Periodic Table Worksheet Answers: Simplify Your Learning

The periodic table stands as an indispensable tool for students in various disciplines, from chemistry to environmental science, serving as a map to the vast world of elements. While some aspects of its study might seem straightforward, mastering it can be daunting for many, especially when it comes to addressing worksheets and answer keys. In this comprehensive guide, we'll unravel the mysteries of the periodic table worksheet answers, ensuring you grasp the concepts with ease and confidence.
Understanding the Periodic Table
Before diving into worksheet answers, let’s establish a clear understanding of the periodic table:
- Periods: Horizontal rows in the table, indicating the energy level of electrons.
- Groups: Vertical columns, where elements share similar properties due to the same number of valence electrons.
- Atomic Number: Reflects the number of protons in an element’s nucleus, which correlates with its position in the table.
- Chemical Symbols: One- or two-letter abbreviations for elements.
- Electronegativity: A measure of an atom’s attraction for shared electrons in a chemical bond.
Periodic Table Worksheet: Common Questions and Answers

Here are some commonly asked questions on periodic table worksheets, with their answers:
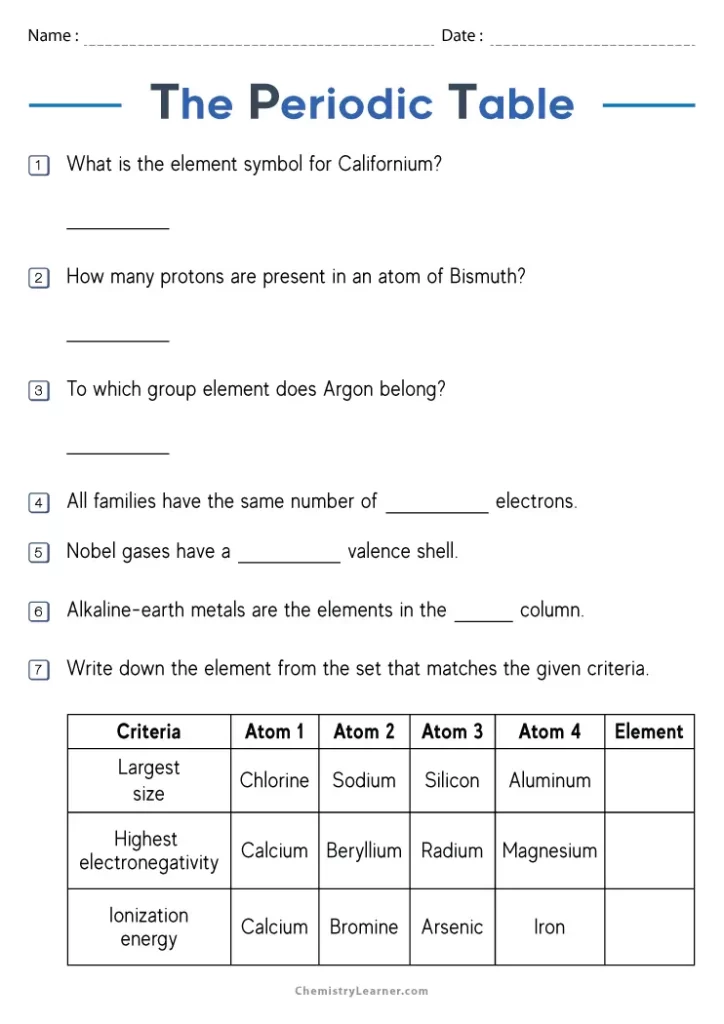
1. Identify the Group and Period for Each Element

Let’s create a table to help with this query:
| Element | Group | Period |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen (H) | 1 | 1 |
| Helium (He) | 18 | 1 |
| Sodium (Na) | 1 | 3 |
| Carbon © | 14 | 2 |

