Master Phet Balancing Chemical Equations with Our Worksheet

In the world of chemistry, balancing chemical equations is a fundamental skill that forms the backbone of understanding how chemical reactions occur. Just like mastering a new language, mastering the art of balancing chemical equations requires practice, patience, and a reliable tool. The Master Phet Balancing Chemical Equations Worksheet is an excellent resource designed to provide students, educators, and chemical enthusiasts with a structured approach to mastering this key concept.
Introduction to Balancing Chemical Equations

Chemical reactions are processes where reactants transform into products. For a reaction to be correctly represented, the number of atoms for each element must be the same on both sides of the equation. Here are some basic points to understand:
- Law of Conservation of Mass: Matter cannot be created or destroyed in chemical reactions. Therefore, the number of atoms must remain constant.
- Balancing Coefficients: These are whole numbers placed before chemical formulas to balance the equation.

How to Use the Master Phet Worksheet

The Master Phet Worksheet utilizes a clear, step-by-step methodology to guide users through the balancing process:
- Identify Reactants and Products: List down all the reactants and products from the given equation.
- Count the Atoms: Count the atoms for each element on both sides of the equation.
- Apply Balancing Coefficients: Use coefficients to balance the atoms of one element at a time, working systematically through all elements.
🔬 Note: Balancing an equation by adjusting subscripts in the chemical formulas is incorrect and changes the compound’s identity.
Practical Examples

Here’s how to use the worksheet with a simple example:
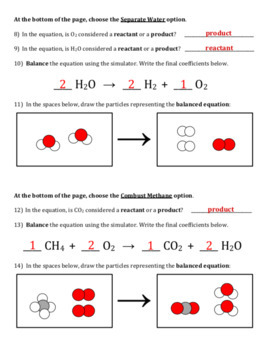
Example 1: H2 + O2 = H2O
| Element | Reactant Side | Product Side |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen (H) | 2 | 2 |
| Oxygen (O) | 2 | 1 |

To balance this, we adjust the coefficients:
- 2H2 + O2 = 2H2O
Example 2: More Complex Balancing

Consider the equation Fe + O2 → Fe2O3:
- Count Atoms:
- Iron (Fe) = 1 (reactant) and 2 (product)
- Oxygen (O) = 2 (reactant) and 3 (product)
- Balance Iron by placing a 2 in front of Fe: 2Fe + O2 → Fe2O3
- Balance Oxygen:
- Right now, we have 2 (reactant) and 3 (product). Let’s multiply the entire equation by 2 to make the oxygen balance out: 4Fe + 3O2 → 2Fe2O3
Advanced Tips and Tricks

- Begin with Simple Molecules: Balance the equation by starting with the simplest molecule or polyatomic ions.
- Check for Fractional Coefficients: If necessary, multiply by the lowest common multiple to eliminate fractions.
- Double-Check: Ensure all atoms are balanced after adjusting any coefficient.
The Value of the Master Phet Worksheet

Utilizing the Master Phet Worksheet for learning and teaching the art of balancing chemical equations offers numerous advantages:
- Clear Structure: The worksheet breaks down the process into manageable steps, making complex reactions easier to grasp.
- Immediate Feedback: The worksheet provides instant feedback, helping users quickly identify where they might have gone wrong.
- Versatility: Suitable for beginners through to advanced learners, it covers a range of difficulty levels.
- Engagement: The interactive elements make learning more engaging than traditional methods.
In conclusion, the Master Phet Balancing Chemical Equations Worksheet is an invaluable tool in the arsenal of anyone looking to excel in chemistry. Whether you're a student, teacher, or hobbyist, this resource provides a structured, practical, and engaging way to understand and practice this essential skill. By focusing on the methodical approach to balancing equations, users can not only improve their understanding of chemical reactions but also enhance their problem-solving skills in science.
Why do I need to balance chemical equations?

+
Balancing chemical equations is necessary to ensure the law of conservation of mass is respected, where the total mass of the reactants equals the mass of the products. This reflects the reality of chemical reactions.
What are the common mistakes when balancing equations?

+
Common mistakes include changing subscripts, overlooking polyatomic ions, and not balancing in a systematic manner. Always double-check your work to avoid these pitfalls.
Can I balance chemical equations using a computer program?

+
Yes, there are several software and online tools available that can automatically balance chemical equations. However, understanding the manual process is invaluable for learning.
Is there an easy way to remember how to balance equations?

+
Using mnemonic devices like “HOPB” (Hydrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, Balance last) or working from the most complex molecule to the simplest can help. Practice is key to making the process feel natural.