Plate Boundaries Unveiled: 5 Essential Worksheet Answers

Understanding the movement and interaction of plate boundaries is pivotal in grasping the dynamic nature of our planet’s surface. Plate tectonics, the theory that Earth’s lithosphere is broken into tectonic plates that move, has been instrumental in explaining various geological phenomena such as earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountain building. Here, we’ll explore five essential worksheet questions and answers that help demystify these boundaries.
What Are Plate Boundaries?

Plate boundaries are the edges where two tectonic plates meet. They can be thought of as the seams where Earth’s crust is either being created, destroyed, or transformed. Here are the three primary types:
- Divergent Boundaries: Plates move away from each other. This is where new crust is created from magma that rises from the mantle. The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is a classic example.
- Convergent Boundaries: Plates move towards each other. This interaction can lead to subduction zones where one plate sinks beneath another, or to the collision of continents, forming mountain ranges like the Himalayas.
- Transform Boundaries: Plates slide past each other horizontally. This movement often causes significant earthquakes due to the friction between plates, as seen with the San Andreas Fault in California.
🌍 Note: While these are the primary types, not all plate boundaries fit neatly into these categories; there are also examples of more complex interactions.
How Do Plate Boundaries Affect the Surface?
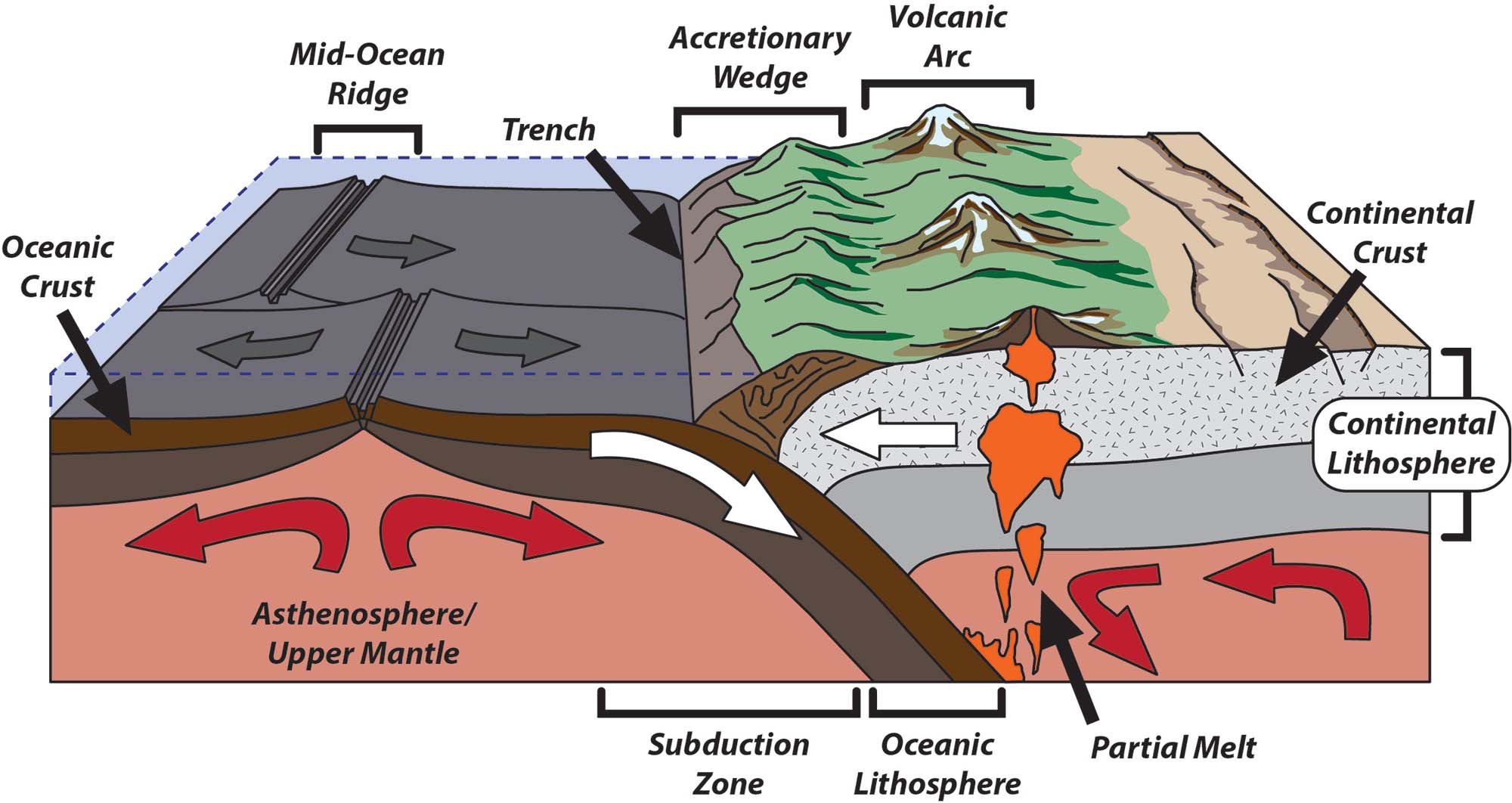
Plate boundaries are directly responsible for shaping our planet’s surface in profound ways:
- Earthquakes: The movement along these boundaries often results in earthquakes due to the sudden release of built-up strain. For instance, at transform boundaries, the plates slip and slide past each other, causing seismic activity.
- Volcanoes: Most of Earth's volcanoes occur at convergent and divergent boundaries. Volcanic activity is a direct consequence of plates moving apart at mid-ocean ridges or where one plate is forced under another.
- Mountain Formation: Where plates collide, the earth buckles, folds, and uplifts, creating mountain ranges. The Himalayas, formed from the convergence of the Indian and Eurasian plates, showcase this dramatic effect.
How Do Plate Boundaries Impact Human Life?

