5 Tips PFA Exposure
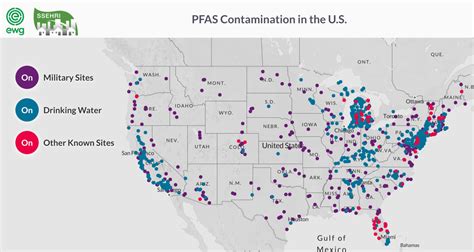
Introduction to PFA Exposure

PFA, or Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl substances, are a group of chemicals that have been widely used in various products, including non-stick cookware, food packaging, and firefighting foam. However, PFA exposure has been linked to several health problems, including cancer, reproductive issues, and thyroid disease. In this article, we will discuss 5 tips to reduce PFA exposure and minimize its harmful effects on our health.
Understanding PFA Exposure

PFA exposure can occur through various routes, including food and water contamination, air pollution, and skin contact with PFA-containing products. To reduce PFA exposure, it is essential to understand the sources of exposure and take steps to minimize them. Here are some key facts about PFA exposure: * PFA can contaminate food and water through packaging and cookware. * PFA can be released into the air through industrial processes and waste incineration. * PFA can be absorbed through the skin through contact with PFA-containing products.
Tip 1: Choose PFA-Free Cookware

One of the most common sources of PFA exposure is non-stick cookware. To reduce PFA exposure, choose PFA-free cookware made from materials such as stainless steel, cast iron, or ceramic. These alternatives are safer and more environmentally friendly. When shopping for cookware, look for products that are labeled as “PFA-free” or “non-toxic.”
Tip 2: Avoid Food Packaging with PFA

Food packaging is another significant source of PFA exposure. To minimize exposure, avoid foods packaged in PFA-containing materials, such as microwave popcorn bags and fast food wrappers. Instead, choose fresh, whole foods and cook at home using PFA-free cookware. You can also check the packaging for PFA-free labels or opt for glass or stainless steel containers for storing food.
Tip 3: Filter Your Water

PFA can contaminate water sources, including drinking water. To reduce PFA exposure, filter your water using a high-quality water filter that can remove PFA and other contaminants. You can also check your water quality by contacting your local water utility or using a water testing kit.
Tip 4: Avoid PFA-Containing Products

PFA is often used in stain-resistant and waterproof products, such as carpets, upholstery, and clothing. To minimize PFA exposure, avoid products that contain PFA and opt for alternative materials that are PFA-free. You can also check the labels for PFA-free certifications or look for natural, sustainable materials.
Tip 5: Support PFA Regulation

Finally, support regulation and policy changes that aim to reduce PFA exposure. You can contact your local representatives and express your concerns about PFA exposure. You can also support organizations that work to reduce PFA exposure and promote environmental health.
📝 Note: Reducing PFA exposure requires a collective effort from individuals, communities, and governments. By taking these 5 tips into practice, we can minimize our exposure to PFA and promote a healthier environment.
As we conclude our discussion on PFA exposure, it is essential to remember that every small step counts. By making informed choices and taking action, we can reduce our exposure to PFA and promote a healthier, more sustainable future. The key takeaways from this article include choosing PFA-free cookware, avoiding food packaging with PFA, filtering your water, avoiding PFA-containing products, and supporting PFA regulation. By following these tips, we can minimize our exposure to PFA and protect our health and the environment.
What are the health effects of PFA exposure?

+
PFA exposure has been linked to several health problems, including cancer, reproductive issues, and thyroid disease.
How can I reduce PFA exposure in my daily life?

+
You can reduce PFA exposure by choosing PFA-free cookware, avoiding food packaging with PFA, filtering your water, avoiding PFA-containing products, and supporting PFA regulation.
What are some alternatives to PFA-containing products?

+
Some alternatives to PFA-containing products include stainless steel, cast iron, and ceramic cookware, as well as natural, sustainable materials for clothing and upholstery.



