5 Key Differences: Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration

Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are two fundamental biological processes that underpin life on Earth, each playing a critical role in the cycling of energy and nutrients through ecosystems. Despite their interconnected nature, they exhibit several key differences which are crucial for understanding how plants, animals, and microorganisms sustain life. Here's an in-depth look into these differences:
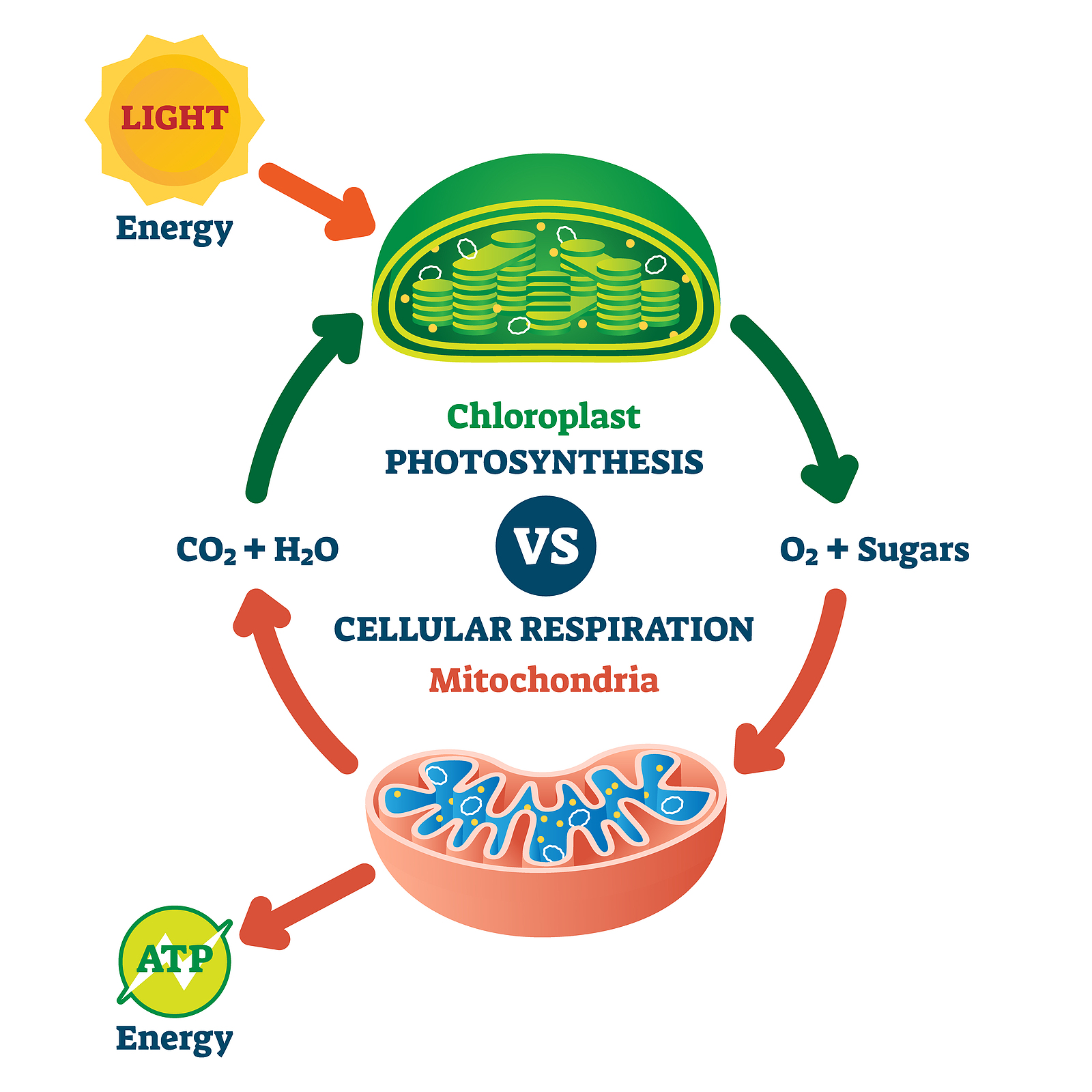
Process and Location

