Master Photosynthesis: Essential Vocabulary Worksheet for Students

Photosynthesis is a fundamental biological process where plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy. This process not only fuels their growth but also sustains the planet's ecosystem. To fully appreciate and understand photosynthesis, mastering the vocabulary associated with this process is crucial. Here, we explore key terms and concepts that will deepen your understanding of how life on Earth relies on this magical conversion of sunlight into energy.
Key Concepts in Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis can be broken down into several steps and components:
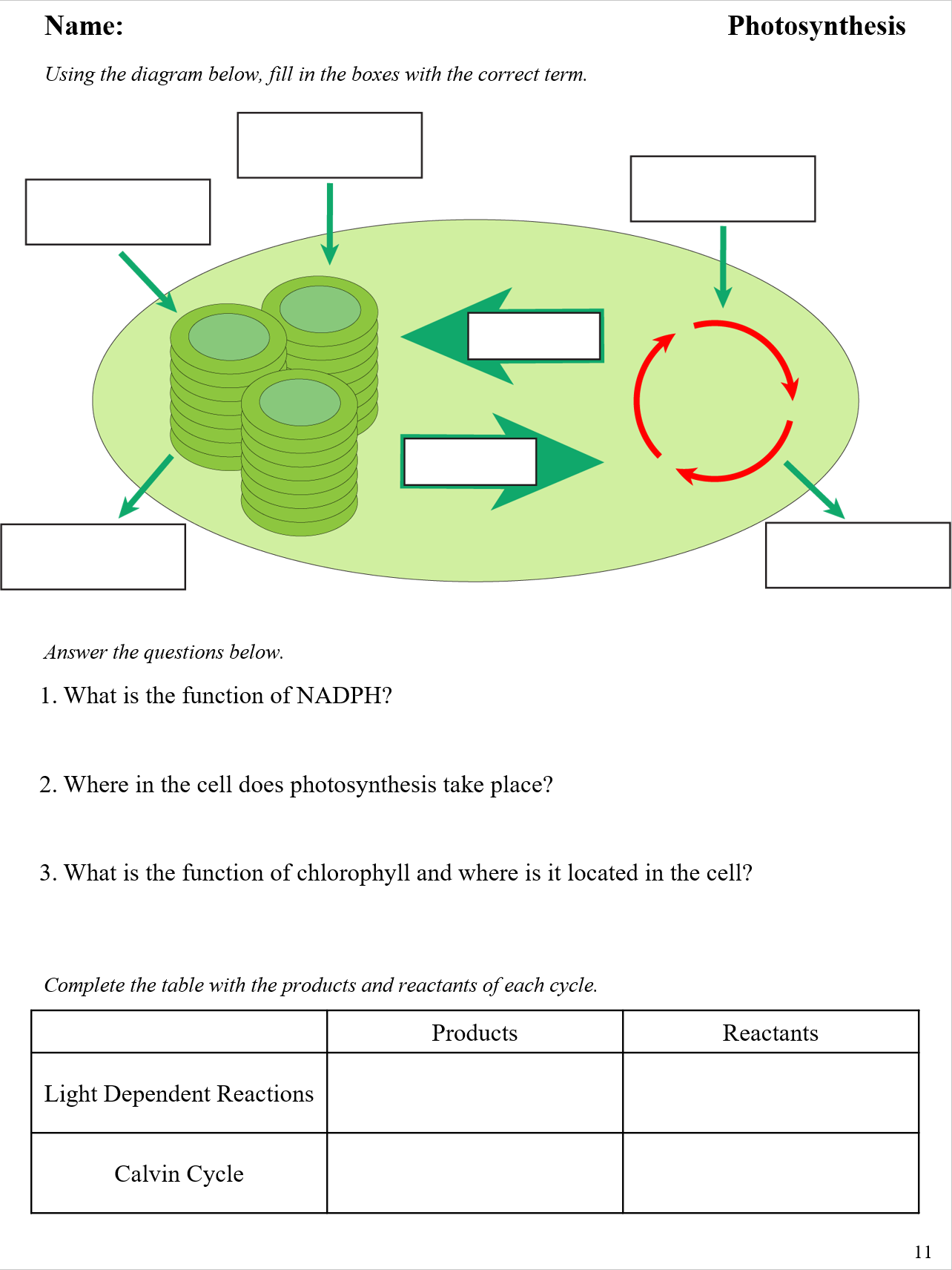
- Light-dependent Reactions: Occurring in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts, these reactions use light energy to generate ATP and NADPH.
- Calvin Cycle (or Light-independent Reactions): This cycle, located in the stroma of chloroplasts, uses ATP and NADPH to fix carbon dioxide into sugars.
- Chlorophyll: The primary pigment involved in capturing light energy. Chlorophyll is vital for the photosynthesis process as it absorbs light in the violet-blue and the orange-red parts of the spectrum, which is then used for photosynthesis.
- Photosynthesis Equation: This equation summarizes the process: [ \text{6CO}_2 + \text{6H}_2\text{O} + light \rightarrow \text{C}6\text{H}{12}\text{O}_6 + \text{6O}_2 ]
Essential Vocabulary