2. Classify Elements as Metals, Non-Metals, or Metalloids
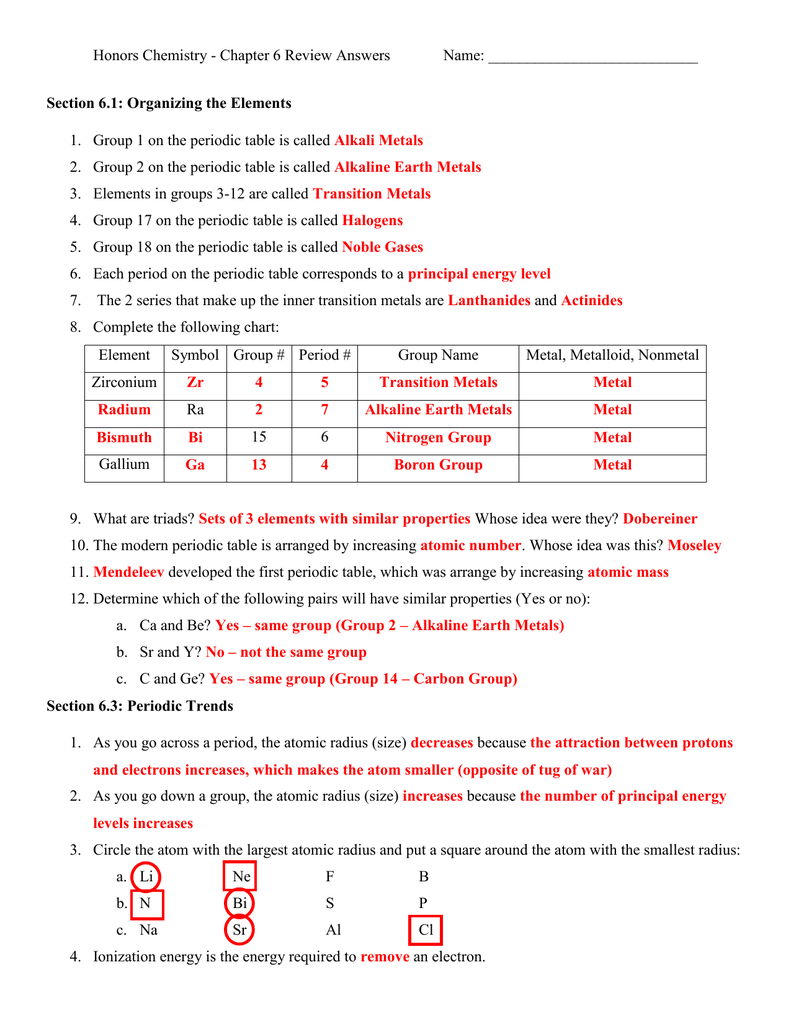
To classify elements, refer to the following general locations in the periodic table:
- Metals are to the left and middle of the table.
- Non-metals are on the right side.
- Metalloids form a diagonal line between these two areas.
3. Describe Trends in Atomic Radius

The trend in atomic radius is as follows:
- From left to right across a period, atomic radius decreases due to increased effective nuclear charge.
- From top to bottom within a group, atomic radius increases as energy levels are added.
🔎 Note: Remember that exceptions to these trends do exist, like transition metals and lanthanides, but these general rules are accurate for main group elements.
4. Determine the Number of Valence Electrons

The number of valence electrons can often be deduced from the group number:
- Groups 1 to 2 have the same number of valence electrons as their group number.
- Groups 13 to 18 have valence electrons equal to their group number minus 10.
Utilizing Interactive Tools and Apps for Learning

To enhance your understanding and make learning interactive, here are a few useful tools and apps:
- Periodic Table Apps: Some popular apps include “Mendeleev’s Periodic Table,” “Periodic Table,” and “Element Visualizer.”
- Online Resources: Websites like Ptable and Chemspider offer detailed periodic table data with interactive features.
Making Sense of Periodic Trends

Understanding periodic trends is crucial for predicting chemical behavior:
Ionization Energy

- Ionization energy increases from left to right across a period and decreases from top to bottom within a group.
- This trend is due to the attraction of electrons to the nucleus and the shielding effect.
Electronegativity

- Similar to ionization energy, electronegativity increases from left to right and decreases from top to bottom.
- It’s a measure of how much an atom will attract shared electrons.
🔬 Note: The Pauling scale is the most commonly used scale for measuring electronegativity.
Electron Affinity

- Electron affinity reflects the energy change when an electron is added to a neutral atom.
- Unlike ionization energy, there’s less of a clear trend for electron affinity, but it tends to increase from left to right and decrease from top to bottom.
In Closing

This blog post has aimed to demystify the periodic table worksheet answers, offering insights into common questions, trends, and classifications within the table. By understanding these basics, you’ll be better equipped to tackle periodic table worksheets with confidence. Remember, while the periodic table is a complex map, mastering it opens the door to a deeper understanding of chemistry, making seemingly complex concepts accessible and practical.
Why is the periodic table important in chemistry?

+
The periodic table is essential because it organizes elements in a way that reveals their properties, electron configurations, and chemical behavior. It allows scientists to predict how elements might react and form compounds, facilitating research and understanding of chemical reactions.
What are the main group elements?

+
The main group elements, or representative elements, are those in groups 1, 2, and 13 to 18. These elements follow the octet rule more consistently in their electron configurations and chemical behavior.
Can periodic trends be predicted accurately?

+
Periodic trends provide a general guideline but not always an exact prediction due to exceptions, like the “d-block contraction” affecting atomic radius, and other factors like electron-electron interactions.