Photosynthesis occurs primarily in plant cells, some algae, and certain bacteria. The process involves capturing light energy and converting it into chemical energy stored in glucose. The main site for photosynthesis is the chloroplasts, which contain the pigment chlorophyll responsible for absorbing sunlight.
- Key stages: Light-dependent reactions and Calvin cycle.
- Organelle: Chloroplasts.
In contrast, cellular respiration is a process common to all living organisms including plants, animals, fungi, and bacteria. It involves the oxidation of organic compounds to release stored energy for cellular activities. This takes place in the mitochondria, often called the 'powerhouse of the cell.'
- Key stages: Glycolysis, Citric Acid Cycle, Electron Transport Chain.
- Organelle: Mitochondria.
🌱 Note: While plants have both chloroplasts and mitochondria, their activities are time-regulated; photosynthesis predominates during daylight while respiration happens 24/7.
Reactants and Products

The reactants in photosynthesis are water, carbon dioxide, and light energy, producing glucose, oxygen, and water. Here’s a simple representation:
| Reactants | Products |
|---|---|
| 6 CO₂ + 6 H₂O + Light Energy | C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6 O₂ + 6 H₂O |

Cellular respiration, on the other hand, uses glucose and oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water, and ATP (adenosine triphosphate, the cell's primary energy currency):
| Reactants | Products |
|---|---|
| C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6 O₂ | 6 CO₂ + 6 H₂O + ATP + Heat |
Energy Transformation

Photosynthesis captures light energy and converts it into chemical energy through the formation of ATP and NADPH in the light-dependent reactions, which are then utilized to fix carbon dioxide into glucose in the Calvin cycle.
- Energy Transformation: Light to Chemical Energy (stored in glucose).
Cellular respiration involves the degradation of complex molecules into simpler ones with the release of energy:
- Energy Transformation: Chemical Energy (glucose) to Chemical Energy (ATP).
Ecological Role

Photosynthesis is the foundation of the food chain, converting solar energy into chemical energy that can be passed along to other organisms:
- Role: Primary production, oxygen production for aerobic organisms.
Cellular respiration ensures the efficient use of energy by breaking down the products of photosynthesis for use in various life processes:
- Role: Energy release and consumption.
Interdependence

Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are interconnected in a cycle of energy and gas exchange. During the day, plants fix carbon dioxide into sugars while releasing oxygen, which other organisms utilize for respiration. At night, plants engage in respiration, releasing carbon dioxide which is utilized by photosynthetic organisms during the day.
- Interdependence: One produces what the other consumes, creating a balanced ecosystem.
Both photosynthesis and cellular respiration involve intricate biochemical pathways, each with specialized enzymes and molecules. This delicate balance exemplifies the complexity and beauty of life's biochemical processes. Understanding these differences not only deepens our appreciation for how life sustains itself but also informs our efforts in fields ranging from agriculture to bioengineering and ecology.
Recapping the major distinctions, we've explored how photosynthesis and cellular respiration differ in their process and location, reactants and products, energy transformation, ecological roles, and their profound interdependence. These processes are integral to life, not just through the energy they provide but through the cycles they perpetuate, ensuring the continuous flow of life on Earth.
What is the main source of energy for photosynthesis?
+
The main source of energy for photosynthesis is sunlight, which is captured by chlorophyll within the plant’s chloroplasts.
Can plants perform cellular respiration?

+
Yes, plants perform cellular respiration in their mitochondria. It occurs all the time, with plants consuming the oxygen they produce during photosynthesis to generate ATP for energy needs.
Is photosynthesis the reverse of cellular respiration?

+
While they seem to be the reverse of each other, photosynthesis does not exactly reverse cellular respiration. The reactants of photosynthesis are the products of respiration, and vice versa, but the biochemical pathways differ significantly.
Why do we need to understand these processes?

+
Understanding these processes is key to advancing fields like agriculture, where crop yield can be optimized through understanding plant energy dynamics, or in medicine, where metabolic disorders can be studied in the context of energy production and utilization.