Plant and Animal Cell Diagrams: Educational Worksheet Fun

Exploring the microscopic world of cells is a fantastic way to delve into the wonders of biology. Whether you're a student, a teacher, or simply curious about life's building blocks, understanding plant and animal cell diagrams can illuminate how organisms function at their most basic level. In this educational worksheet, we'll explore both types of eukaryotic cells through diagrams, learning to identify their structures and understand their functions.
Understanding Plant Cell Structure

The plant cell, a prime example of eukaryotic cell complexity, features several unique structures that distinguish it from its animal counterpart:
- Cell Wall: Made of cellulose, this structure provides structural support and rigidity, helping the plant withstand environmental pressures.
- Chloroplasts: These organelles contain chlorophyll, enabling photosynthesis where light energy is converted into chemical energy stored in sugars.
- Vacuole: Often large and singular, the central vacuole in plant cells stores water, nutrients, and waste, also maintaining turgor pressure.

Understanding Animal Cell Structure
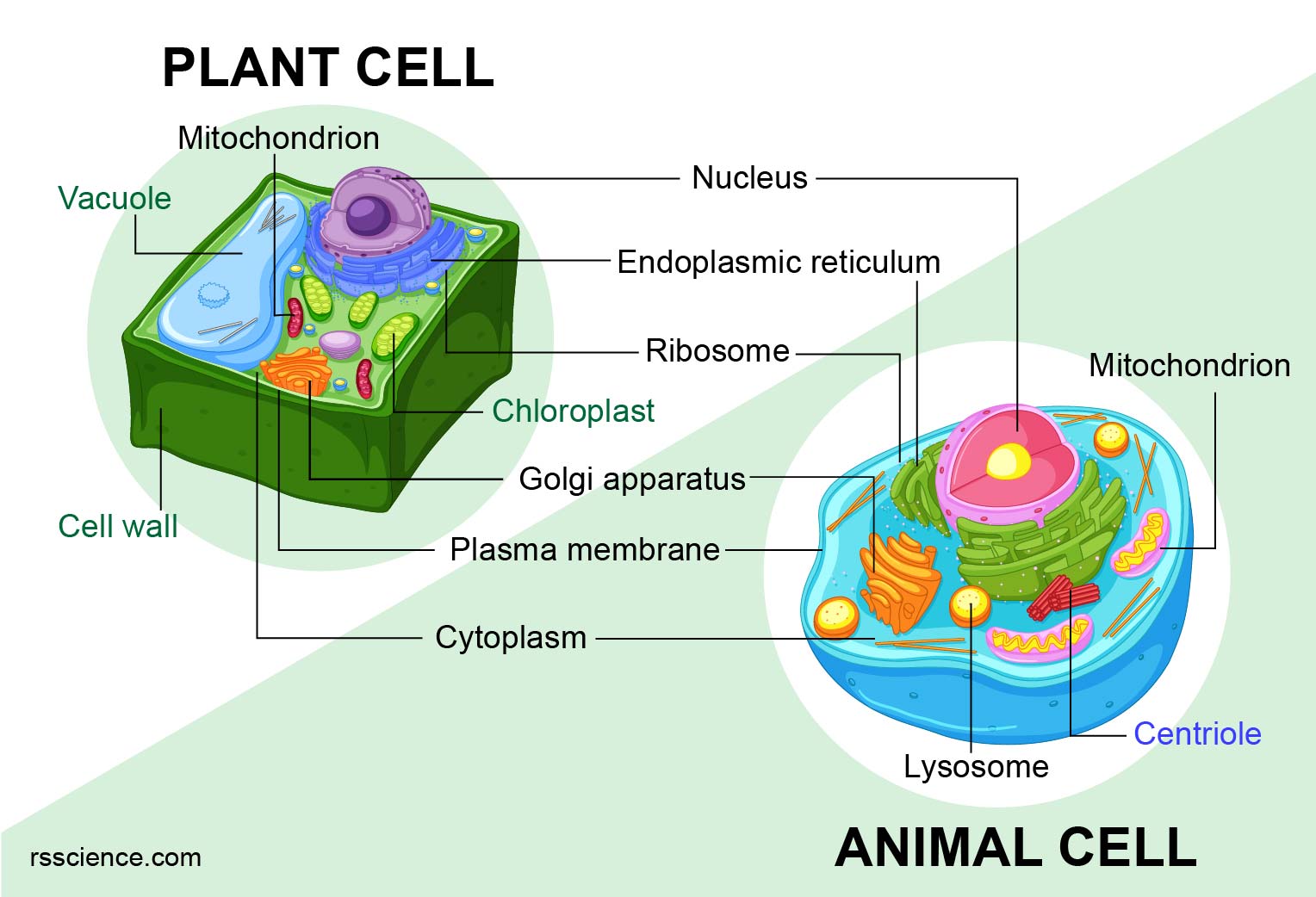
Animal cells share many components with plant cells, but they lack certain specialized structures:
- No Cell Wall: Animal cells only have a plasma membrane, allowing for greater flexibility in cell movement and interaction.
- Lysosomes: These contain digestive enzymes to break down waste materials or damaged organelles, which plants use their vacuoles for.
- Smaller, Multiple Vacuoles: Unlike the large central vacuole of plants, animal cells might have smaller vacuoles for storage and waste removal.

Interactive Learning with Educational Worksheets

Worksheets are invaluable tools for learning about cell structure and function. Here are some engaging activities you can include in your educational worksheets:
- Labeling Exercises: Provide diagrams where students label different organelles. This helps in memorizing and recognizing cell parts.
- Compare and Contrast: Set up worksheets where learners compare plant and animal cells, noting similarities and differences.
- Quiz Games: Use fill-in-the-blanks or true/false questions to test students' understanding of cellular components.
- Drawing Exercises: Ask students to draw plant or animal cells, encouraging them to include all the essential parts accurately.
✍️ Note: When preparing worksheets, ensure diagrams are clear and accurately labeled. Encourage students to use colored pencils or markers to differentiate organelles for better visual learning.
Benefits of Learning with Diagrams

Visual learning through diagrams has multiple benefits:
- Comprehension: Diagrams help visualize the abstract concepts of cellular biology, making complex structures more tangible.
- Memory Retention: Visual cues from diagrams enhance memory retention compared to text-only learning.
- Engagement: Diagrams can make learning fun, encouraging active participation from students, especially when interactive elements are involved.
Here's a table to summarize the functions of major organelles in both types of cells:
| Organelle | Plant Cell Function | Animal Cell Function |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | Contains genetic material, control center | Same as plant cell |
| Mitochondria | Energy production | Same as plant cell |
| Cell Wall | Protection, shape maintenance | Not present |
| Chloroplast | Photosynthesis | Not present |

To summarize, exploring plant and animal cell diagrams through educational worksheets provides a comprehensive understanding of cellular structures. By interacting with these visual aids, learners can better appreciate the complexity of life at the cellular level, from the energy-producing mitochondria to the photosynthetic chloroplasts in plants. This knowledge not only forms the foundation of biology education but also ignites curiosity about the natural world, fostering a deeper connection with the sciences.
What is the primary difference between plant and animal cells?

+
The primary difference is that plant cells have a cell wall and chloroplasts for photosynthesis, while animal cells do not.
Can animal cells perform photosynthesis?

+
No, animal cells do not have chloroplasts, so they cannot perform photosynthesis.
Why do plant cells have large vacuoles?

+
Plant cells have a large central vacuole to store water, nutrients, and waste, which also helps maintain turgor pressure for structural support.