The impact of plate tectonics on human life is both direct and indirect:
- Natural Hazards: Living near plate boundaries increases the risk of experiencing earthquakes, tsunamis, and volcanic eruptions, which can be catastrophic.
- Economic Resources: These boundaries are hotspots for minerals and fuels. For example, many gold deposits are found in areas with extensive faulting due to plate tectonics.
- Climate and Ecosystems: Tectonic activity influences topography, which in turn affects climate, weather patterns, and ecosystems. Mountain ranges can block monsoon winds or create rain shadows.
🔍 Note: While plate boundaries pose risks, they also provide invaluable resources. Understanding these dynamics aids in risk mitigation and resource exploration.
How Can We Study Plate Boundaries?
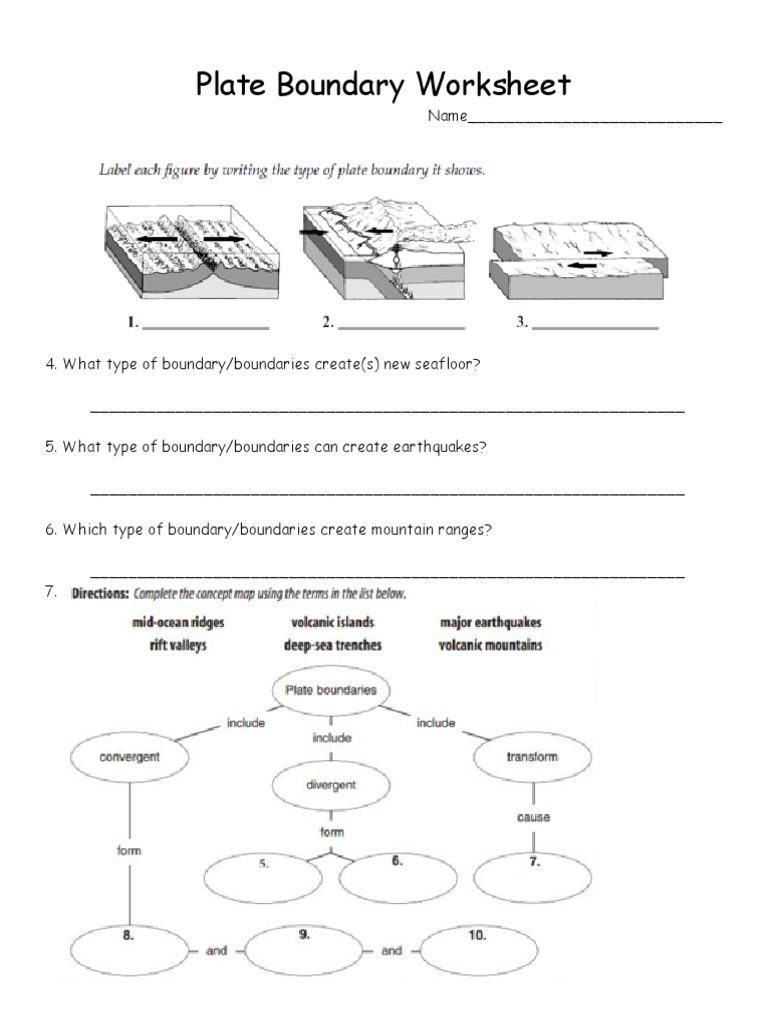
Researchers employ several methods to study plate boundaries:
- Seismology: By studying seismic waves from earthquakes, scientists can map plate boundaries and understand what happens at these margins.
- GPS Data: Continuous GPS measurements give precise data on plate movement, helping to predict future plate interactions.
- Paleomagnetism: Studying the Earth's magnetic field preserved in rocks helps in understanding the historical movement of plates.
- Remote Sensing: Satellites and aircraft equipped with sensors provide real-time data on ground deformation at plate boundaries.
| Method | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Seismology | Analyzing seismic waves from earthquakes | Magnitude and depth analysis, seismic wave velocity changes |
| GPS Data | Tracking movement with global positioning systems | Real-time deformation of the Earth's surface |
| Paleomagnetism | Studying magnetic signatures in rocks | Paleomagnetic stripes on the ocean floor |
| Remote Sensing | Using satellite and aerial technology for data collection | Topographic and thermal mapping |

