Photosynthesis and Respiration: Educational Worksheet Fun

In the world of biology, two processes stand as fundamental pillars for life on Earth: photosynthesis and cellular respiration. These complementary processes are not only vital for the survival of plants and animals but also interdependent in a way that beautifully illustrates the cycle of life. This blog post delves into these intriguing biological phenomena, offering an educational worksheet that will help both educators and students grasp these concepts in an engaging manner.
What is Photosynthesis?

Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into carbohydrates (sugars) and oxygen. Here’s how it works:
- Light absorption: Chlorophyll, located in the chloroplasts, captures light energy.
- Splitting Water: Water molecules (H2O) are split to release oxygen (O2), hydrogen ions (H+), and electrons (e-).
- Carbon Fixation: CO2 from the atmosphere is fixed into glucose through the Calvin Cycle.
- ATP and NADPH Formation: Light energy drives the formation of ATP (energy) and NADPH (energy carrier).
- Sugar Production: ATP and NADPH power the synthesis of glucose.
🌿 Note: Remember, the overall equation for photosynthesis is: 6CO2 + 6H2O + Light Energy → C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6O2
Understanding Cellular Respiration

Cellular respiration is essentially the opposite of photosynthesis. Here, organisms convert sugars back into energy:
- Glycolysis: Breaks down glucose into pyruvate, producing ATP and NADH.
- Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle): Further oxidizes pyruvate to produce more ATP, NADH, FADH2, and CO2.
- Electron Transport Chain: Uses electrons from NADH and FADH2 to create a proton gradient, which drives ATP synthesis.
💡 Note: Aerobic respiration uses oxygen, while anaerobic processes (like fermentation) do not. The overall equation for aerobic respiration is: C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP + heat)
Interdependence of Photosynthesis and Respiration

These two processes are intrinsically linked:
- Photosynthesis produces oxygen, which animals and plants use for respiration.
- Respiration releases carbon dioxide, a critical raw material for photosynthesis.
- Both processes generate ATP, the universal energy currency for life.
| Process | Starting Molecule | Products | Location in Cells |
|---|---|---|---|
| Photosynthesis | CO2, H2O | O2, Glucose | Chloroplasts |
| Respiration | Glucose, O2 | CO2, H2O, ATP | Mitochondria |

🌱 Note: Without one, the other would fail, creating a delicate balance in ecosystems.
Educational Worksheet Fun

Here are some worksheet ideas to make learning about photosynthesis and respiration fun and interactive:
Word Search Puzzle

Create a word search puzzle with terms related to photosynthesis and respiration. This can include words like chlorophyll, mitochondria, Calvin Cycle, etc.
Crossword Puzzle

Develop a crossword puzzle where clues relate to definitions or processes in photosynthesis and respiration. This helps with vocabulary and recall.
Fill in the Blank

Provide sentences or paragraphs with blanks to be filled in with the appropriate terms or values:
- _____ is the pigment in plant cells responsible for capturing light energy.
- The main product of the Calvin Cycle is ____.
Labeling Diagrams

Include diagrams of chloroplasts and mitochondria for students to label:
- Thylakoid, stroma, etc., for chloroplasts.
- Cristae, matrix, etc., for mitochondria.
Matching Game

Match descriptions with processes or structures:
- "Oxygen is produced here" matches with "Photosynthesis"
- "Krebs Cycle happens here" matches with "Mitochondria"
🔍 Note: These activities not only reinforce learning but also engage students in different learning modalities, improving retention and understanding.
Summary of Key Points
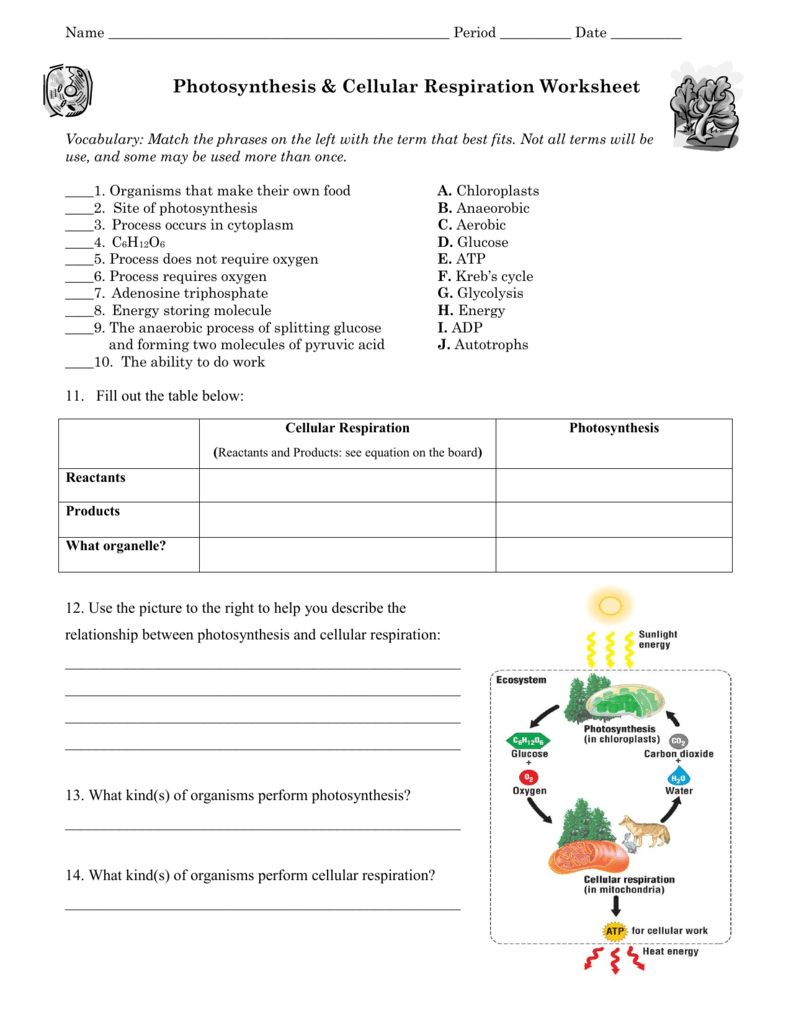
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are pivotal in maintaining life’s balance on Earth. Photosynthesis captures solar energy to produce organic compounds, while respiration converts these compounds back into energy, releasing CO2 and H2O. Their interconnection is crucial, as they feed into each other's cycles, ensuring the sustenance of both plant and animal life. Educational tools like worksheets can make these complex subjects accessible and interesting, providing a foundation for further scientific exploration and understanding.
Why are plants green?

+
Plants appear green because chlorophyll, the main pigment involved in photosynthesis, absorbs light most efficiently in the blue and red regions of the visible spectrum, reflecting green light back to our eyes.
Can photosynthesis occur in the dark?

+
No, photosynthesis requires light as it’s the energy source for the process. In the absence of light, plants can perform respiration to meet their energy needs.
Do animals perform photosynthesis?

+
Animals generally do not perform photosynthesis. However, some marine animals like corals and sea slugs can host photosynthetic symbionts that provide them with the ability to use light energy for food production.
What happens if there’s no photosynthesis?

+
Without photosynthesis, there would be no oxygen production, leading to an absence of aerobic life forms. Additionally, the food chain would collapse due to the lack of primary producers.
How does respiration differ between plants and animals?

+
While both plants and animals perform cellular respiration to generate ATP, plants have an additional option of using photosynthesis to produce glucose, which they can then use in respiration. Animals must consume food to obtain glucose.