Photosynthesis Diagram Worksheet: Unlock Plant Energy Secrets

In the intricate world of plants, photosynthesis stands as the fundamental process that fuels life on Earth. It's the magic behind the lush green landscapes, the sweet fruits, and the towering trees. But how exactly do plants harness the sun's energy to produce their food? This blog post delves into the mysteries of photosynthesis, providing an educational guide through a Photosynthesis Diagram Worksheet. This worksheet isn't just an academic tool; it's a key to unlocking the secrets of how plants sustain themselves and, by extension, the entire ecosystem. Whether you're a student, a teacher, or simply a nature enthusiast, understanding this process through visual representation can transform your appreciation of plant biology.
Understanding Photosynthesis


At its core, photosynthesis is a chemical process where plants, algae, and certain bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy. This chemical energy, stored in the form of glucose or other sugars, becomes the foundation of the food chain. The general equation that illustrates this transformation is:
6 CO2 + 12 H2O + Light Energy → C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 6 H2O
Here’s a breakdown of what happens:
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere is captured by the plant’s leaves.
- Water (H2O) absorbed through the roots is transported to the leaves.
- Light Energy in the form of sunlight is absorbed by the chlorophyll pigment in the chloroplasts.
- Glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen (O2) are produced as the end products.
💡 Note: Plants use the energy stored in glucose for growth, reproduction, and other metabolic activities.
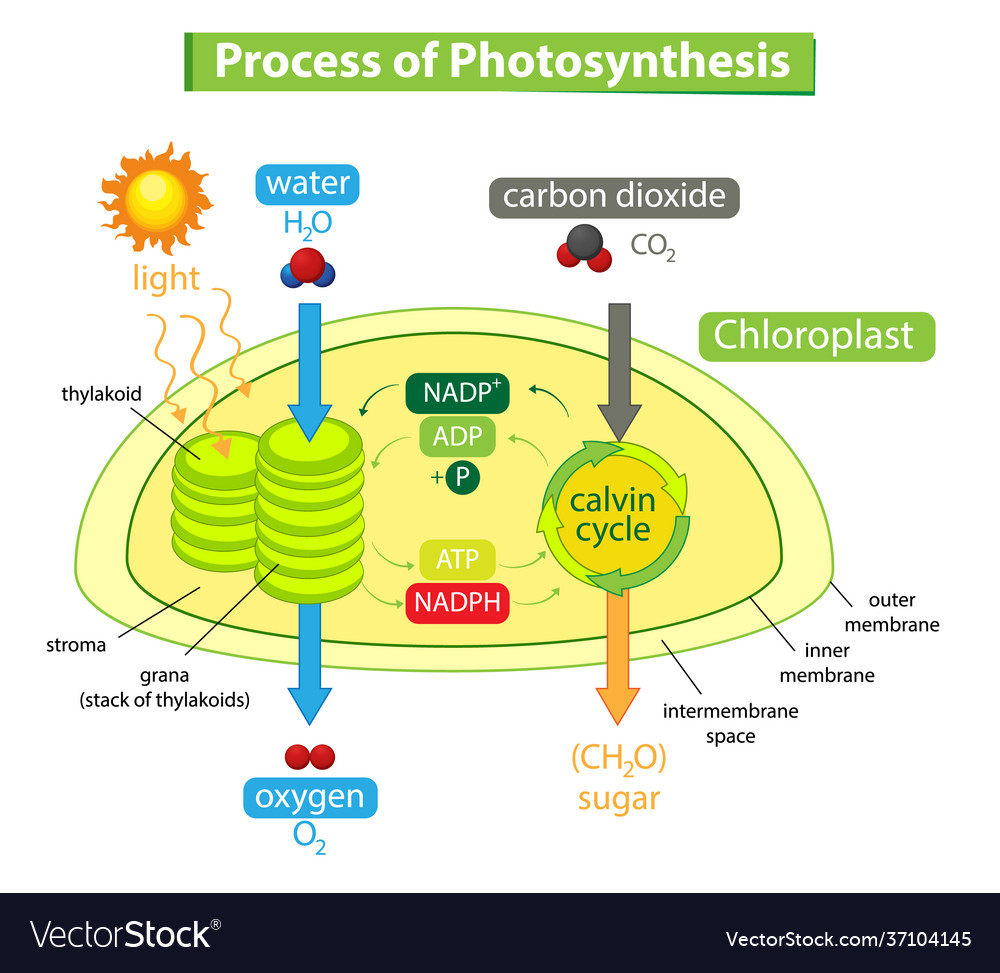
The Photosynthesis Diagram Worksheet