In summary, plate boundaries are not just lines on a map; they are dynamic zones where the Earth’s crust is in a constant state of flux. Understanding these interactions helps us prepare for natural disasters, explore new resources, and comprehend the evolution of our planet’s surface over geological time scales.
Through these methods, we gain insights into how continents have moved, mountains have risen, and oceans have formed. This knowledge not only enriches our understanding of the Earth’s history but also guides us in managing our planet’s future.
What is the difference between a convergent and divergent plate boundary?
+
At convergent boundaries, plates move towards each other, leading to the creation of mountain ranges, subduction zones, and volcanic arcs due to one plate being forced under another. At divergent boundaries, plates move apart, allowing magma to rise from the mantle and create new crust, typically seen at mid-ocean ridges.
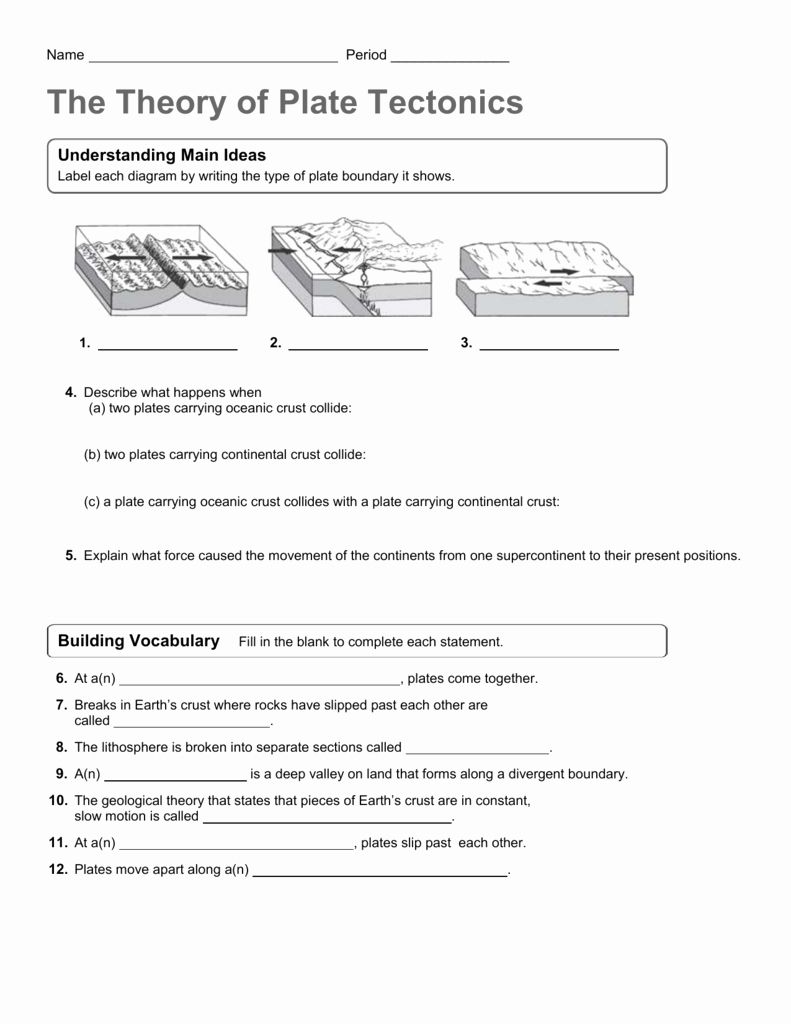
How do plate boundaries contribute to natural disasters?
+
Plate boundaries are often the sites of significant seismic and volcanic activity, leading to natural disasters like earthquakes, tsunamis, and volcanic eruptions. The interaction at these boundaries releases stored energy, causing the ground to shake, volcanoes to erupt, or, in coastal regions, tsunamis to form.
Can we predict earthquakes or volcanic eruptions?

+
Predicting specific earthquakes with precision is currently impossible, though areas prone to seismic activity due to known plate boundaries can be monitored. Volcanic eruptions can be forecasted with more accuracy due to signs like increased seismic activity, gas emissions, and ground deformation.
Why is studying plate boundaries important for resource exploration?

+
Plate boundaries are rich in geological activity, which often results in the concentration of valuable mineral resources. For example, many deposits of gold, copper, and other minerals are found along fault lines or in areas with volcanic activity.
How have plate tectonics shaped the Earth’s geography?

+
Plate tectonics have directly influenced the formation of continents, the rise of mountain ranges, the creation and destruction of ocean basins, and even climate patterns due to the resultant changes in geography. For instance, the collision of continents has formed mountain ranges like the Alps and the Himalayas.