Let’s dive into the vocabulary crucial for understanding photosynthesis:
Chloroplasts

Chloroplasts are the cellular organelles in plant cells where photosynthesis takes place. They contain:
- Thylakoids: Disc-shaped membranes within chloroplasts where the light-dependent reactions occur.
- Grana: Stacks of thylakoids.
- Stroma: The fluid surrounding the thylakoids where the Calvin cycle takes place.
Photosynthesis Pigments

These pigments absorb light and make photosynthesis possible:
- Chlorophyll a: The primary pigment that directly absorbs light energy.
- Chlorophyll b: An accessory pigment that helps broaden the spectrum of light absorption.
- Carotenoids: Pigments that absorb in the blue-green light range and protect chlorophyll from photodamage.
The Process

Here’s a more detailed look at the steps involved:
- Photon Absorption: The initial step where light is absorbed by chlorophyll.
- Water Splitting: Known as photolysis, this process occurs during the light-dependent phase where water is split into oxygen, protons, and electrons.
- Electron Transport Chain: A series of redox reactions that transfer electrons from water through the thylakoid membrane, producing ATP and NADPH.
- ATP and NADPH: These are energy-rich molecules used in the Calvin cycle.
- Carbon Fixation: The incorporation of CO2 into organic molecules.
- Calvin Cycle Phases: It includes carbon fixation, reduction, and regeneration.
Other Important Terms
- Rubisco: The enzyme responsible for the first step of carbon fixation, known for its inefficiency.
- Photorespiration: A process that competes with photosynthesis in C3 plants when CO2 levels are low, reducing efficiency.
- Compensation Point: The point at which the rate of photosynthesis equals the rate of respiration.
- Quantum Yield: The efficiency with which a photosynthetic reaction occurs under given conditions.
🌿 Note: Photosynthesis vocabulary not only helps in understanding how plants produce food but also gives insights into plant adaptation and evolution.
Understanding these terms provides a foundation for studying the complexities of photosynthesis, how it varies among plants, and its impact on global climate and food production. For students and plant enthusiasts alike, these words are keys that unlock the secrets of plant life.
In summary, mastering the vocabulary of photosynthesis illuminates the intricate process that allows plants to harness sunlight, convert it into chemical energy, and sustain life on Earth. From the basic components like chlorophyll to the complex mechanisms like the electron transport chain, each term offers a glimpse into how plants achieve this essential task.
Why is understanding photosynthesis vocabulary important?

+
Mastering photosynthesis vocabulary enhances understanding of how plants convert light energy into chemical energy, aiding in deeper biological and ecological knowledge.
What are the primary pigments in photosynthesis?

+
The primary pigments are chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and carotenoids. They absorb different light wavelengths, maximizing the plant’s use of the sun’s energy.
How does the Calvin cycle differ from light-dependent reactions?

+
The light-dependent reactions produce ATP and NADPH using light energy, whereas the Calvin cycle uses these compounds to fix CO2 into sugars, independent of light.
What is photorespiration, and why is it harmful to plants?

+
Photorespiration occurs when the enzyme Rubisco, instead of fixing CO2, uses oxygen in a process that doesn’t produce sugars but consumes energy, thus reducing photosynthetic efficiency.