example 2: Metaphor

The world is a stage, where everyone has their part to play.
Here, the world is directly compared to a stage, suggesting life is a performance. This metaphor invites readers to consider their roles and interactions in life.
Example 3: Personification

The wind howled in anger through the night.
By personifying the wind, the poet conveys not only its ferocity but also the emotional impact of the storm, adding a layer of intensity to the poem.
Example 4: Alliteration

Peter Piper picked a peck of pickled peppers.
This tongue twister showcases alliteration with the repeated ‘p’ sound, creating a rhythmic and fun reading experience.
Example 5: Assonance

Try as I might, the light seems to elude my sight.
The repetition of the ‘i’ sound adds musicality and subtly emphasizes the longing for light, enhancing the emotional effect.
Enhancing Poetic Interpretation
Understanding these devices isn’t just about naming them; it’s about seeing how they contribute to the poetry’s overall effect:
- Imagery: Devices like simile, metaphor, and personification create vivid mental images, making the poem come alive for the reader.
- Mood and Tone: Alliteration, assonance, and consonance can set the mood, from playful to melancholy, influencing how readers perceive the poem’s emotions.
- Rhythm and Sound: Through sound devices, poets can manipulate the poem’s rhythm, which can mimic natural speech patterns, echo emotions, or highlight important themes.
📖 Note: Engaging with poetic devices enhances your ability to appreciate and analyze poetry, deepening your connection with literary works.
To summarize our exploration, recognizing and understanding poetic devices like simile, metaphor, personification, alliteration, assonance, and consonance is crucial in unlocking the full spectrum of poetry's charm. They not only enrich the text's meaning but also evoke sensory experiences, emotions, and make the reading or listening experience immersive. Poets craft their work with these tools to guide, surprise, and connect with their audience. As readers, when we become adept at spotting and interpreting these devices, we engage more deeply with the poetry, savoring its complexity and beauty. This deeper engagement allows for a more profound appreciation of literary artistry, turning the act of reading poetry into an enriching, multi-sensory journey through language.
What is the difference between simile and metaphor?

+
A simile uses “like” or “as” to make a comparison (e.g., “as fast as a cheetah”), whereas a metaphor directly states that something is something else (e.g., “time is a thief”).
Why do poets use personification?

+
Poets use personification to give human traits to non-human elements, which helps in creating vivid imagery, engaging readers emotionally, and often making abstract concepts more relatable.
Can one poem use multiple poetic devices?
+
Yes, poets often layer their work with several poetic devices to create rich, multi-dimensional poems. For instance, alliteration might be combined with imagery or metaphors to enhance the poem’s impact.