The Photosynthesis Diagram Worksheet serves as a visual guide to understanding this complex process:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Chloroplast | The site of photosynthesis within plant cells. |
| Thylakoids | Membrane-bound compartments within chloroplasts where the light reactions occur. |
| Stroma | The space outside the thylakoid membranes where the Calvin cycle takes place. |
| Chlorophyll | The green pigment that absorbs light energy. |
| Light Reactions | Photosystems convert light energy into ATP and NADPH. |
| Calvin Cycle | Uses ATP and NADPH to fix carbon dioxide into glucose. |

🌿 Note: The worksheet also includes space for students to label key parts of the process, which enhances their understanding and memory retention.
Exploring the Light Reactions


The light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis are a fascinating spectacle:
- Photosystem II (PSII): Here, light energy excites electrons, which are then passed along an electron transport chain, creating ATP.
- Water Splitting: Water molecules are split to replace the lost electrons, releasing oxygen as a byproduct.
- Photosystem I (PSI): This system generates NADPH by transferring high-energy electrons to NADP+.
The energy from light photons is the driving force behind these reactions, captured and converted into ATP and NADPH, which will be used in the Calvin Cycle.
Delving into the Calvin Cycle


After the light-dependent reactions, the Calvin cycle uses the energy-rich ATP and NADPH to:
- Carbon Fixation: CO2 combines with ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP) to form an unstable 6-carbon compound, which splits into two 3-carbon molecules.
- Reduction Phase: These molecules are reduced to form glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P), using ATP and NADPH.
- Regeneration of RuBP: Some G3P molecules are used to regenerate RuBP, allowing the cycle to continue.
Educational Benefits of Using Diagrams
Diagrams like the Photosynthesis Diagram Worksheet are vital for education:
- They provide a visual aid that helps students visualize abstract processes.
- They enable interactive learning, as students can label parts, enhancing their engagement.
- Visual representations help with memory recall and comprehension.
📘 Note: Visual aids often make the information more accessible to students with different learning styles.
Photosynthesis Beyond the Basics

The complexity of photosynthesis doesn’t end with the diagram worksheet:
- Photorespiration: When oxygen levels are high and CO2 levels are low, plants can undergo this less efficient process.
- C4 and CAM Photosynthesis: Some plants have developed different pathways to increase efficiency or adapt to extreme conditions.
- Chloroplast-to-Nucleus Signaling: Plants communicate between organelles, ensuring efficient resource management.
This additional complexity shows how plants are not just passive in their energy production but have evolved mechanisms to optimize photosynthesis under various conditions.
Applications and Importance in Agriculture

Understanding photosynthesis isn’t just academic; it has practical implications:
- Plant Breeding: Insights into photosynthesis help scientists breed more efficient, productive crops.
- Fertilizers: Nutrient requirements for plants can be better understood and managed.
- Artificial Photosynthesis: Exploring ways to harness this process for sustainable energy.
Photosynthesis underpins our food production systems, and any improvements in this area can have profound effects on agriculture.
Wrapping Up

Through the lens of the Photosynthesis Diagram Worksheet, we’ve explored the intricate dance of molecules and energy that keeps the plant kingdom alive. Photosynthesis, as we’ve seen, is more than just a biological curiosity; it’s a cornerstone of life on Earth, supporting ecosystems, providing oxygen, and driving agriculture. By understanding this process, we gain insights into how plants adapt, survive, and even thrive under various conditions. This knowledge not only fuels our curiosity about the natural world but also inspires innovation in various fields, from renewable energy to enhancing food security.
What is the importance of the Photosynthesis Diagram Worksheet?

+
The worksheet provides a visual and interactive learning tool, aiding in the comprehension and retention of photosynthesis concepts through structured diagrams and labeling exercises.
Can photosynthesis be improved for agriculture?
+
Yes, by understanding the mechanisms of photosynthesis, scientists can develop crops with higher efficiency, impacting food security and yield potential.
What role does light play in photosynthesis?

+
Light energy is the driving force of photosynthesis, absorbed by chlorophyll to kickstart the light-dependent reactions, converting it into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH.