Master Your Body: Peripheral Nervous System Explained

The intricacies of the human body are often a subject of wonder, with its myriad of systems working in concert to maintain life. One of these vital systems is the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which acts as the bridge between the central nervous system (CNS) and the rest of the body. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the fascinating world of the peripheral nervous system, exploring its function, structure, and its critical role in our daily life.
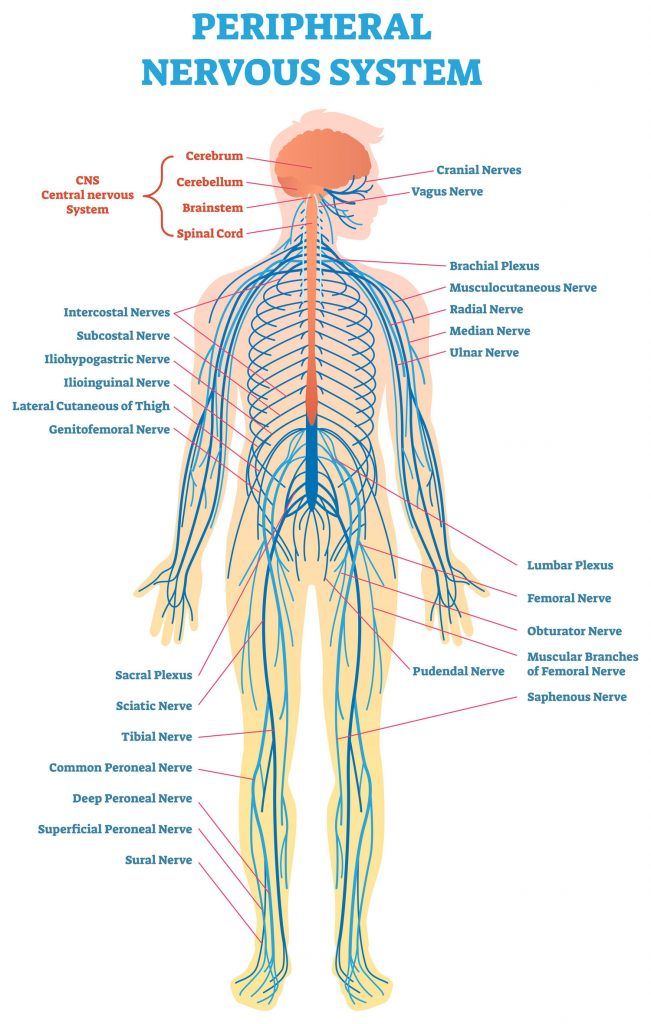
Anatomy of the Peripheral Nervous System

The peripheral nervous system extends beyond the brain and spinal cord, which are part of the CNS, to include nerves and ganglia outside these central regions. Here’s a breakdown:
- Cranial Nerves: Twelve pairs of nerves that originate from the brain.
- Spinal Nerves: Thirty-one pairs stemming from the spinal cord.
- Ganglia: Collections of nerve cells, often found near the spinal cord or along nerve pathways.
🏠 Note: Ganglia are not central to the PNS but serve as key junction points.
Functional Divisions

The PNS can be divided into two main functional parts:
- Somatic Nervous System: This system is responsible for voluntary movements, controlling the skeletal muscles. It involves sensory neurons that convey sensory information to the CNS and motor neurons that transmit signals from the CNS to muscles and glands.
- Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): Divided further into:
- Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS): Prepares the body for “fight or flight” responses.
- Parasympathetic Nervous System (PSNS): Promotes the “rest and digest” functions, aiding in relaxation and recovery.
The Role of the PNS in Daily Life

Every day, the PNS orchestrates numerous activities, often without our conscious effort:
- Sensory Input: From the touch of silk to the aroma of coffee, sensory information is gathered and sent to the CNS for processing.
- Motor Output: From running to typing, it’s the PNS that sends signals to muscles to execute these movements.
- Autonomic Regulation: It controls heart rate, digestion, pupil dilation, and much more, ensuring a balanced internal environment.
Understanding Nerve Damage and Disorders

The PNS, like any system in the body, is susceptible to various diseases and injuries:
- Neuropathy: A general term for disorders affecting nerves outside the brain and spinal cord, causing numbness, tingling, or pain.
- Guillain-Barré Syndrome: An acute condition where the immune system attacks the peripheral nerves, leading to weakness or paralysis.
- Radiculopathy: Compression or damage to nerve roots often leading to radicular pain.
💡 Note: Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in managing PNS disorders.
Strategies for Enhancing PNS Health

Maintaining the health of the peripheral nervous system involves a holistic approach:
- Nutrition: A diet rich in vitamins B1, B6, B12, and E supports nerve health.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity improves circulation and can prevent peripheral nerve damage.
- Proper Posture: Can reduce the risk of nerve compression.
- Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate conditions affecting the PNS, hence relaxation techniques are beneficial.
- Vitamin Supplementation: When diet alone isn’t sufficient, supplements can help.
- Regular Checkups: Ensure you’re monitoring your health to catch any issues early.
Wrapping It Up

The peripheral nervous system plays an indispensable role in our daily life, from the simple act of touching something to the complex coordination required in sports. By understanding how the PNS works, we can appreciate the delicate balance it maintains in our bodies. It’s fascinating to recognize that something so essential to our existence operates largely out of our conscious awareness. When we take care of our bodies, eat healthily, exercise, manage stress, and attend regular checkups, we are also nurturing our peripheral nervous system. Here’s to mastering our body’s intricate connections and ensuring the peripheral nervous system functions at its best for a fulfilling life.
What are the main signs of peripheral nerve damage?

+
Signs of peripheral nerve damage can include numbness, tingling, muscle weakness, sensitivity to touch, or pain, often described as burning or prickling. In some cases, people might experience a loss of coordination or balance.
How can I improve my nerve health?
+
To enhance nerve health, consider adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, practicing stress management techniques, and avoiding toxins or habits that could harm nerve function. Consulting with healthcare providers about potential supplements could also be beneficial.
What’s the difference between the CNS and the PNS?

+
The Central Nervous System (CNS) consists of the brain and spinal cord, which are the command centers for the body. The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) extends outward from the CNS to connect the body with the outside world, including nerves, ganglia, and nerve endings. While the CNS processes information, the PNS transmits signals to and from the CNS to the rest of the body.