Ph And Poh Worksheet Answer Key

In understanding the complexities of chemistry, particularly acids and bases, pH and pOH serve as critical measurements. This blog post delves deep into what pH and pOH signify, how they relate to each other, and how to solve pH and pOH problems efficiently. We will also provide an answer key for a pH and pOH worksheet to reinforce the concepts covered.
What are pH and pOH?

pH stands for the “potential of hydrogen.” It’s a scale used to specify how acidic or basic a substance is. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14:
- pH < 7: The substance is acidic.
- pH = 7: The substance is neutral (like pure water).
- pH > 7: The substance is basic or alkaline.
pOH refers to the “potential of hydroxide,” essentially the opposite of pH, representing the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-) in a solution. Here’s how they relate:
⚗️ Note: At 25°C, pH + pOH = 14. This equation helps in understanding the logarithmic relationship between pH and pOH.
Calculating pH and pOH

Calculating pH or pOH involves using the following formulas:
- pH: pH = -log[H+]
- pOH: pOH = -log[OH-]
Where [H+] is the concentration of hydrogen ions, and [OH-] is the concentration of hydroxide ions.
Example Calculation

Let’s say a solution has a [H+] concentration of 0.0001M:
- pH = -log(0.0001) = 4
- pOH = 14 - pH = 14 - 4 = 10
Thus, a solution with a pH of 4 would have a pOH of 10.
How to Use the pH and pOH Worksheet

The provided worksheet helps students practice converting between pH and pOH, understanding how these values interact, and identifying whether a solution is acidic, neutral, or basic. Here are some problems you might encounter:
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Calculate the pH of a solution with a [OH-] concentration of 1x10-8 M |
First, calculate pOH: pOH = -log(1x10-8) = 8 Now, calculate pH: pH = 14 - 8 = 6 So, the pH of this solution is 6. |
| Determine if a solution with a pH of 11 is acidic, neutral, or basic. | Since pH > 7, the solution is basic. |
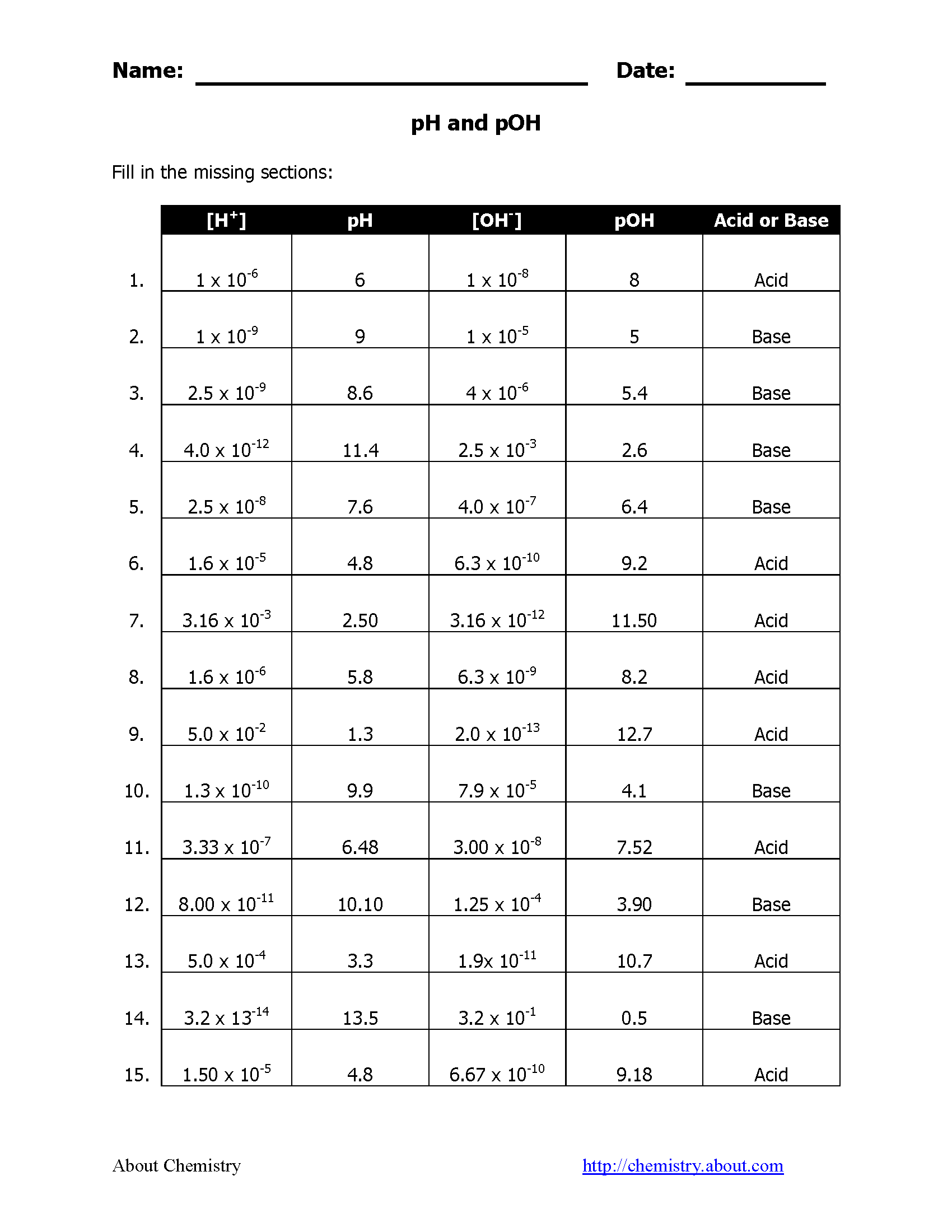
Answer Key for pH and pOH Worksheet

Here are the solutions to some common worksheet problems:
- Problem 1: If the pH is 9, what is the pOH?
- Answer: pOH = 14 - 9 = 5
- Problem 2: Calculate the [H+] for a solution with a pH of 2.
- Answer: pH = -log[H+], so [H+] = 10-pH = 10-2 = 0.01M
- Problem 3: Determine the pH if the pOH is 13.
- Answer: pH = 14 - pOH = 14 - 13 = 1
🔬 Note: Ensure your calculator is in scientific or normal notation to correctly calculate logarithms and exponents.
To sum up, pH and pOH are fundamental concepts for understanding the acidic, neutral, or basic nature of a solution. The ability to convert between these values and interpret their implications is crucial for students and professionals in chemistry alike. By practicing with worksheets, one can grasp these calculations easily, reinforcing the basic principles of acid-base chemistry.
What does a pH of 7 mean?

+
A pH of 7 indicates that the substance is neutral, neither acidic nor basic. This is the pH of pure water at 25°C.
How do temperature changes affect pH and pOH?
+
Temperature changes affect the dissociation of water, thereby influencing the pH and pOH values. As temperature increases, water dissociates more, leading to a decrease in pH (becoming more acidic) and an increase in pOH (becoming less basic).
Why is it important to understand pH and pOH?

+
Understanding pH and pOH is essential for fields like medicine, agriculture, environmental science, and industrial processes where maintaining specific pH levels is crucial for the effectiveness or safety of the process or environment.
Can you have a negative pH or pOH?

+
Yes, while rare, it is theoretically possible to have negative pH or pOH values in highly acidic or basic solutions, respectively, where the concentration of H+ or OH- ions exceeds 1 Molar.